Blue Carbon - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how coastal ecosystems help fight climate change by storing carbon!
What is Blue Carbon?

Blue carbon is the term for carbon captured and stored by the world's ocean and coastal ecosystems. These amazing natural systems include mangrove forests, salt marshes, and seagrass meadows.
Think of these coastal ecosystems as nature's superheroes in the fight against climate change! They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, just like plants on land. But what makes them special is that they can store much more carbon for much longer periods of time - sometimes for thousands of years!
Carbon Fact!
Coastal blue carbon ecosystems can store up to 10 times more carbon per acre than land forests!
Blue Carbon Ecosystems
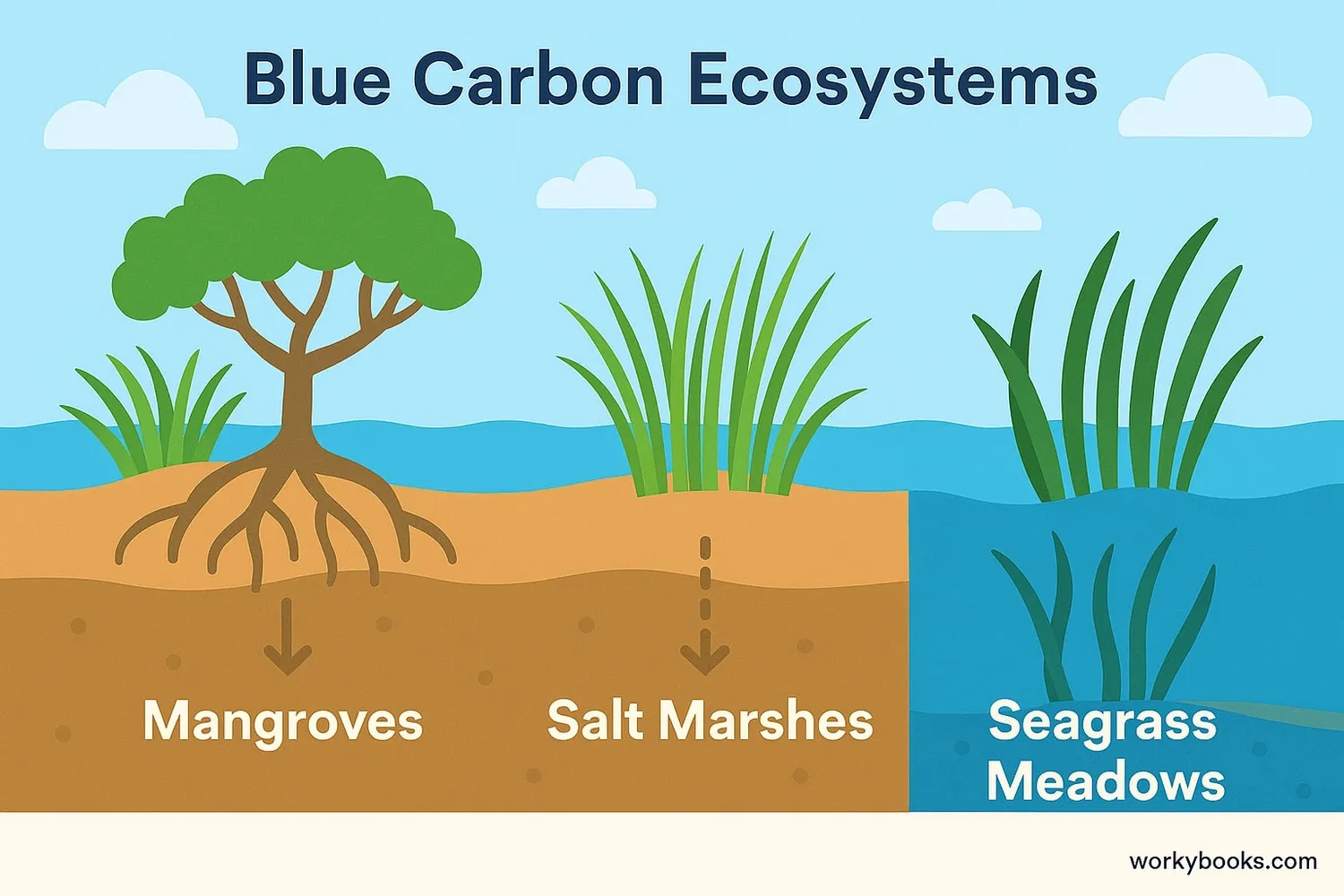
There are three main types of coastal ecosystems that are excellent at carbon sequestration (that's the scientific term for capturing and storing carbon):
Mangrove Forests
Trees that grow in salty coastal waters in tropical areas. Their tangled roots trap sediment and organic material.
Salt Marshes
Grassy areas flooded by salt water or brackish water, found along sheltered coastlines.
Seagrass Meadows
Flowering plants that form dense underwater meadows in shallow coastal waters.
These ecosystems are especially good at carbon sequestration because:
• Their waterlogged soils are low in oxygen, which slows down decomposition
• They continuously build layers of organic material that trap carbon
• They can store carbon in their biomass and sediments for very long periods
Ecosystem Fact!
Mangrove forests protect coastlines from erosion and provide nursery habitats for many fish species!
Why Blue Carbon is Important

Blue carbon ecosystems play a crucial role in climate change mitigation. Here's why they're so important:
Climate Protection
They capture and store large amounts of carbon dioxide, helping reduce greenhouse gases
Biodiversity Support
They provide habitat for many marine species and support fisheries
Coastal Protection
They buffer coastlines from storms and prevent erosion
Unfortunately, these important ecosystems are threatened by:
• Coastal development and pollution
• Climate change impacts like sea level rise
• Unsustainable fishing practices
When these ecosystems are damaged or destroyed, they can release their stored carbon back into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Protecting and restoring them is an important strategy for climate change mitigation.
Blue Carbon Quiz
Test your blue carbon knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about blue carbon:
Interesting Blue Carbon Facts
Discover some amazing facts about blue carbon ecosystems!
Carbon Storage Champions
Mangrove forests can store up to 4 times more carbon per acre than tropical rainforests! Their dense root systems trap organic material in oxygen-poor soils where decomposition is very slow.
Ancient Carbon Stores
Some blue carbon ecosystems have been storing carbon for thousands of years. The carbon in seagrass sediment can be over 6,000 years old—that's older than the pyramids of Egypt!
Natural Coastal Defense
Mangrove forests reduce wave height by up to 66%, providing valuable protection against storms and tsunamis for coastal communities. This helps prevent erosion and saves lives and property.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Blue carbon ecosystems support incredible biodiversity. Mangrove forests are nursery grounds for about 75% of commercially caught fish in tropical areas, supporting fisheries that feed millions of people.





