Tipping Point - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding critical thresholds in our climate system
What Are Climate Tipping Points?

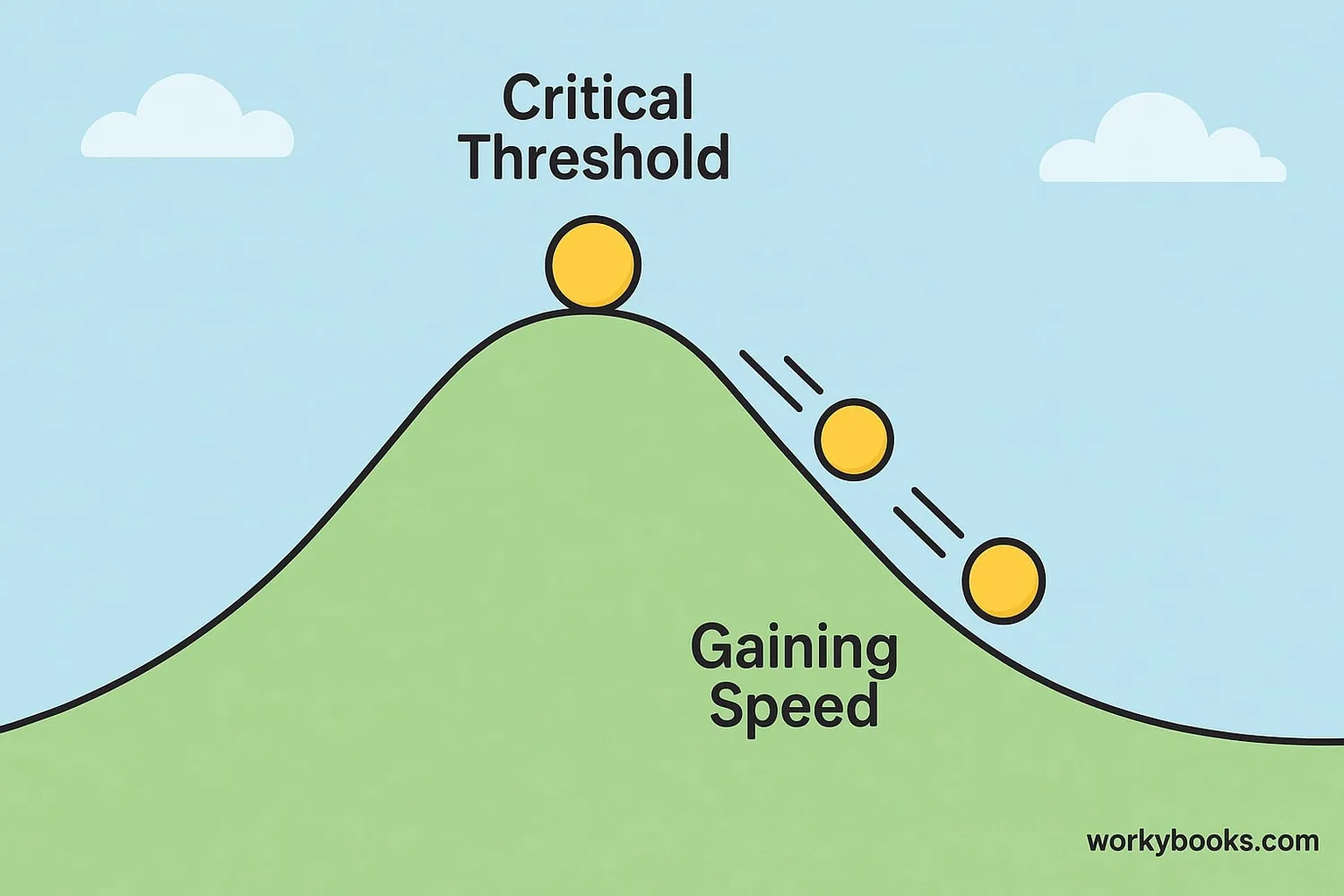
A climate tipping point is like a critical threshold in Earth's systems. Think of it as a point of no return - once we cross it, changes become irreversible and can lead to big impacts on our planet.
Imagine leaning back in a chair. At first, you're stable. But if you lean too far, you'll tip over and fall. Climate tipping points work similarly. Small changes might not cause big problems at first, but after a certain point, everything changes quickly.
Science Fact!
Scientists have identified at least 16 major climate tipping points in Earth's systems. Crossing even a few could dramatically change life on our planet.
How Climate Tipping Points Work
Climate tipping points involve four key stages:
Gradual Change
Slow changes like rising temperatures from greenhouse gases
Critical Threshold
A point where small changes cause big effects
Feedback Loop
Changes that speed up the process (like melting ice causing more warming)
Irreversible Impact
Changes that continue even if we stop the original cause
Once a tipping point is crossed, it can trigger a chain reaction. For example, melting Arctic ice reduces the Earth's ability to reflect sunlight, causing more warming and more melting - a dangerous cycle!
Climate Connection!
Tipping points are interconnected. Crossing one could trigger others, creating a "domino effect" of climate changes.
Key Climate Tipping Point Examples
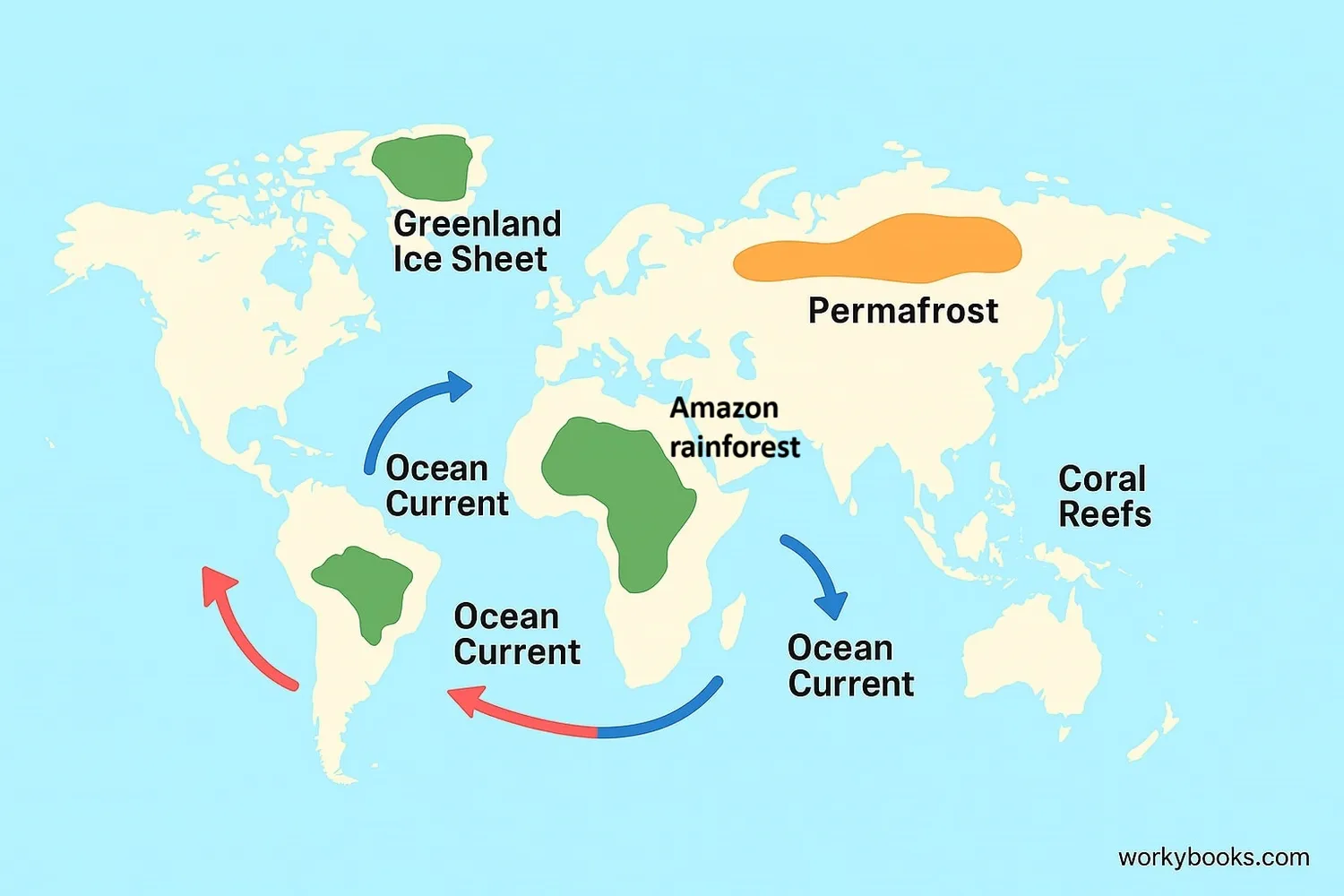
Scientists have identified several critical tipping points in Earth's climate system:
Greenland Ice Sheet
If melting passes a critical point, it could raise sea levels by 7 meters
Amazon Rainforest
Deforestation and drought could turn it into a savanna, releasing stored carbon
Ocean Currents (AMOC)
Melting ice could disrupt currents that regulate global weather patterns
Permafrost
Thawing could release massive amounts of methane, a powerful greenhouse gas
Coral Reef Die-offs
Warmer oceans cause coral bleaching, destroying marine ecosystems
These tipping points are like Earth's natural systems that have been stable for thousands of years. But human activities are pushing them toward dangerous thresholds that could change our planet forever.
Climate Tipping Points Quiz
Test your knowledge about climate tipping points with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about climate tipping points:
Earth System Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about Earth's climate systems:
Ancient Ice
The Greenland ice sheet is over 100,000 years old! If it completely melted, global sea levels would rise about 7 meters (23 feet).
Forest Carbon
The Amazon rainforest stores about 200 billion tons of carbon - equivalent to 15-20 years of global human CO2 emissions!
Ocean Highways
The Atlantic Ocean's current system (AMOC) moves as much water as 100 Amazon Rivers! It helps regulate temperatures across Europe and North America.
Frozen Time Capsule
Arctic permafrost contains remains of plants and animals frozen since the Ice Age. As it thaws, these ancient organisms decompose, releasing greenhouse gases.




