The Coriolis Effect - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how Earth's rotation affects winds, oceans, and weather patterns
What is the Coriolis Effect?
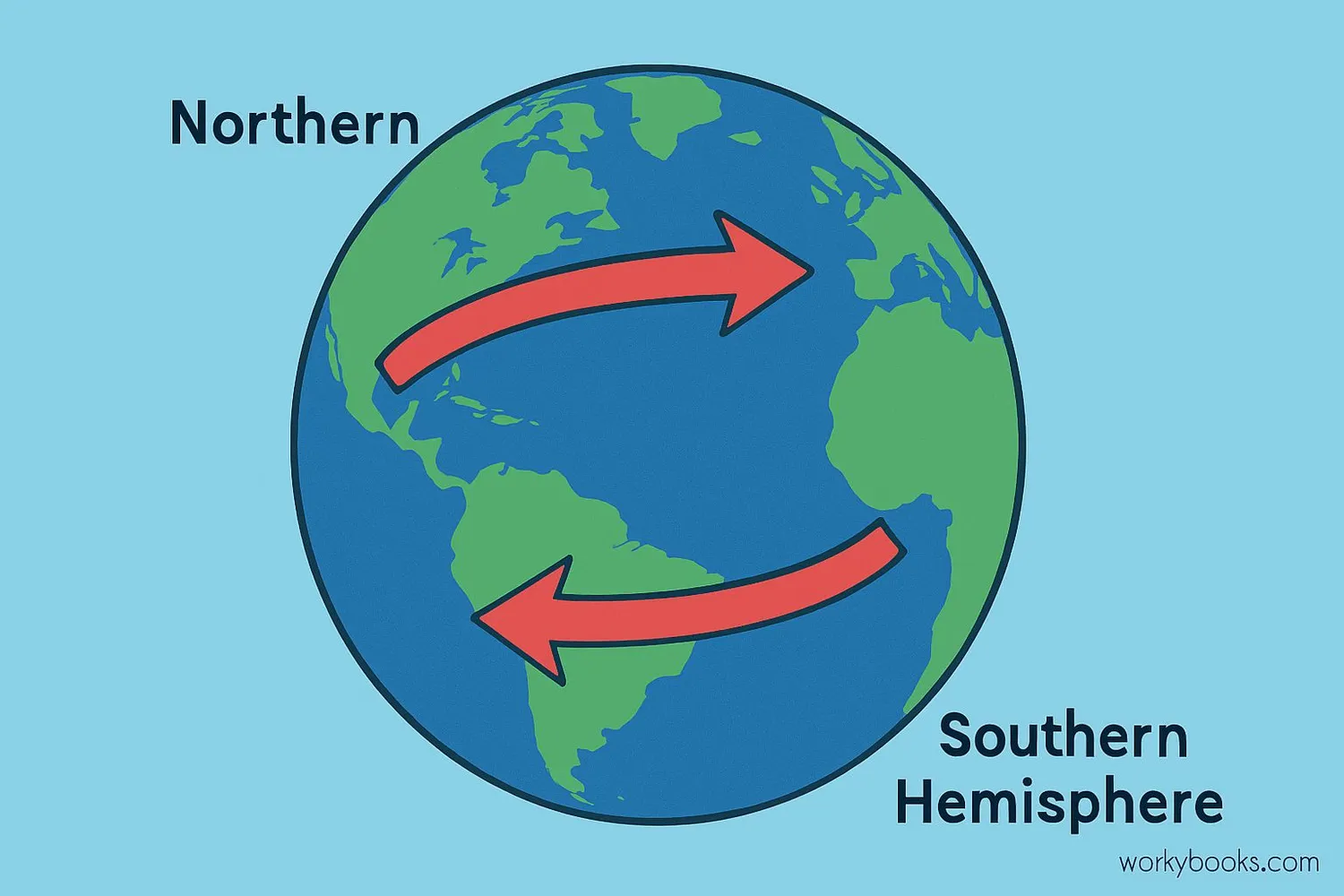
The Coriolis Effect is an apparent force that causes moving objects like air, water, or even airplanes to curve as they travel across Earth's surface. This happens because Earth is constantly rotating beneath us!
Imagine you're standing at the North Pole and throw a ball to a friend at the equator. By the time the ball reaches the equator, Earth has rotated eastward, making it look like the ball curved to the right. This apparent deflection is the Coriolis Effect.
Important to Remember
The Coriolis Effect doesn't actually change the direction of objects - it only appears to because we're standing on a rotating planet!
How the Coriolis Effect Works
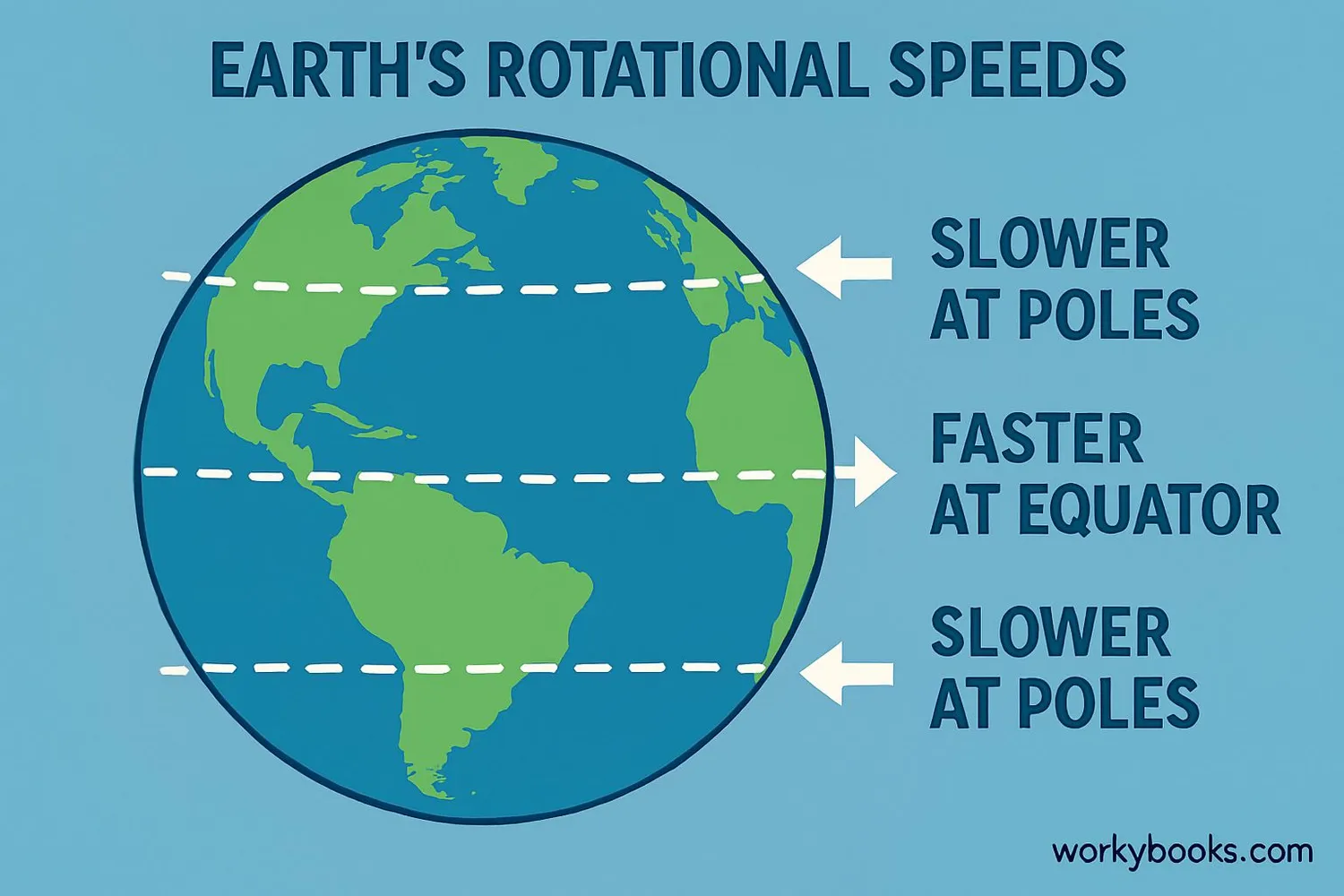
The Coriolis Effect happens because different parts of Earth rotate at different speeds:
Rotation Speed
Earth rotates faster at the equator than at the poles
Moving Objects
When objects move north or south, they keep their original speed
Apparent Curve
This speed difference makes their path appear curved
Northern Hemisphere
Objects curve to the right of their direction of motion
Southern Hemisphere
Objects curve to the left of their direction of motion
The strength of the Coriolis Effect depends on two things:
1. Latitude - It's strongest at the poles and weakest at the equator
2. Object Speed - Faster moving objects experience a stronger effect
Impact on Weather & Oceans
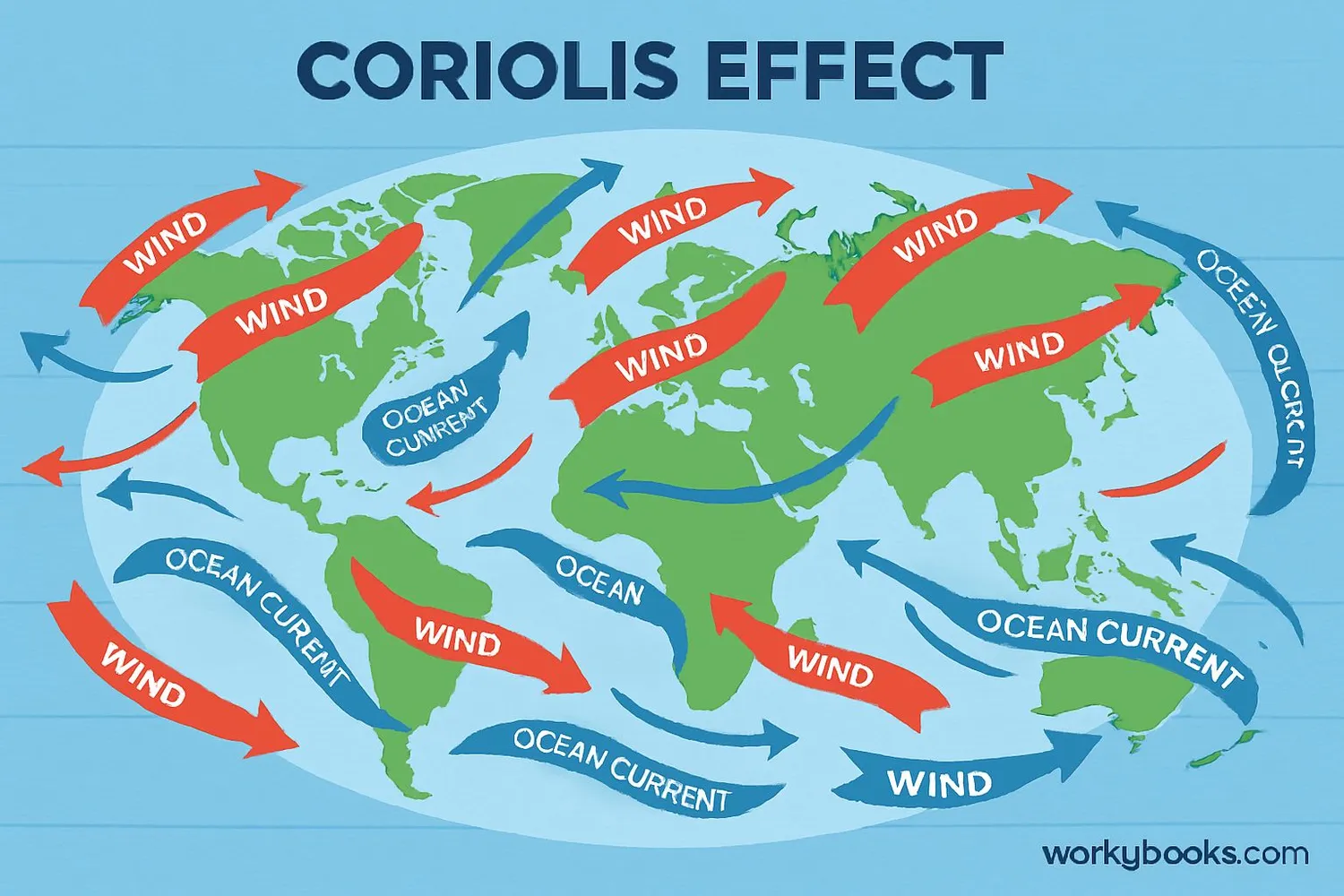
The Coriolis Effect has powerful impacts on our planet:
Wind Patterns
Creates trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies
Ocean Currents
Causes circular gyres in ocean basins
Storm Rotation
Makes hurricanes spin counter-clockwise in Northern Hemisphere
Hurricanes and Cyclones: The Coriolis Effect causes these massive storms to rotate. In the Northern Hemisphere, they spin counter-clockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere they spin clockwise. This rotation is why meteorologists can predict storm paths.
Ocean Currents: The Coriolis Effect combines with winds to create massive circular ocean currents called gyres. These currents help distribute heat around the planet and affect marine ecosystems.
Long-Range Shooting: Military snipers and artillery operators must account for the Coriolis Effect when firing over long distances!
Coriolis Effect Quiz
Test your understanding with this interactive quiz. Select the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to common questions about the Coriolis Effect:
Science Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about the Coriolis Effect:
Beyond Earth
The Coriolis Effect exists on other planets too! Jupiter's Great Red Spot and Saturn's hexagonal storm at its north pole are both influenced by their rapid rotation.
Military Importance
During World War I, artillery officers had to calculate Coriolis corrections for long-range guns. Missing these calculations could mean missing targets by hundreds of meters!
Tornado Rotation
While large storms follow the hemisphere patterns, small tornadoes can rotate in either direction regardless of hemisphere. Their rotation is more influenced by local weather conditions.
Deep Ocean Currents
The Coriolis Effect influences deep ocean currents too, creating the Ekman Spiral - a phenomenon where water moves at angles to the wind direction, gradually turning with depth.





