Scattering - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how light and waves interact with matter all around us!
What is Scattering?
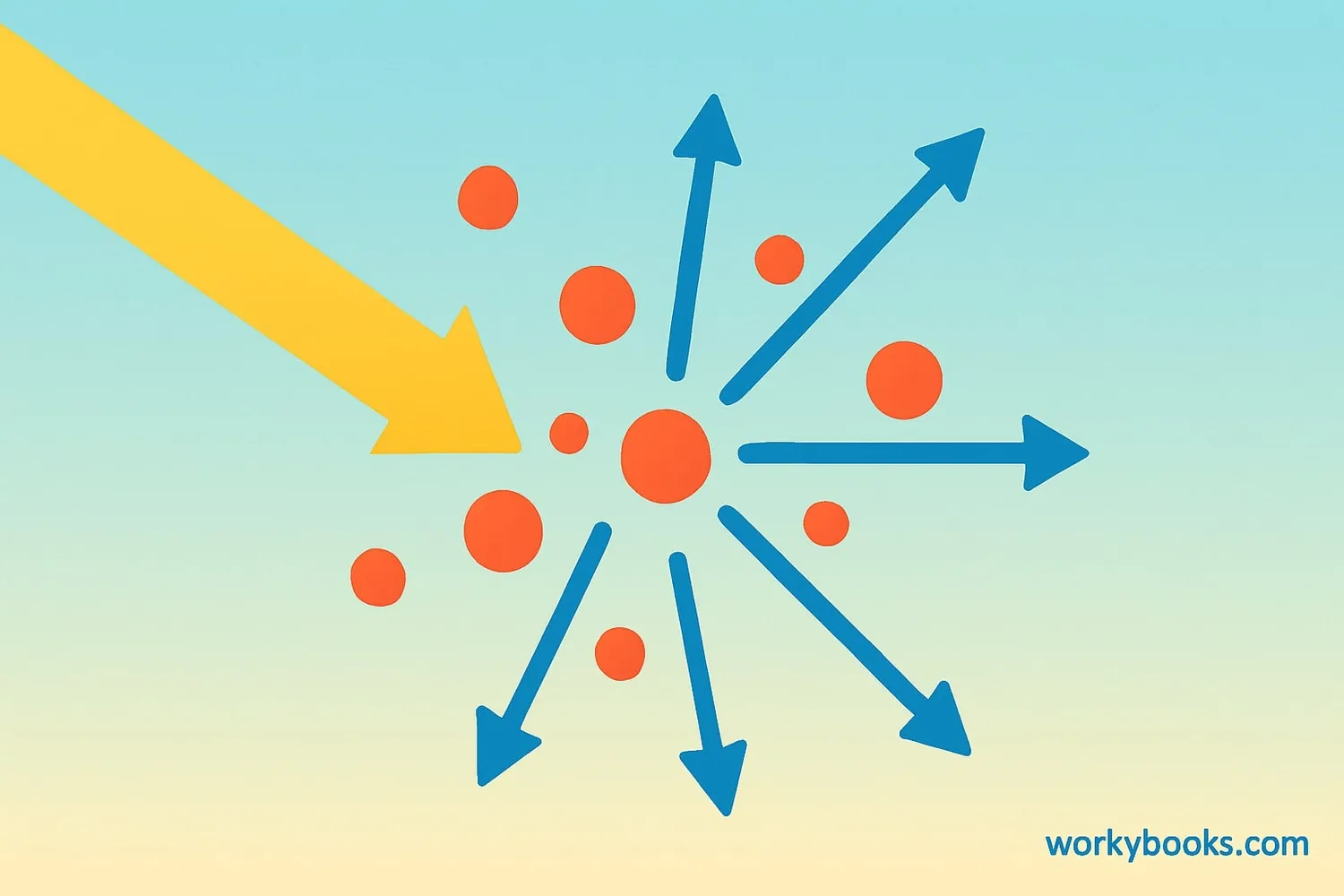
Scattering is what happens when light or other types of waves hit particles and bounce off in different directions! It's like when you throw a ball against a wall covered with bumpy textures - it doesn't bounce back straight but goes in various directions.
Think of scattering as nature's way of redirecting energy. When sunlight enters our atmosphere, it doesn't come straight to your eyes. Instead, it bounces off air molecules, dust, and water droplets, which is why we can see light even when we're not looking directly at the sun.
Science Fact!
The blue color of the sky is caused by scattering! Blue light scatters more than other colors because it travels as shorter, smaller waves.
Types of Scattering
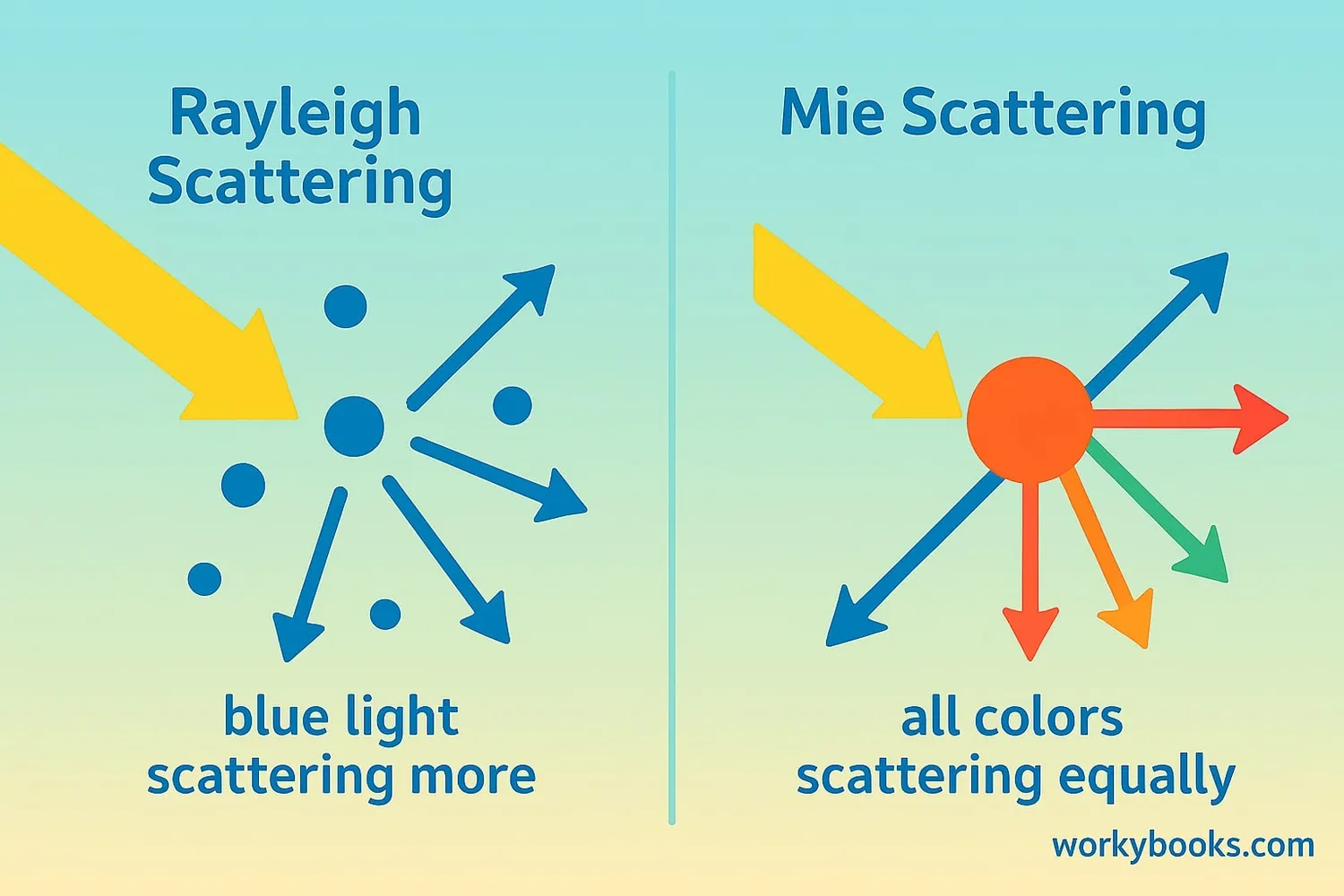
Scientists have identified different types of scattering based on the size of particles that the light hits:
Rayleigh Scattering
Happens when light hits very tiny particles (like air molecules)
Mie Scattering
Occurs with larger particles (like dust or pollen)
Tyndall Effect
Scattering in colloids that makes beams of light visible
Rayleigh scattering explains why the sky is blue - because blue light scatters more easily than other colors. During sunrise and sunset, when sunlight travels through more atmosphere, we see more red and orange colors because the blue light has been scattered away.
Everyday Example!
When you see a beam of sunlight through a window and notice dust particles floating in the air, you're observing scattering in action!
Why Scattering Matters
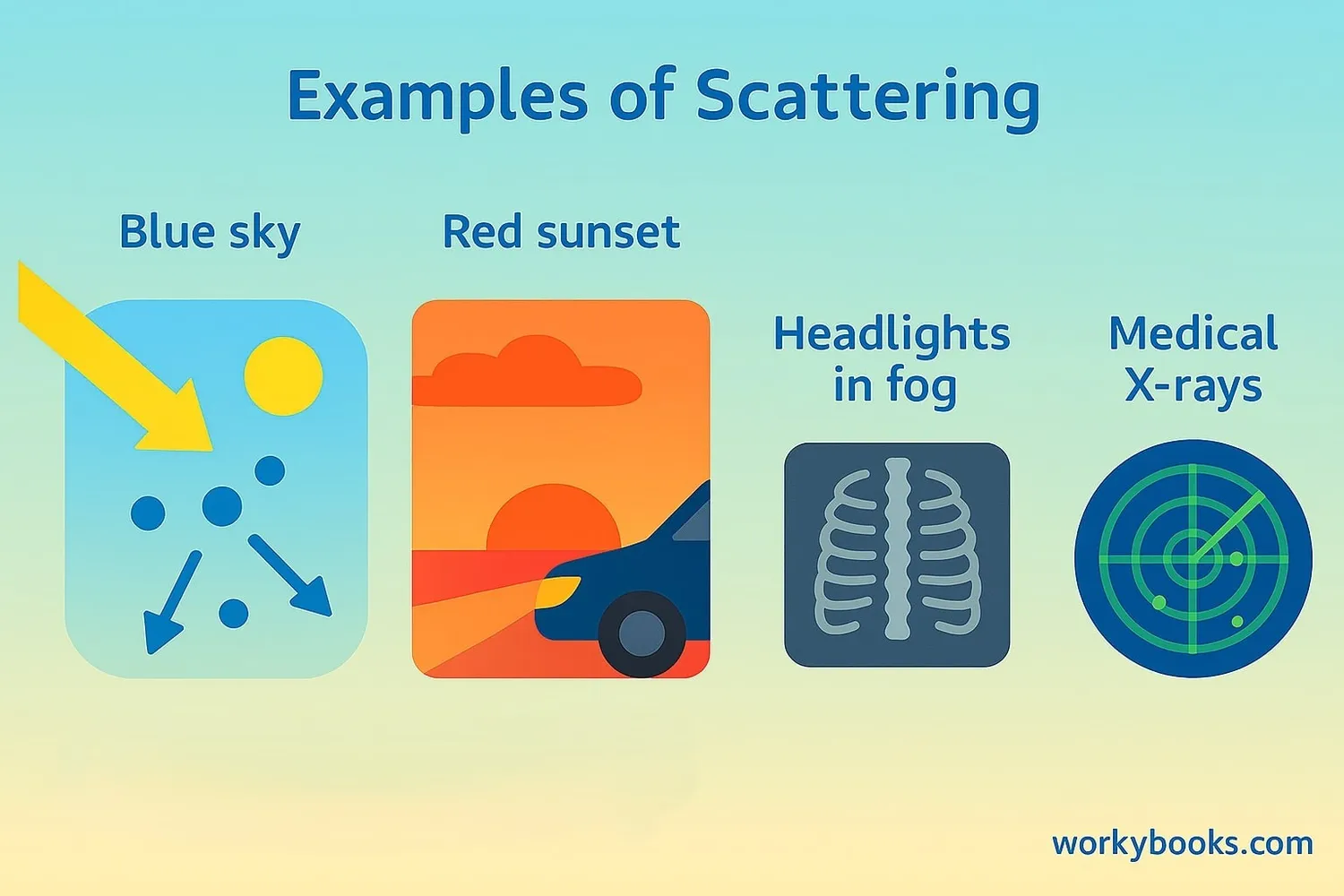
Scattering isn't just a cool science concept - it's essential to many things we experience every day:
Sky Colors
Creates blue skies and colorful sunsets
Vision
Allows us to see objects that aren't directly illuminated
Technology
Used in radar, medical imaging, and communications
Without scattering, we would have:
• A black sky instead of a blue one
• Extremely dark shadows with no soft edges
• No colorful sunrises or sunsets
• Difficulty with wireless communications
Scientists use scattering principles in many technologies, from weather radar that detects rain to medical devices that help doctors see inside our bodies!
Scattering Quiz
Test your knowledge about scattering with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about scattering:
Science Facts About Scattering
Discover some amazing facts about scattering!
Moon Sky
The moon has no atmosphere, so no scattering occurs there. That's why the sky appears black on the moon, even during the day!
Animal Vision
Some animals see scattering differently! Bees can see ultraviolet light scattering patterns on flowers that are invisible to humans, helping them find nectar.
Space Communication
NASA scientists account for scattering when communicating with spacecraft. Radio waves scatter in Earth's atmosphere, so they use special techniques to ensure clear signals.
Scientific Discovery
Lord Rayleigh first explained why the sky is blue in the 1870s. His work on scattering won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1904.





