Polarization - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how light waves travel and why some materials change their behavior
What is Polarization?
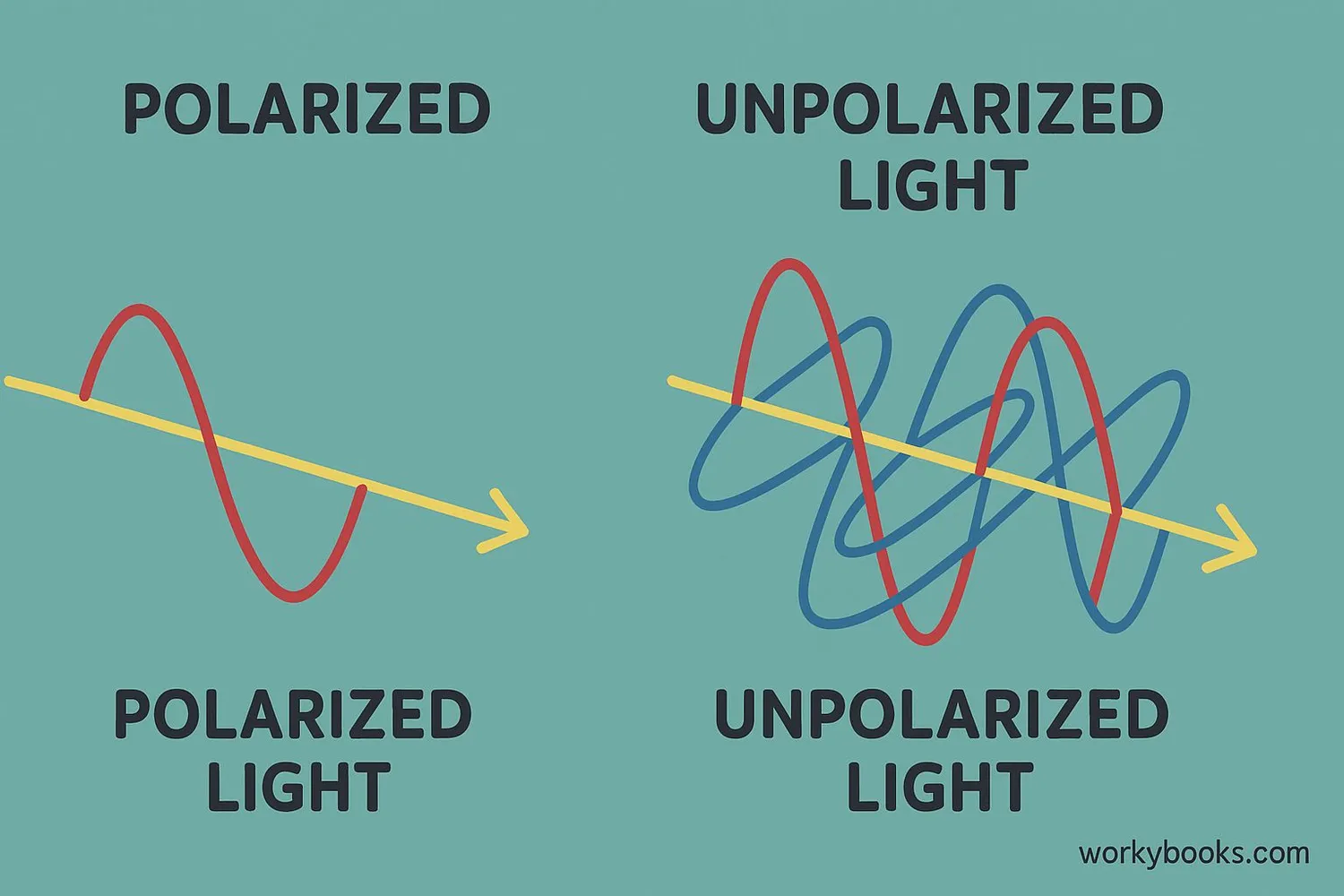
Polarization is a special property of light waves that describes the direction in which they vibrate.
Imagine light waves as tiny ropes being shaken. Normally, light vibrates in all directions - up and down, side to side, and everything in between. Polarized light is different because it vibrates in just one direction - like a rope that only moves up and down.
Polarization happens naturally with sunlight reflecting off surfaces like water or glass, and we can create it using special filters called polarizers.
Science Fact!
Light from the sun is unpolarized - its waves vibrate in all directions. But when sunlight reflects off water or roads, it becomes partially polarized!
Types of Polarization
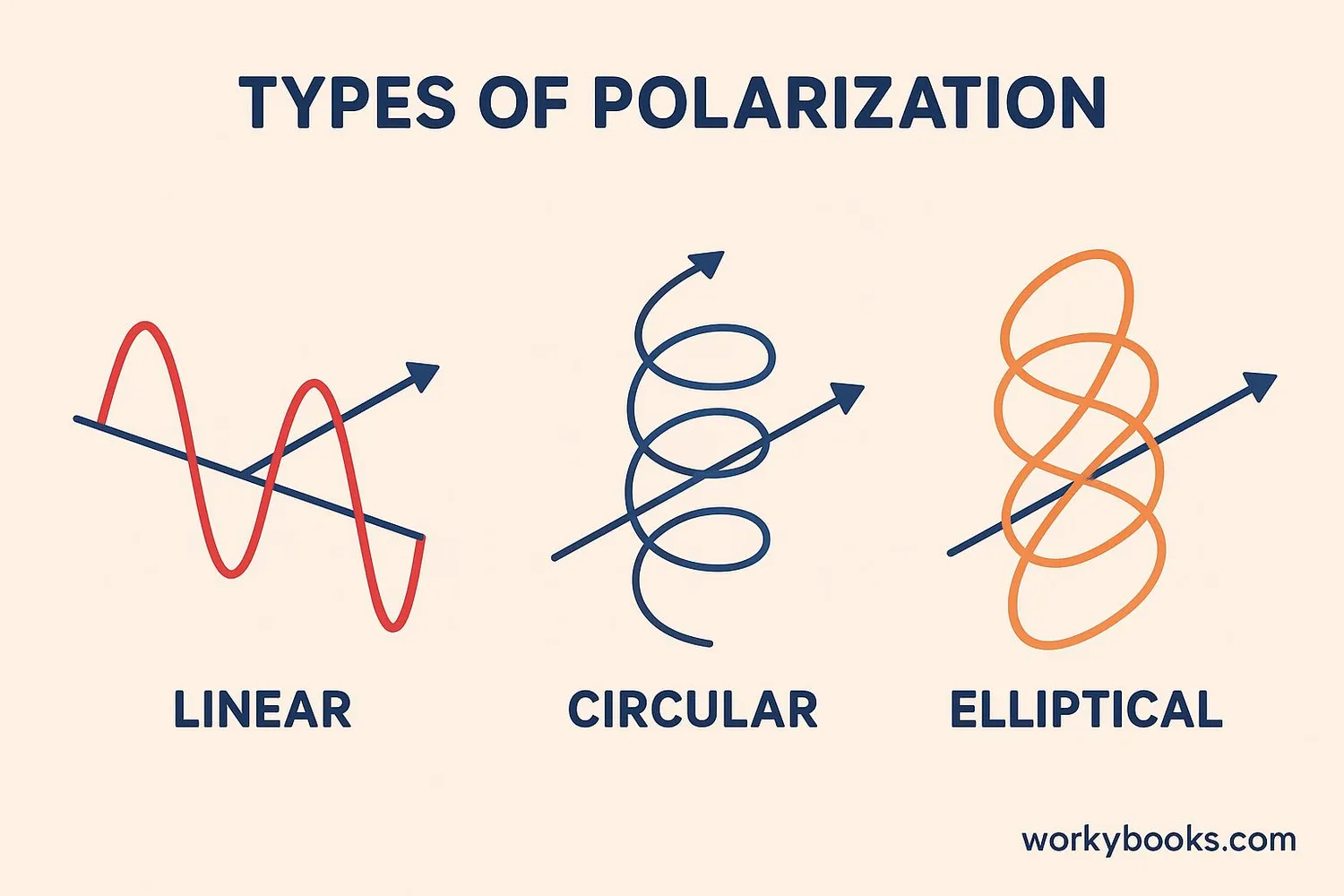
Scientists have discovered several different ways that light can be polarized:
Linear Polarization
Light waves vibrate in a single plane
Circular Polarization
Light waves rotate as they travel
Elliptical Polarization
Light waves rotate but change shape
Linear polarization is the simplest and most common type. This is what polarized sunglasses use to reduce glare. Circular polarization is more complex and is used in 3D movie technology and some types of photography.
Polarization Discovery
Polarization was discovered in 1808 by French physicist Étienne-Louis Malus while looking through a calcite crystal at sunlight reflecting off windows!
How Polarization Works
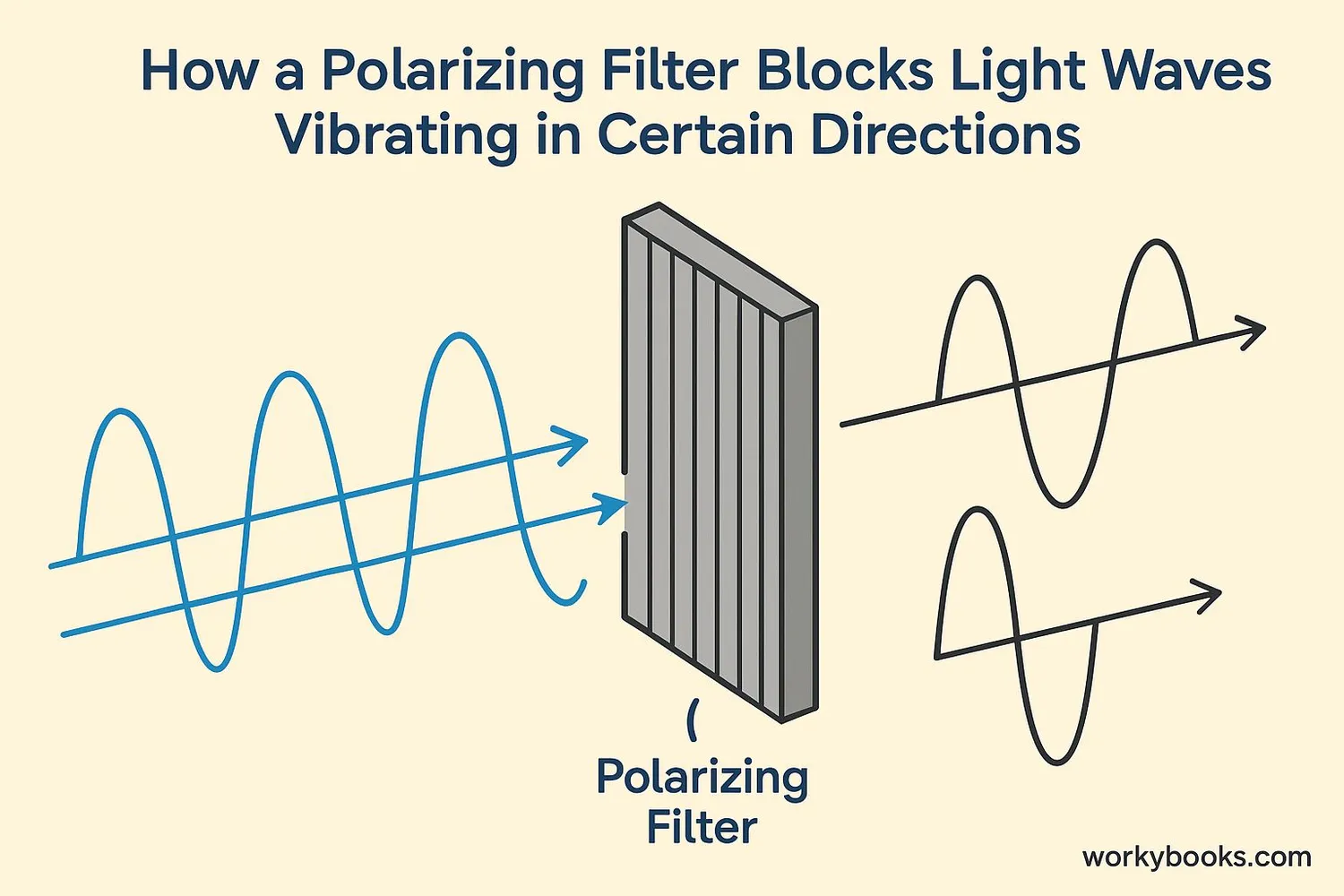
Polarizers are special materials that only allow light vibrating in a certain direction to pass through. Think of them like a picket fence:
• Light waves that are vibrating vertically can slip through the vertical slots
• Light waves vibrating horizontally get blocked by the fence
When unpolarized light hits a polarizing filter, only the light vibrating in the filter's direction passes through. The rest is absorbed or reflected.
Polarizing Filters
Special materials that block light vibrating in certain directions
Brewster's Angle
Light reflecting at a specific angle becomes completely polarized
Double Refraction
Some crystals split light into two polarized beams
Applications of Polarization
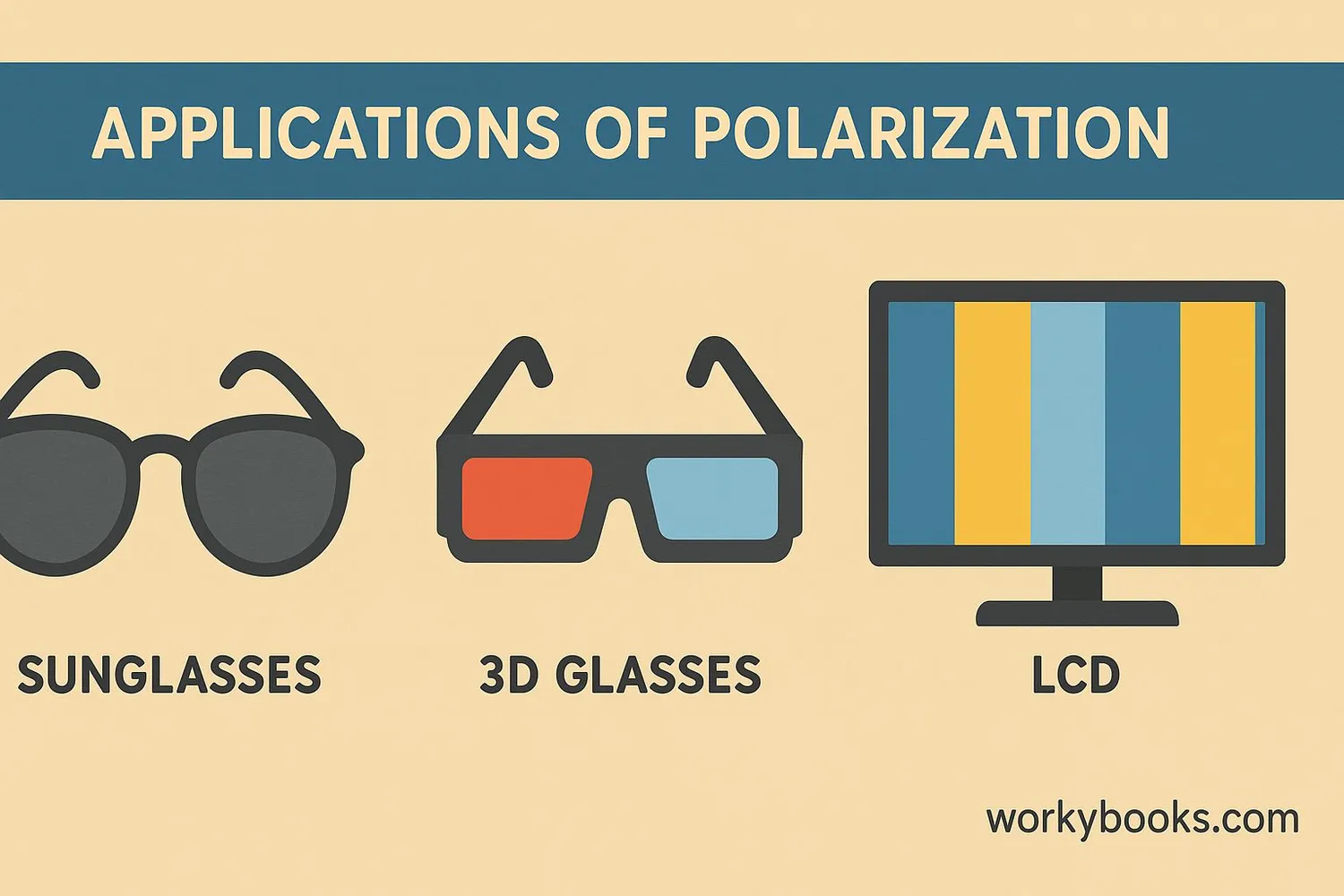
Polarization isn't just a science concept - it has many practical uses in our daily lives:
Polarized Sunglasses
Reduce glare from water, roads, and other reflective surfaces
3D Movies
Different images sent to each eye using polarized glasses
LCD Screens
Use polarization to control which pixels light up
Other important uses include:
• Photography filters to enhance skies and reduce reflections
• Scientific instruments to study materials
• Fiber optic communication systems
• Stress analysis in engineering
Polarization helps scientists study everything from distant galaxies to the structure of molecules!
Polarization Quiz
Test your polarization knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about polarization:
Fun Polarization Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about polarization!
Bee Navigation
Bees use the polarization pattern of sunlight in the sky to navigate, even on cloudy days! Their eyes have special receptors that detect polarized light.
Cosmic Polarization
Astronomers study polarized light from distant stars and galaxies to learn about magnetic fields in space and the early universe after the Big Bang!
Screens Everywhere
Your phone, computer, and TV screens all use polarization to create images. LCD screens have polarizing filters that control which pixels light up.
Crystal Power
Certain crystals like tourmaline and calcite naturally polarize light. Vikings may have used "sunstones" (calcite crystals) to navigate on cloudy days!





