Botany - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how plants grow, survive, and support all life on Earth
What is Botany?

Botany is the scientific study of plants. It includes learning about how plants grow, what different plants look like, how they interact with their environment, and how people use plants for food, medicine, and other purposes.
Plants are essential for life on Earth! They produce oxygen through photosynthesis, provide food for animals and humans, create habitats for wildlife, and help maintain the planet's climate. Without plants, life as we know it wouldn't exist.
Plant Fact!
There are over 390,000 known plant species on Earth, and scientists discover new ones every year!
Branches of Botany
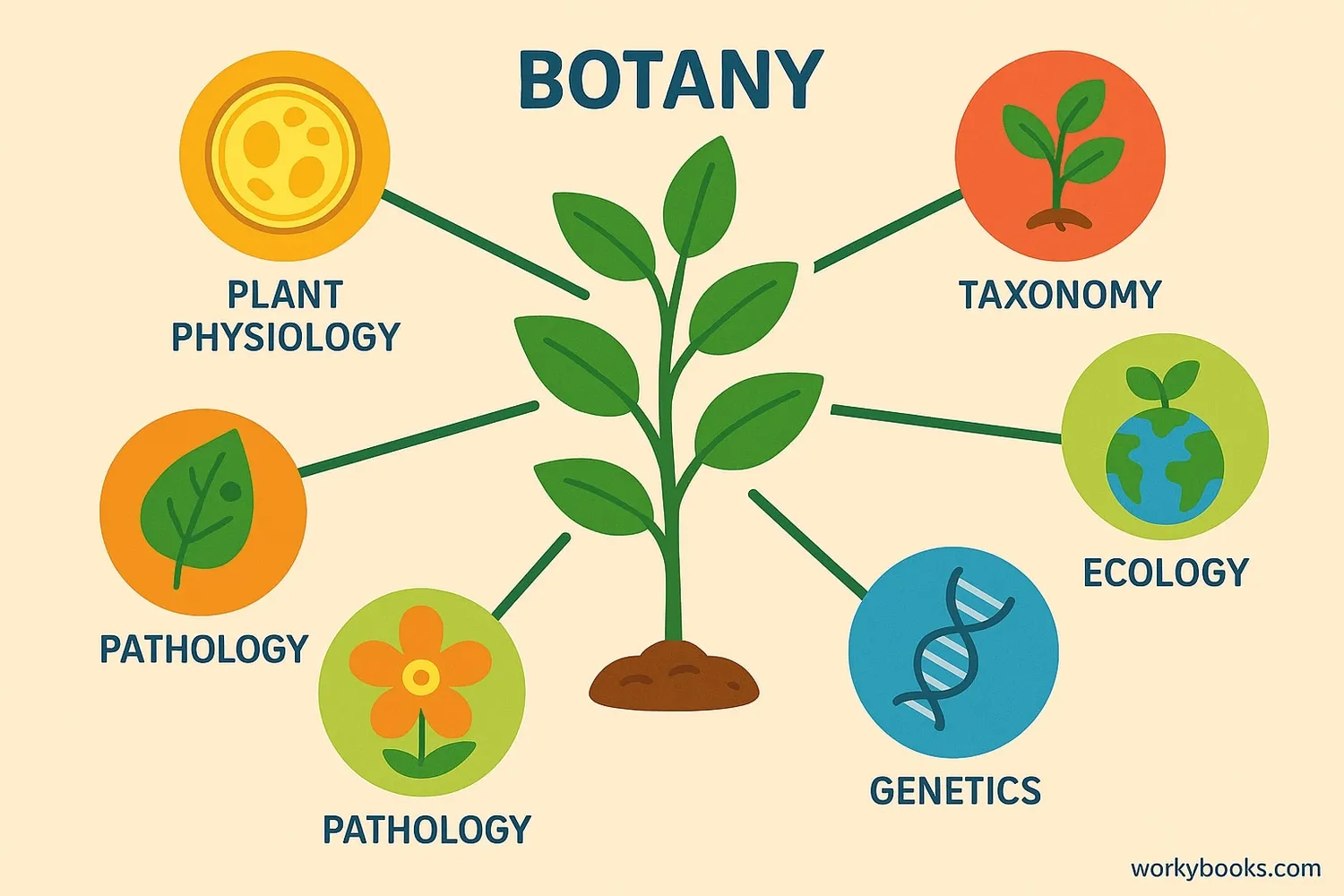
Botany has many specialized branches that focus on different aspects of plant science:
Plant Anatomy
Studies the internal structure of plants
Plant Physiology
Examines how plants function and grow
Plant Taxonomy
Classifies and names plant species
Plant Ecology
Studies how plants interact with their environment
Plant Genetics
Explores how traits are passed down in plants
Did You Know?
Ethnobotany is the study of how people use plants in different cultures for medicine, food, and rituals.
Famous Botanists
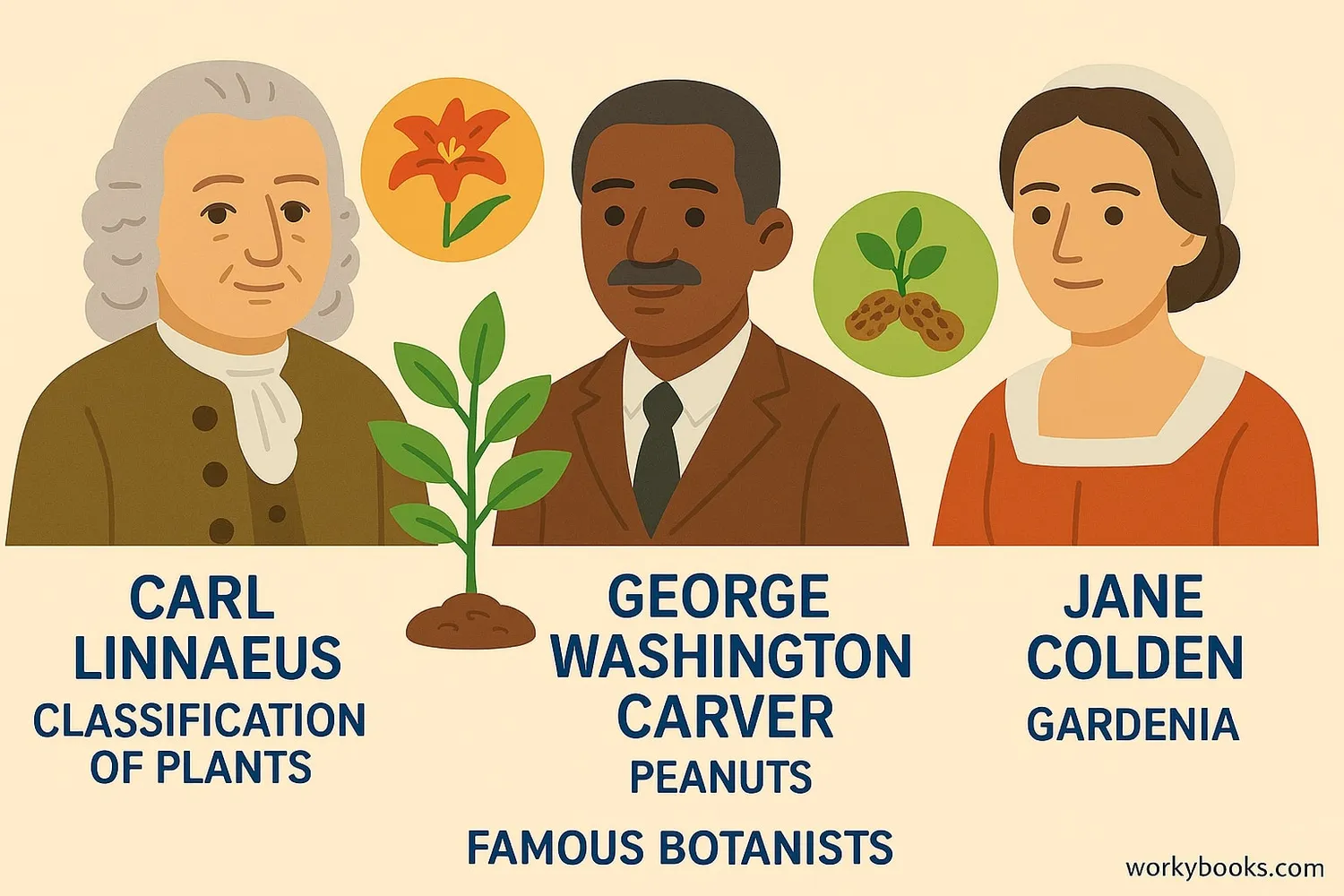
Many scientists have made important contributions to our understanding of plants:
Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778)
Created the system for naming and classifying plants that we still use today. He developed the binomial nomenclature system (genus + species) that gives each plant a unique scientific name.
George Washington Carver (1864-1943)
An agricultural scientist who developed hundreds of uses for peanuts, sweet potatoes, and soybeans. His work helped farmers improve soil quality through crop rotation.
Jane Colden (1724-1766)
America's first female botanist who cataloged New York's flora. She documented over 300 plant species and developed a special technique for making ink impressions of leaves.
History of Botany
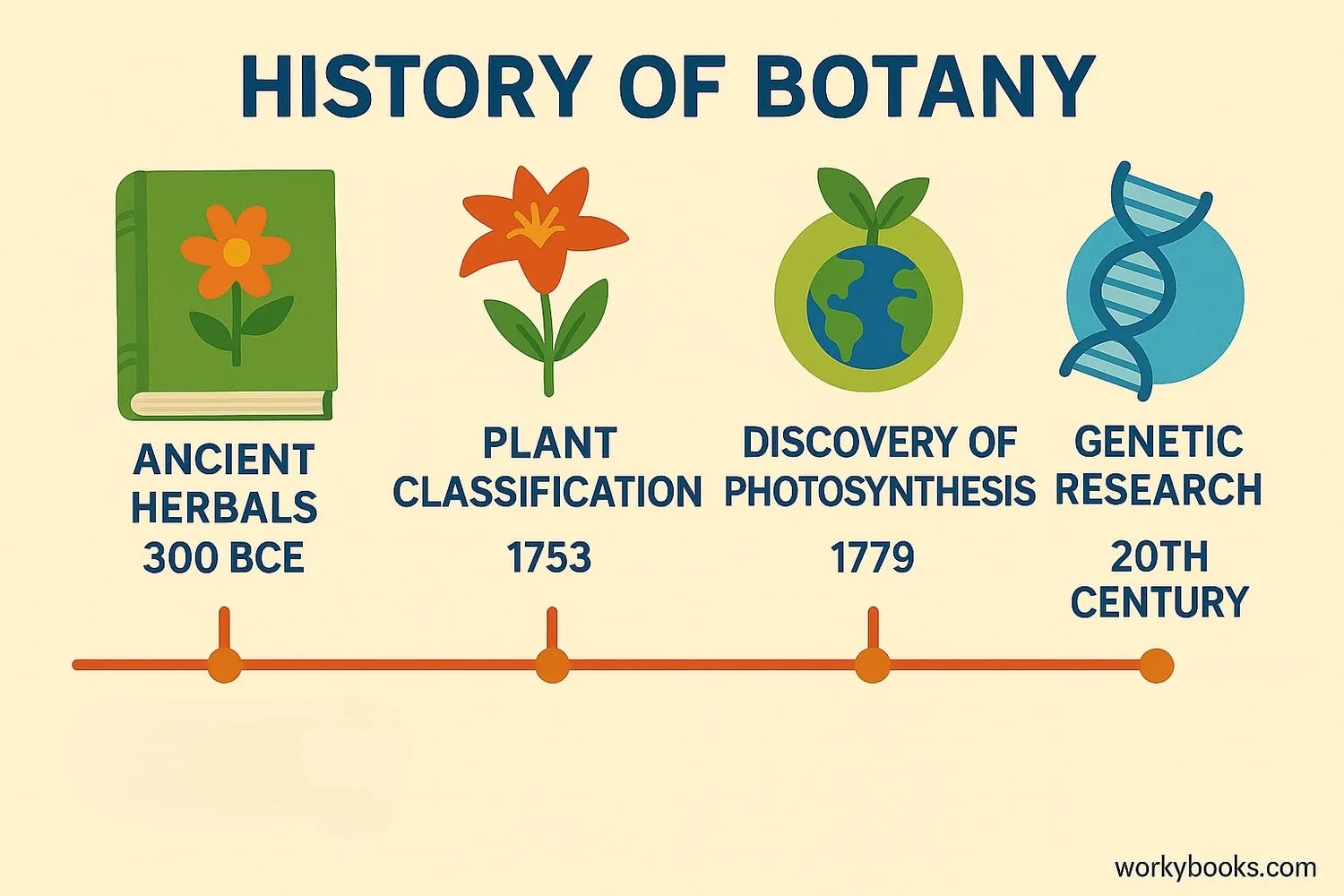
The study of plants has a long and fascinating history:
Ancient Times
Early humans learned about edible and medicinal plants through trial and error. Ancient civilizations like Egypt, China, and Greece documented plant uses.
Middle Ages
Monasteries maintained gardens of medicinal plants. "Herbals" - books describing plants and their uses - became popular.
16th-17th Centuries
Botanical gardens were established in Europe. The microscope was invented, allowing scientists to study plant cells for the first time.
18th Century
Carl Linnaeus developed the plant classification system. Plant exploration expanded as explorers collected specimens worldwide.
19th-20th Centuries
Gregor Mendel discovered genetics through pea plant experiments. The discovery of photosynthesis revolutionized our understanding of how plants work.
Modern Botany
Scientists now study plant genetics, develop new crop varieties, and work to conserve endangered plant species around the world.
Plant Science Quiz
Test your botany knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about botany:
Amazing Plant Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about plants and botany:
Ancient Plants
The oldest living plant is a 5,067-year-old bristlecone pine named Methuselah, growing in California's White Mountains. It was already growing when the pyramids were being built!
Record Height
The tallest tree ever measured was a coast redwood named Hyperion, standing at 380 feet (115.85 meters) tall. That's taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Plant Internet
Plants communicate through an underground network of fungi called the "Wood Wide Web." They use this network to share nutrients and warn each other about dangers.
Medicine Source
About 25% of modern medicines come directly from plants. Aspirin was originally derived from willow bark, and the cancer drug Taxol comes from the Pacific yew tree.




