Mechanical Waves - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how energy travels through different materials as waves!
What are Mechanical Waves?
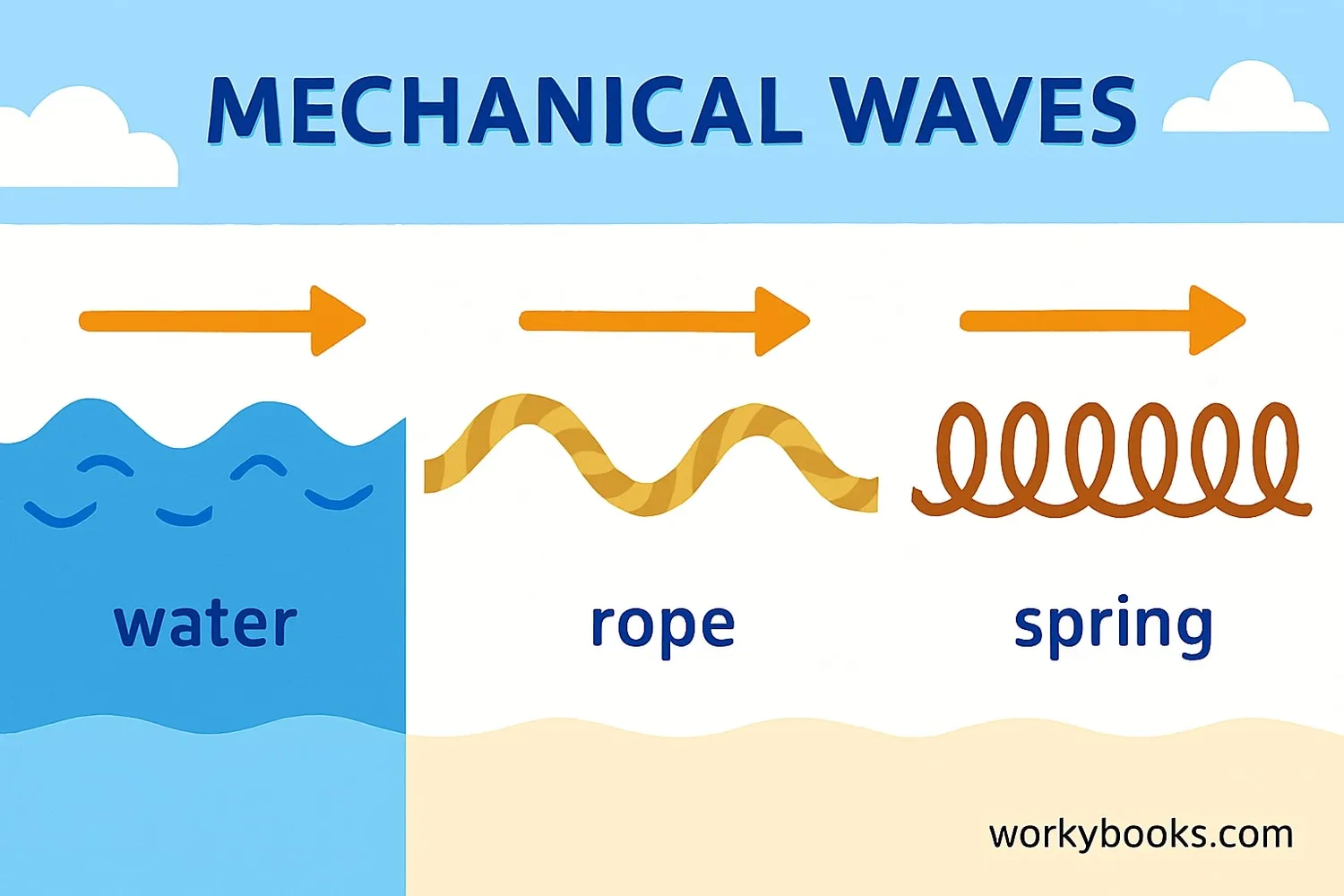
Mechanical waves are disturbances that travel through a medium (material) and transfer energy from one place to another. Unlike electromagnetic waves (like light), mechanical waves need matter to travel through.
Think of mechanical waves like ripples in a pond when you drop a stone. The water doesn't actually travel across the pond - it's the energy that moves through the water. The water particles just move up and down while the wave energy moves forward.
All mechanical waves have common properties:
• Amplitude - the height of the wave
• Wavelength - the distance between wave crests
• Frequency - how many waves pass a point each second
• Speed - how fast the wave travels
Wave Fact!
Sound is a mechanical wave! That's why sound can't travel through empty space where there's no air or other material to vibrate.
Types of Mechanical Waves
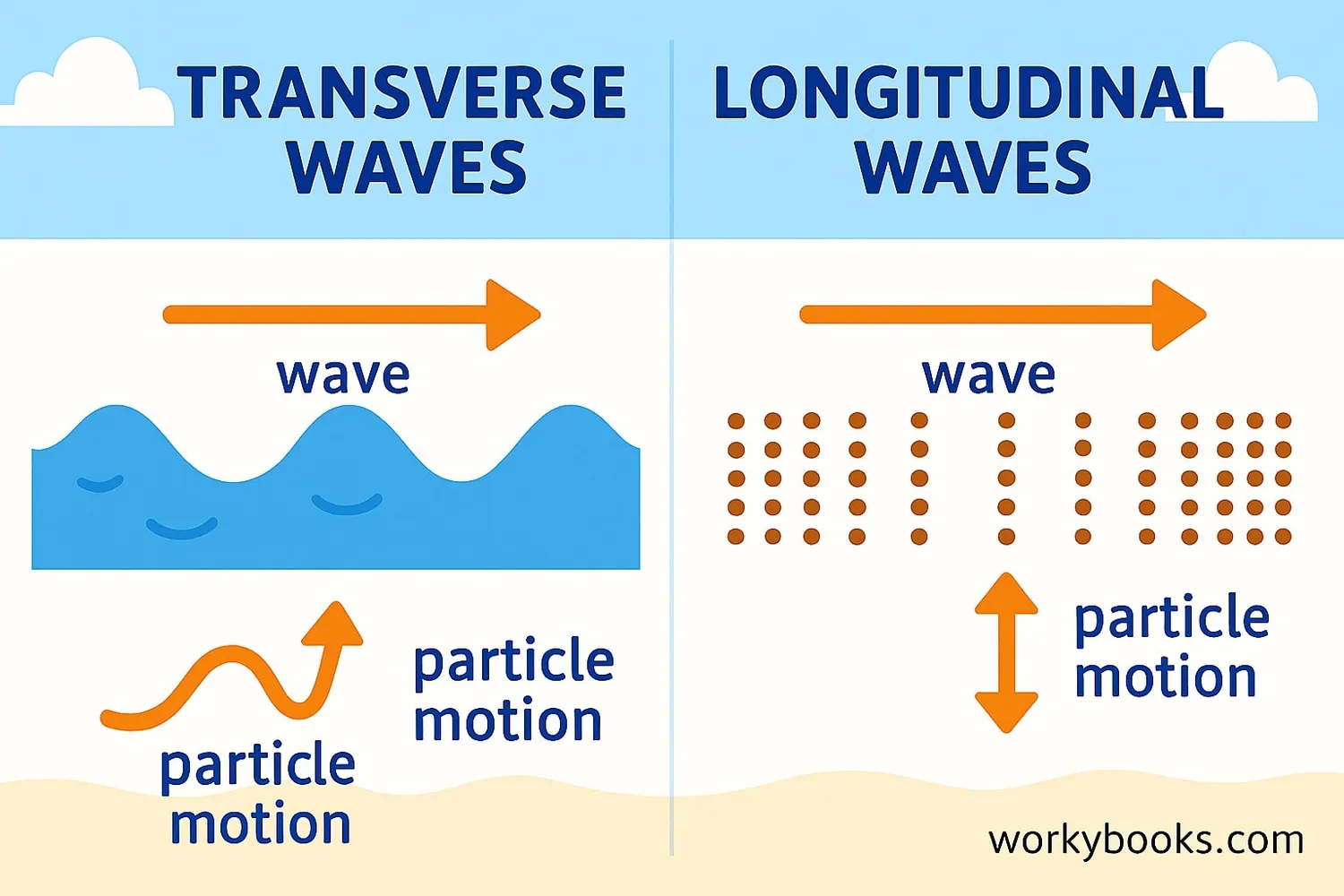
There are two main types of mechanical waves:
Transverse Waves
Particles move perpendicular to the wave direction
Longitudinal Waves
Particles move parallel to the wave direction
Surface Waves
Combination of transverse and longitudinal motion
Transverse Waves move particles up and down while the wave travels horizontally. Examples include waves on a string, water waves, and seismic S-waves.
Longitudinal Waves create compressions and rarefactions where particles bunch together then spread apart. Sound waves and seismic P-waves are longitudinal.
Surface Waves occur at the boundary between two media (like water and air). The particles move in circular patterns, which is why objects in water bob up and down as waves pass.
Wave Motion!
Earthquake waves include both types: P-waves (longitudinal) travel faster than S-waves (transverse), which helps scientists locate earthquake epicenters.
Examples of Mechanical Waves
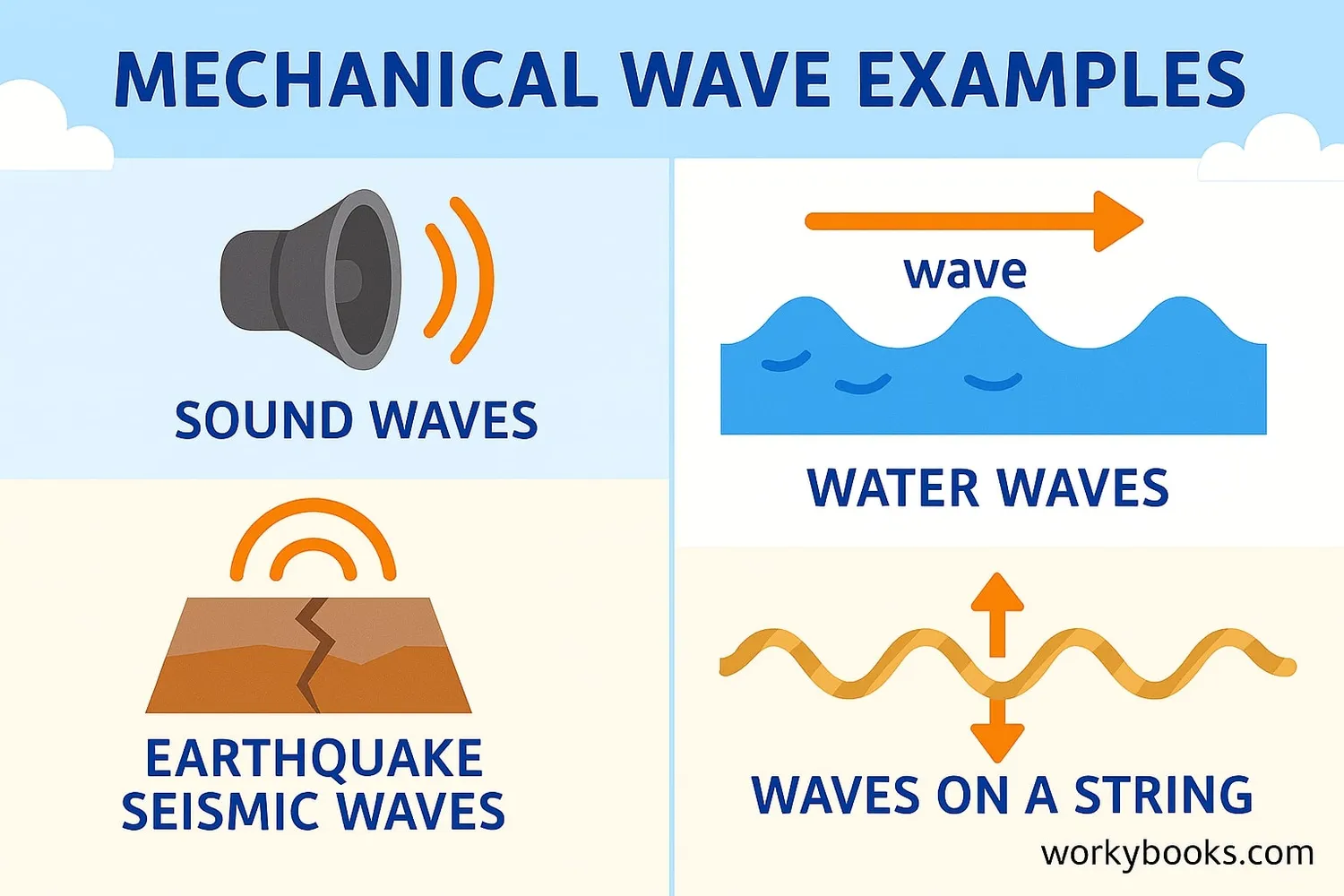
Mechanical waves are all around us! Here are some common examples:
Sound Waves
Vibrations that travel through air, water, or solids to our ears
Water Waves
Disturbances that move across the surface of oceans, lakes, and rivers
Seismic Waves
Waves generated by earthquakes that travel through the Earth
Other examples include:
• Waves on a rope or string
• Waves in a spring or Slinky toy
• Ultrasound waves used in medical imaging
• Waves that travel through the ground from explosions
• Vibrations in musical instruments
Each of these waves requires a medium to travel through and follows the same basic principles of wave motion.
Mechanical vs Electromagnetic Waves
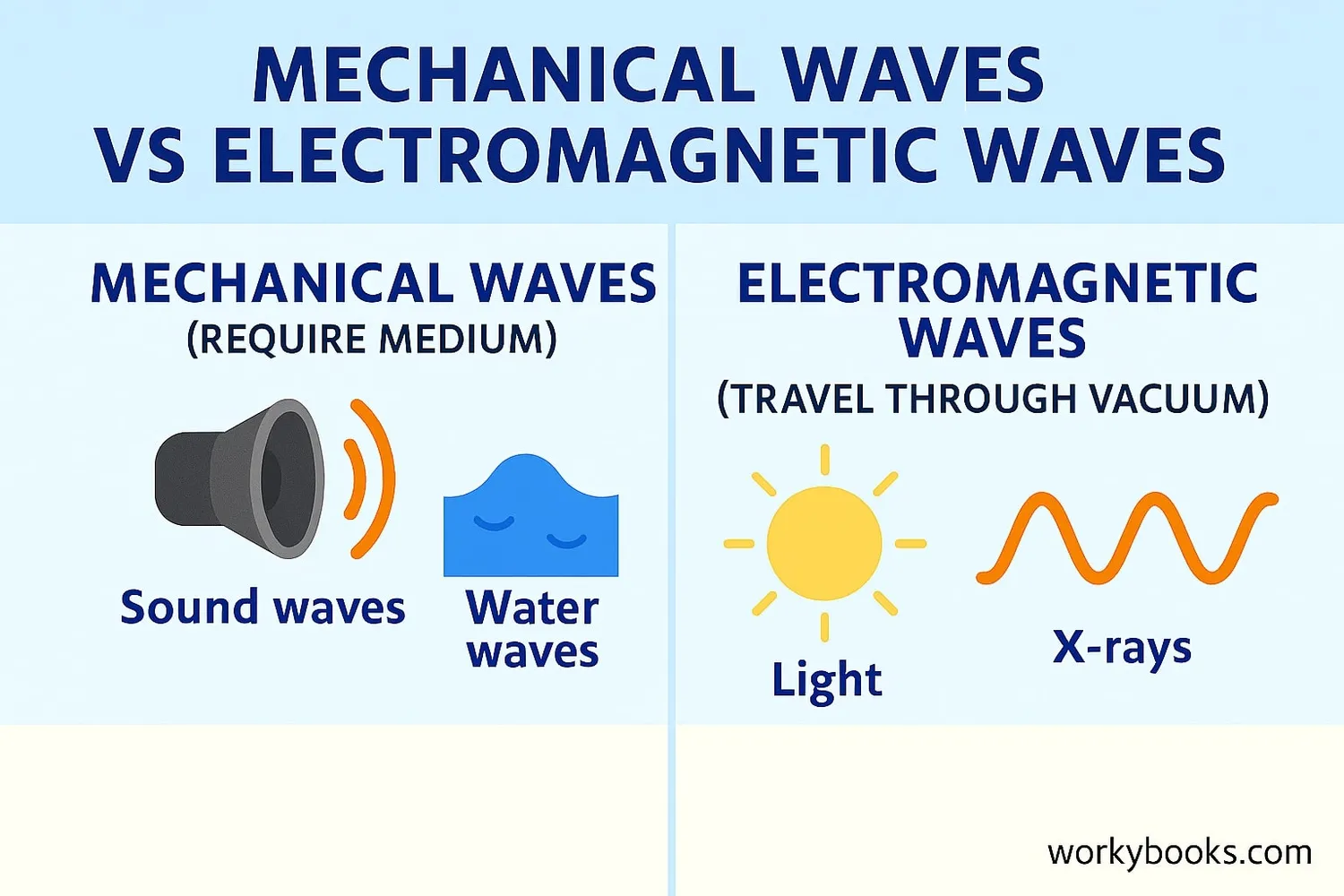
While both mechanical and electromagnetic waves transfer energy, they have important differences:
Mechanical Waves
Require a medium (matter) to travel through
Examples: Sound, water waves, seismic waves
Electromagnetic Waves
Can travel through empty space (vacuum)
Examples: Light, radio waves, X-rays
Key differences:
• Medium requirement: Mechanical waves need matter, electromagnetic waves don't
• Speed: Mechanical waves travel slower than electromagnetic waves
• Composition: Mechanical waves are disturbances in matter, electromagnetic waves are oscillations of electric and magnetic fields
• Examples: Sound vs light, ocean waves vs radio waves
Both types of waves can be described using similar properties like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude, but they follow different physical principles.
Space Fact!
Light from the Sun reaches Earth through the vacuum of space, but if astronauts in space tried to talk without radios, no one would hear them because sound can't travel in vacuum!
Mechanical Waves Quiz
Test your knowledge about mechanical waves with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about mechanical waves:
Mechanical Waves Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about mechanical waves!
Sound Underwater
Sound travels about 4 times faster in water than in air! That's why whales can communicate across entire ocean basins.
Earthquake Waves
Seismic waves from large earthquakes can travel through the entire Earth and be detected on the opposite side of the planet!
Animal Hearing
Dogs can hear higher frequency sound waves than humans, which is why they respond to dog whistles that we can't hear.
Tsunami Power
Tsunami waves in the open ocean may be only a few feet high but can travel at speeds up to 500 mph - as fast as a jet plane!





