Sun Pattern - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover why we have seasons and how the Sun moves through our sky
The Sun's Path in Our Sky
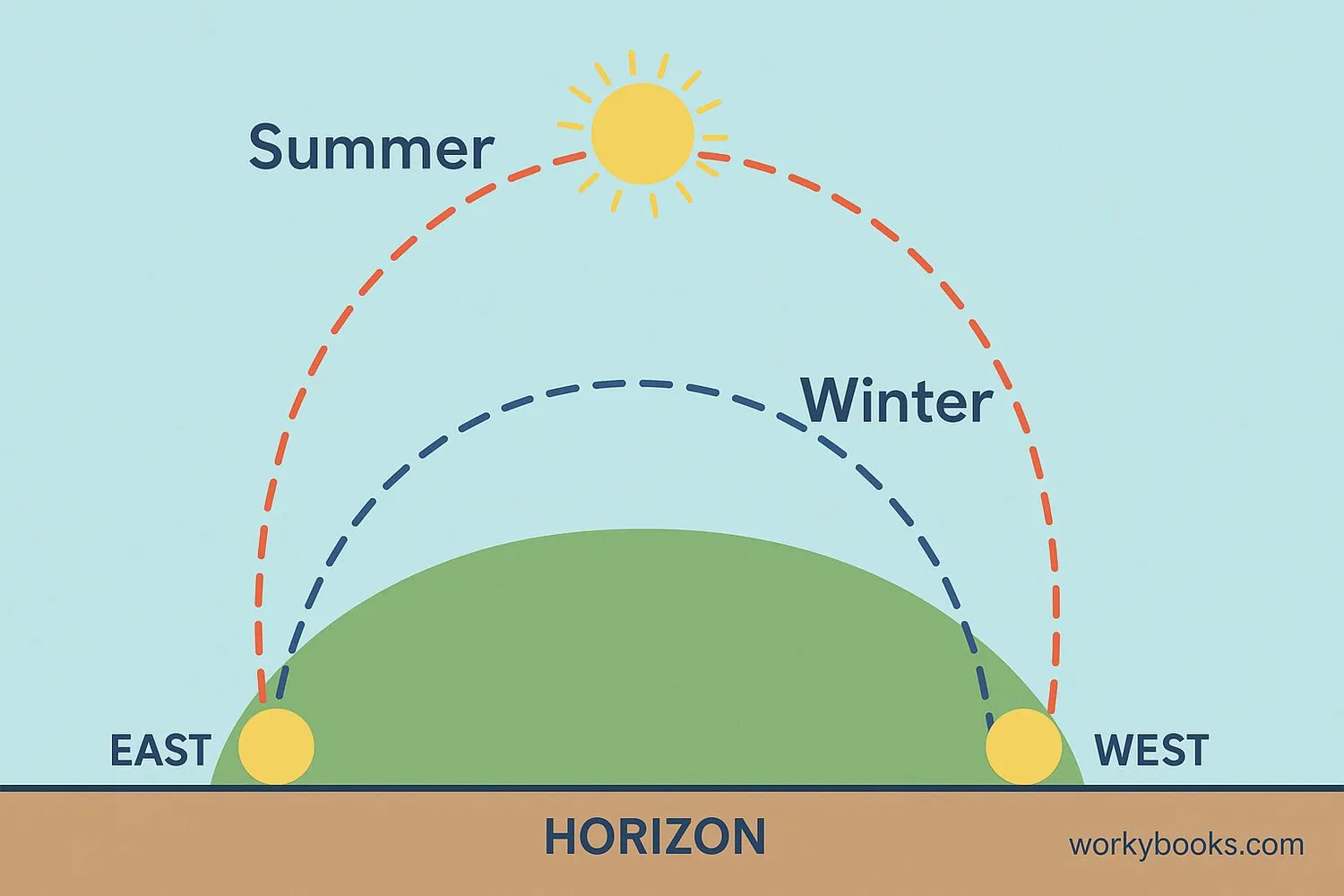
The Sun appears to move across our sky every day, but its path changes throughout the year! This is called the Sun's apparent motion.
Key facts about the Sun's path:
• The Sun always rises in the east and sets in the west
• In summer, the Sun takes a longer, higher path across the sky
• In winter, the Sun takes a shorter, lower path across the sky
• At noon, the Sun is highest in the sky during summer
• The ecliptic is the path the Sun appears to follow through the stars
Did You Know?
At the equator, the Sun rises almost straight up and sets almost straight down every day!
Why Do We Have Seasons?
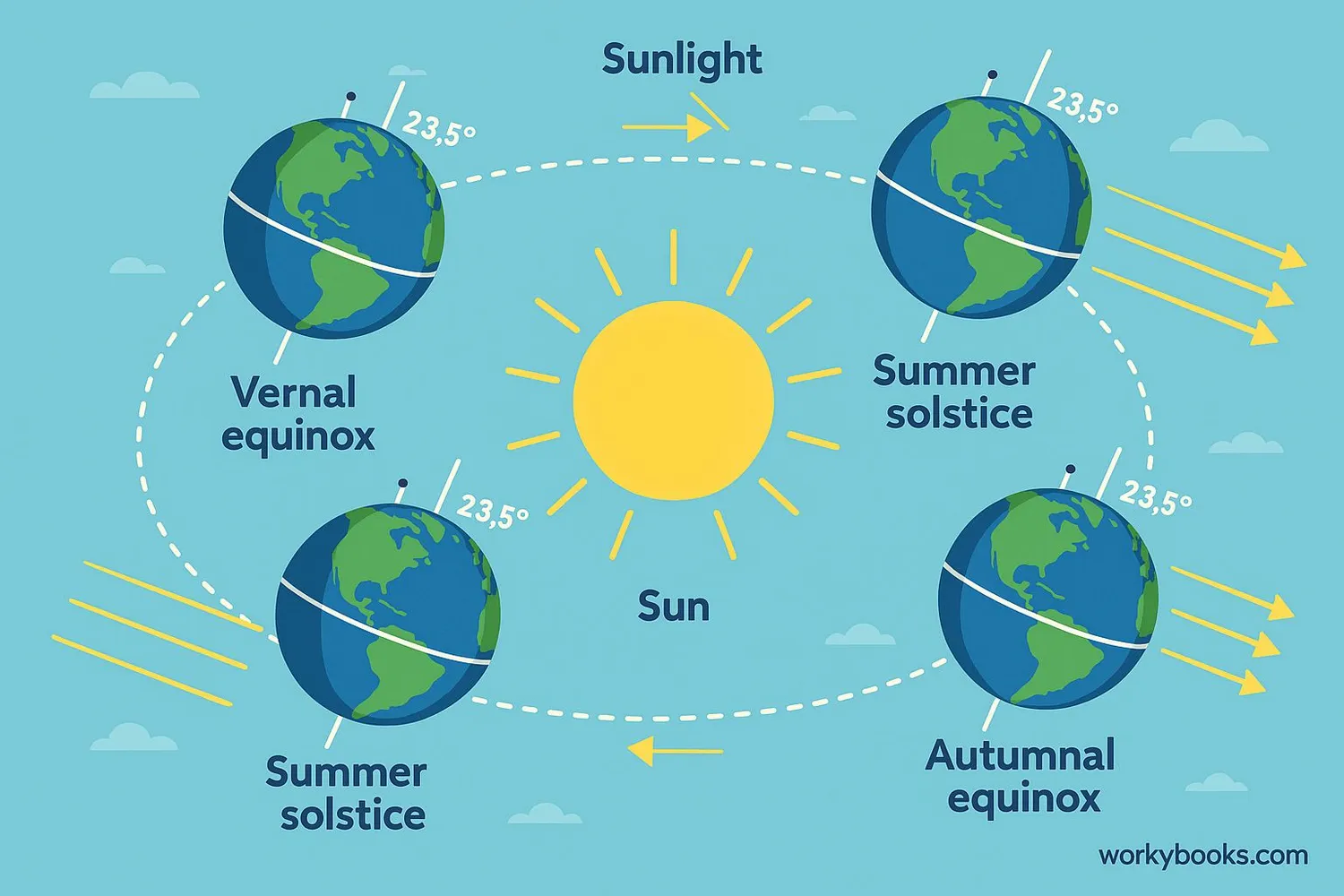
Seasons happen because Earth is tilted on its axis by about 23.5 degrees. As Earth orbits the Sun, different parts of our planet receive different amounts of sunlight.
How seasons work:
• Earth's axis always points in the same direction (toward Polaris)
• When your hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, it's summer
• When your hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, it's winter
• The Sun's rays are more direct in summer, making them warmer
• The Sun's rays are more spread out in winter, making them cooler
Earth's Tilt
Earth rotates on a tilted axis (23.5°)
Orbit
Earth orbits the Sun in one year
Direct Rays
Summer when tilted toward the Sun
Indirect Rays
Winter when tilted away from Sun
Important Fact!
Seasons are NOT caused by Earth being closer to the Sun! Earth is actually farthest from the Sun during northern summer.
Solstices and Equinoxes
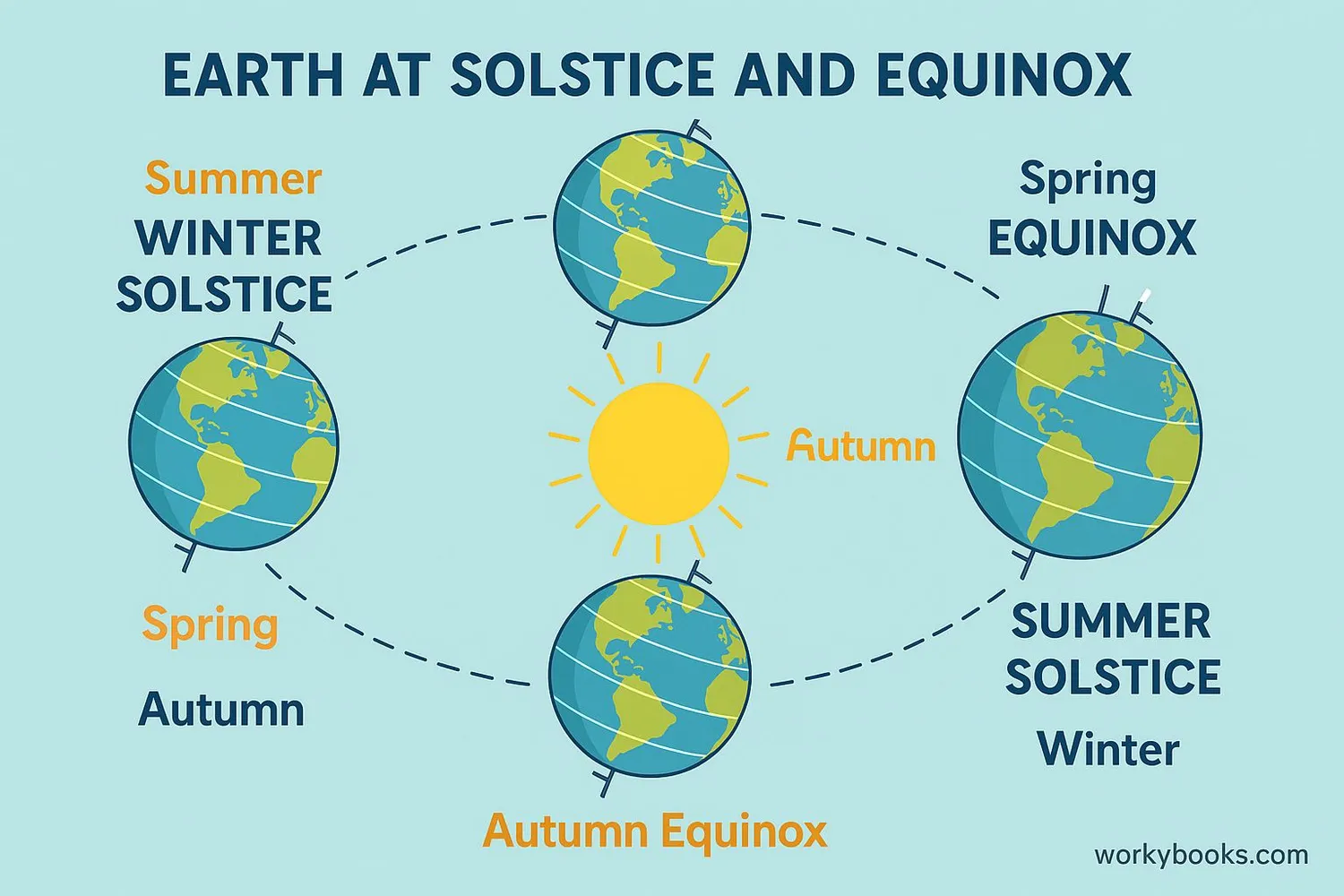
Solstices and equinoxes mark special moments in Earth's journey around the Sun. These are the days when seasons officially change!
Summer Solstice
June 20-22
Longest day in Northern Hemisphere
Sun highest in sky
Winter Solstice
December 20-22
Shortest day in Northern Hemisphere
Sun lowest in sky
Spring Equinox
March 19-21
Equal day and night
Sun rises due east
Fall Equinox
September 21-23
Equal day and night
Sun sets due west
Equinox means "equal night" - during these days, all places on Earth experience about 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness. At the equator, every day is like an equinox!
How Latitude Affects Sunlight
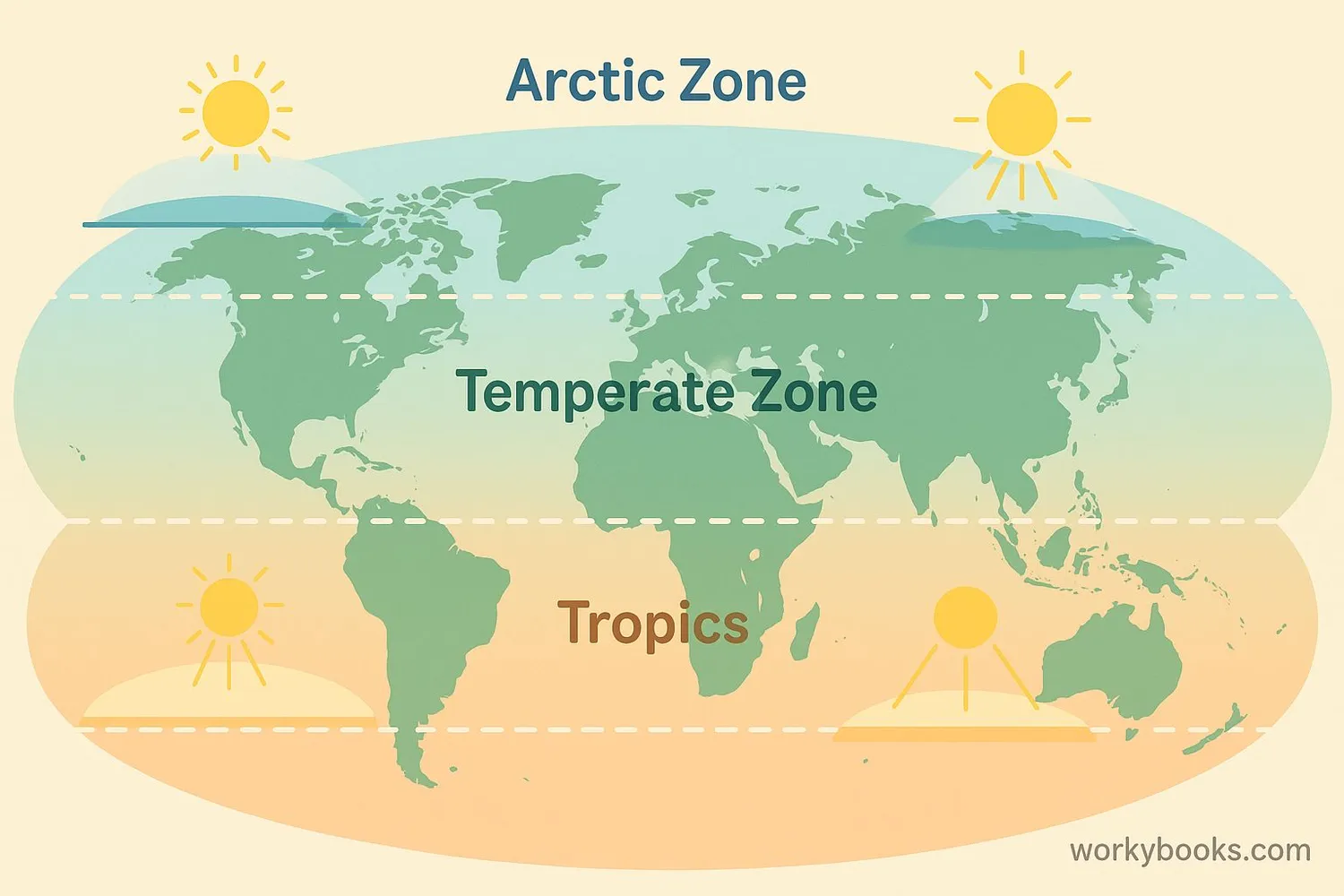
Where you live on Earth dramatically affects how you experience sunlight throughout the year. Latitude measures how far north or south you are from the equator.
Tropics
Between 23.5°N and 23.5°S
Consistent daylight year-round
Temperate Zones
Between 23.5°-66.5° N/S
Distinct seasons with changing day length
Polar Regions
Above 66.5° N/S
Midnight sun in summer, polar night in winter
Special latitude lines:
• Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) - Northernmost point where Sun can be directly overhead
• Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S) - Southernmost point where Sun can be directly overhead
• Arctic Circle (66.5°N) - Area with 24-hour daylight at summer solstice
• Antarctic Circle (66.5°S) - Area with 24-hour darkness at winter solstice
Sun and Seasons Quiz
Test your knowledge about the Sun's patterns and seasons with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Sun and seasons:
Sun and Seasons Trivia
Discover amazing facts about our Sun and seasons!
Sun Distance
Earth is about 93 million miles from the Sun. Sunlight takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach us!
Equal Light Days
Equinox days have nearly equal daylight and darkness, but true equality actually occurs a few days before spring equinox and after fall equinox!
Changing Tilt
Earth's tilt changes very slowly over 41,000 years from about 22.1° to 24.5°. Right now it's 23.4° and decreasing slightly.
Solar Power
In just one hour, the Sun provides more energy to Earth than humans use in an entire year! This solar power drives our seasons and weather patterns.





