Polar Climate - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the frozen regions at the top and bottom of our planet!
What is Polar Climate?

Polar climate refers to the extremely cold weather conditions found at the North and South Poles of our planet. These regions are frozen for most or all of the year and have very special environmental conditions.
Polar climates are the coldest places on Earth! They're located at the top and bottom of our planet where the sun's rays hit at a low angle, spreading the sunlight over a larger area and making it less intense. This is why these areas stay so cold.
The two main characteristics of polar climates are:
• Extremely cold temperatures - often below freezing even in summer
• Little precipitation - these regions are actually deserts because they get so little rain or snow
Climate Fact!
Despite being covered in ice, polar regions get very little snowfall each year—less than some deserts get rain!
Types of Polar Climate

There are two main types of polar climate: the tundra climate and the ice cap climate. Let's explore what makes each one special:
Tundra Climate
Found in areas like northern Alaska, Canada, and Russia where the ground thaws slightly in summer
Permafrost
Permanently frozen ground found in tundra regions
Ice Cap Climate
Found in Greenland and Antarctica where ice covers the land year-round
No Monthly Thaw
In ice cap regions, temperatures never rise above freezing
The main difference between these two polar climates is temperature. In tundra climates, at least one month has average temperatures above freezing (32°F or 0°C), which allows some plants to grow during the short summer. In ice cap climates, no month has average temperatures above freezing, so the landscape remains permanently frozen with no vegetation.
Permafrost Depth
In some tundra regions, permafrost can be more than 1,500 feet (457 meters) deep! The active layer that thaws in summer is usually only 1-4 feet deep.
Polar Ecosystems
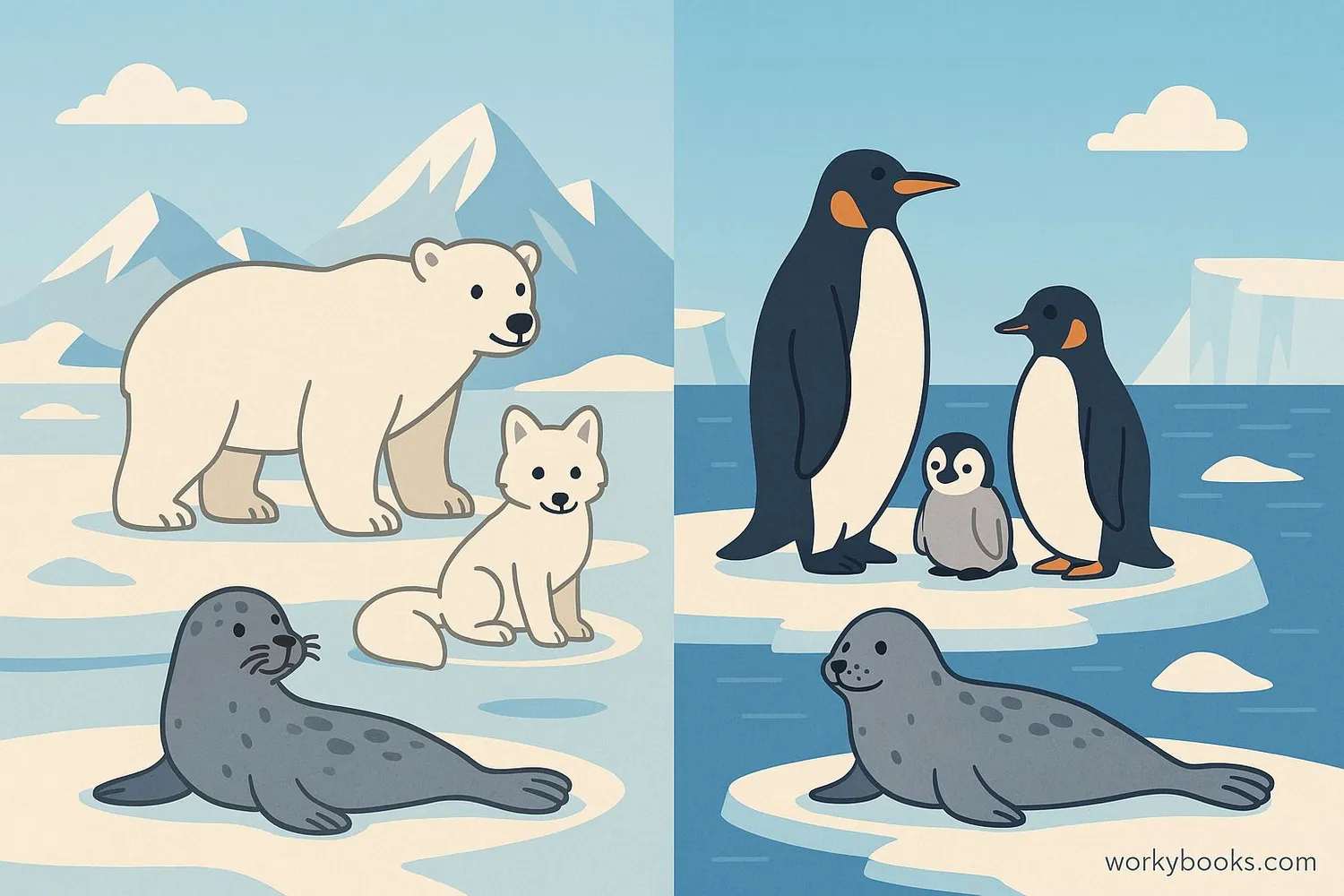

Polar ecosystems are unique environments where plants and animals have developed special adaptations to survive the extreme cold. Despite the challenging conditions, these regions are home to amazing wildlife.
Animal Adaptations
Thick fur, fat layers, and hibernation help animals survive extreme cold
Plant Life
Low-growing plants like mosses, lichens, and small shrubs survive in tundra regions
Seasonal Changes
Animals migrate or change behaviors with the extreme seasonal variations
The Arctic and Antarctic have different ecosystems:
Arctic: Home to polar bears, arctic foxes, caribou, and many seal species. The Arctic has more land animals because it's mostly frozen ocean surrounded by continents.
Antarctic: Mostly covered by the Antarctic ice sheet. Penguins, seals, and whales live here, but no land mammals. The surrounding Southern Ocean is rich with krill, which supports many marine animals.
Importance of Polar Regions
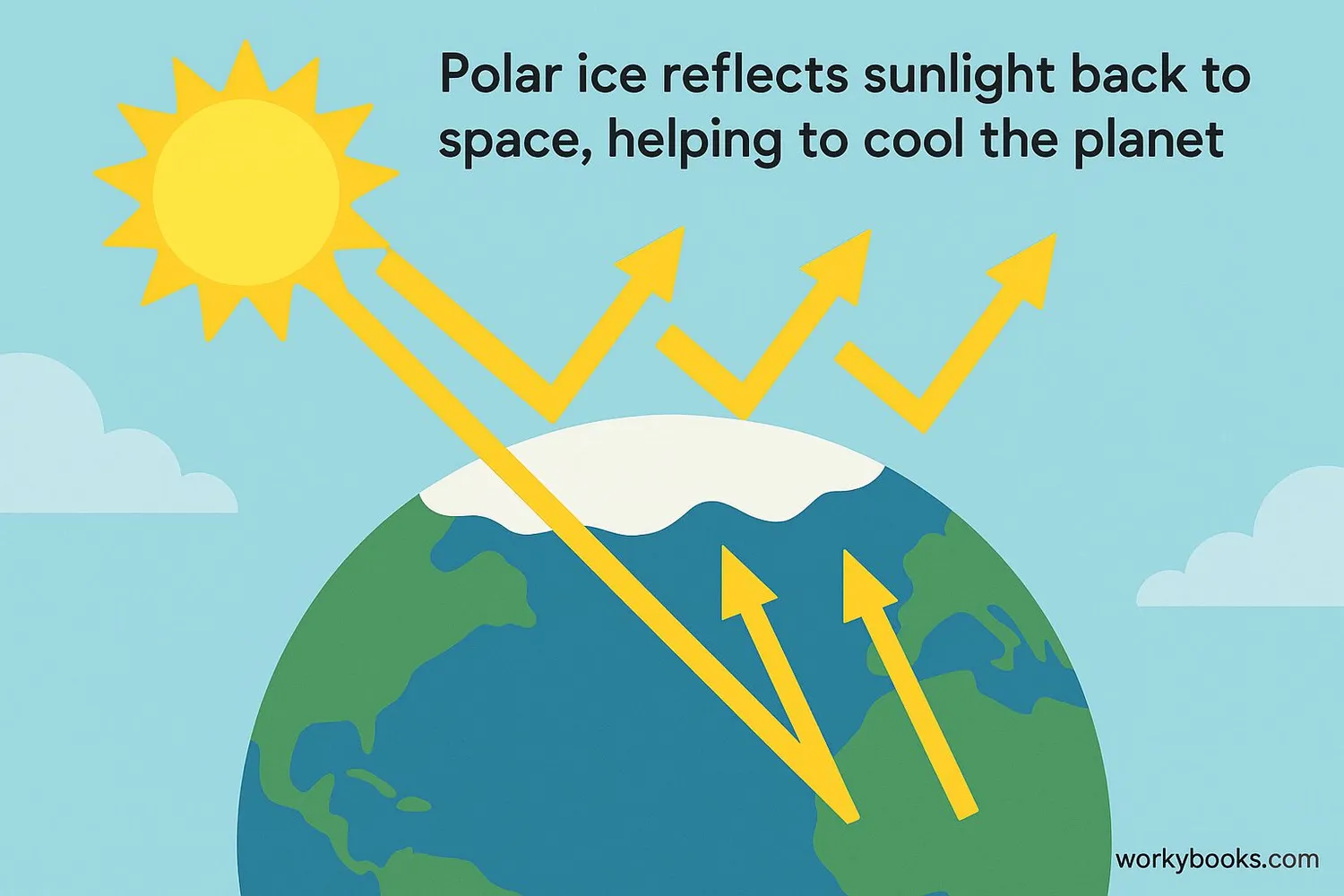
Polar regions are much more than just frozen wastelands—they play vital roles in keeping our planet healthy and balanced. Here's why they're so important:
Climate Regulation
White ice and snow reflect sunlight, helping to cool the planet
Sea Level
Polar ice caps contain most of Earth's fresh water
Scientific Research
Polar regions provide unique opportunities to study Earth's history and climate
The polar regions act like Earth's air conditioning system. The bright white snow and ice reflect sunlight back into space instead of absorbing it as heat. This helps regulate temperatures around the world.
Scientists also study ice cores from polar regions to learn about Earth's climate history. These ice cores contain bubbles of ancient air that tell us about past temperatures and atmospheric conditions.
Additionally, polar regions are important for:
• Ocean currents - Cold, dense water from polar regions drives global ocean circulation
• Unique species - Many animals found only in polar regions
• Indigenous cultures - People have lived in Arctic regions for thousands of years
Polar Climate Quiz
Test your polar climate knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about polar climates:
Polar Climate Facts
Discover some amazing facts about polar climates!
Massive Ice Sheets
The Antarctic ice sheet contains about 90% of the world's fresh water! If all of it melted, sea levels would rise by about 200 feet (61 meters).
Antarctic Krill
Antarctic krill are tiny shrimp-like creatures that form the base of the Southern Ocean food web. Their total biomass is estimated at 379 million tons!
Windiest Place
Antarctica is the windiest continent, with winds regularly exceeding 100 mph (160 km/h). The highest wind speed recorded was 199 mph (327 km/h)!
Ancient Air
Scientists can study Earth's ancient atmosphere by analyzing air bubbles trapped in polar ice. Some ice cores contain air from over 800,000 years ago!





