Gaia Hypothesis - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how Earth works like a living system to maintain life
What is the Gaia Hypothesis?
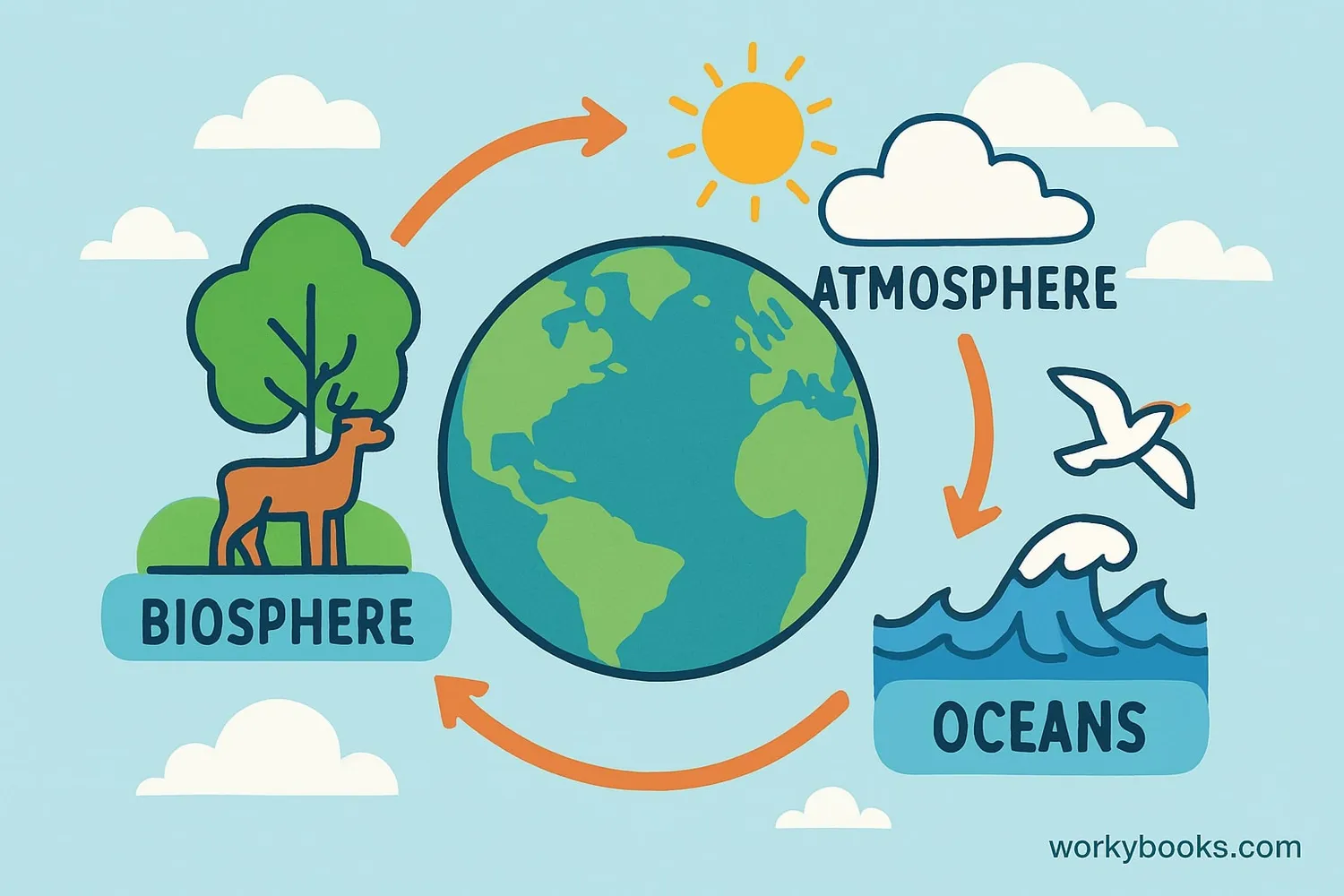
The Gaia Hypothesis is the idea that Earth works like a living system! It suggests that our planet is a self-regulating system where living things and their environment work together to maintain conditions for life.
Proposed by scientist James Lovelock and microbiologist Lynn Margulis in the 1970s, this theory sees Earth as a complex system that can maintain balance, similar to how our bodies regulate temperature.
Think of Earth as a giant spaceship where all parts - the atmosphere, oceans, rocks, and living things - work together to keep conditions just right for life to exist.
Name Origin
The name "Gaia" comes from the ancient Greek goddess of Earth, representing the idea of Earth as a living being.
How the Gaia Hypothesis Works
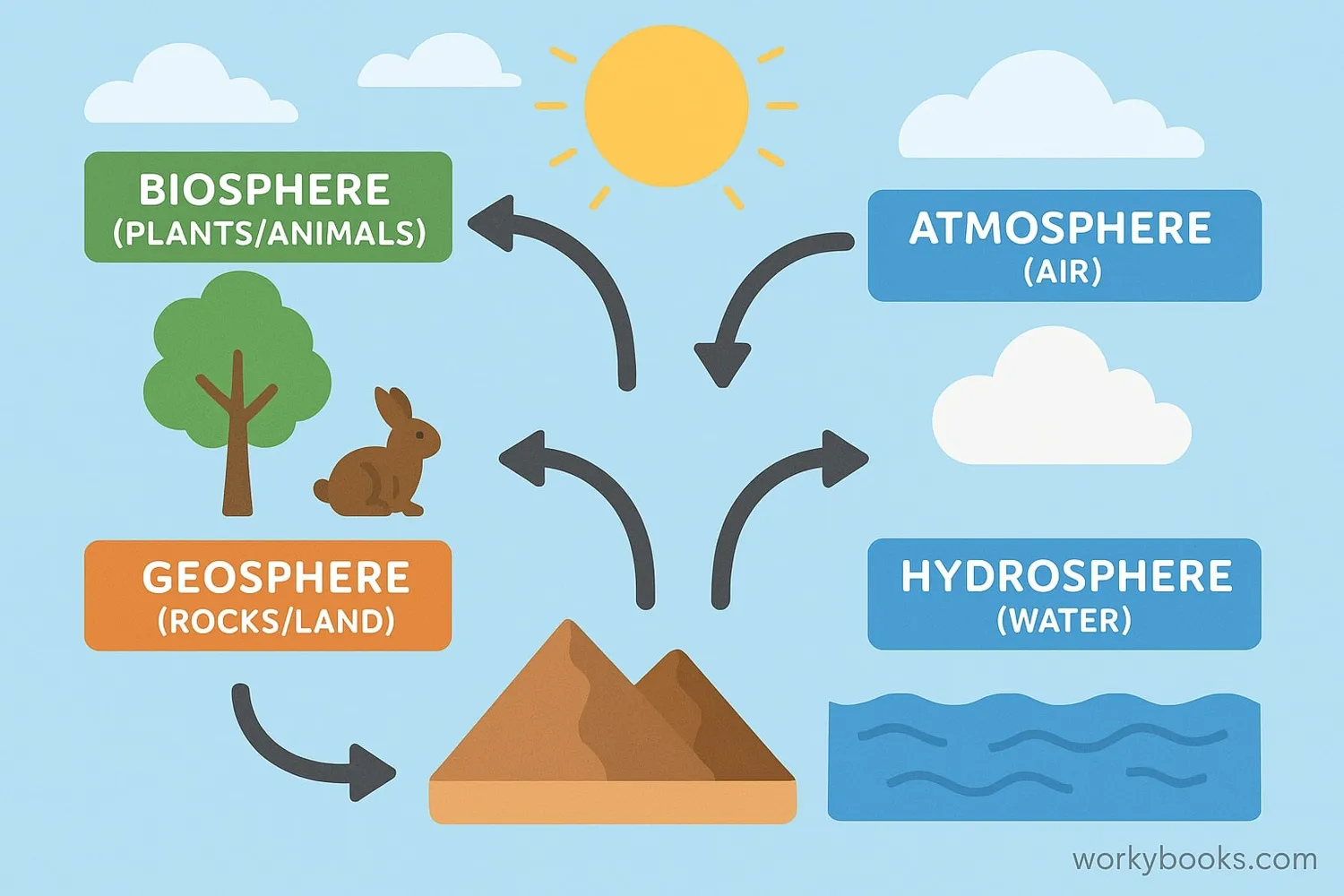
The Gaia Hypothesis explains how Earth maintains homeostasis - a balanced state that supports life. Here's how this amazing system works:
Biosphere
Living organisms interact with their environment
Atmosphere
Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide are regulated
Oceans
Water systems transport heat and nutrients
Biogeochemistry
Chemical cycles connect living and non-living systems
Self-regulation
Systems adjust to maintain life-supporting conditions
The famous Daisyworld model shows how this might work. Imagine a planet with black and white daisies. When the planet warms, white daisies (that reflect heat) thrive and cool the planet. When it cools, black daisies (that absorb heat) thrive and warm it. This creates a balanced temperature!
Homeostasis in Action
Earth's oxygen level has stayed around 21% for millions of years, thanks to the balance between plants producing oxygen and animals using it.
Why the Gaia Hypothesis is Important

Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis helps us see Earth as a connected system and recognize our role in maintaining planetary health:
Climate Change
Shows how human activities disrupt Earth's natural balance
Biodiversity
Highlights the importance of diverse life for system stability
Sustainability
Teaches us to work with Earth's systems, not against them
The Gaia Hypothesis is especially relevant today because:
• We live in the Anthropocene - a time when humans significantly impact Earth's systems
• Understanding Earth as a connected system helps us address climate change
• It shows why protecting biodiversity is essential for planetary health
• It reminds us of our responsibility to maintain Earth's planetary habitability
By seeing Earth as a complex, self-regulating system, we can make better decisions to protect our planet for future generations.
Gaia Hypothesis Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Gaia Hypothesis:
Fun Gaia Hypothesis Trivia
Discover amazing facts about Earth as a self-regulating system!
NASA Connection
James Lovelock developed the Gaia Hypothesis while working for NASA on methods to detect life on Mars. He realized Earth's atmosphere is chemically unstable and must be regulated by life.
Oxygen Balance
Earth's oxygen level has remained around 21% for 300 million years! If it reached 25%, forest fires would burn out of control. At 15%, animals would suffocate. Gaia theory explains this perfect balance.
Ocean Regulation
The ocean's saltiness stays at 3.4% because rivers carry salt to oceans, and salt is removed when seawater seeps into the seafloor. This balance has been maintained for billions of years.
Temperature Control
Despite the sun increasing its heat output by 30% over Earth's history, Earth's temperature has remained stable enough for life. This remarkable stability is evidence of Gaia's self-regulation.





