Cell Division - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how cells multiply to help living things grow and develop
What is Cell Division?
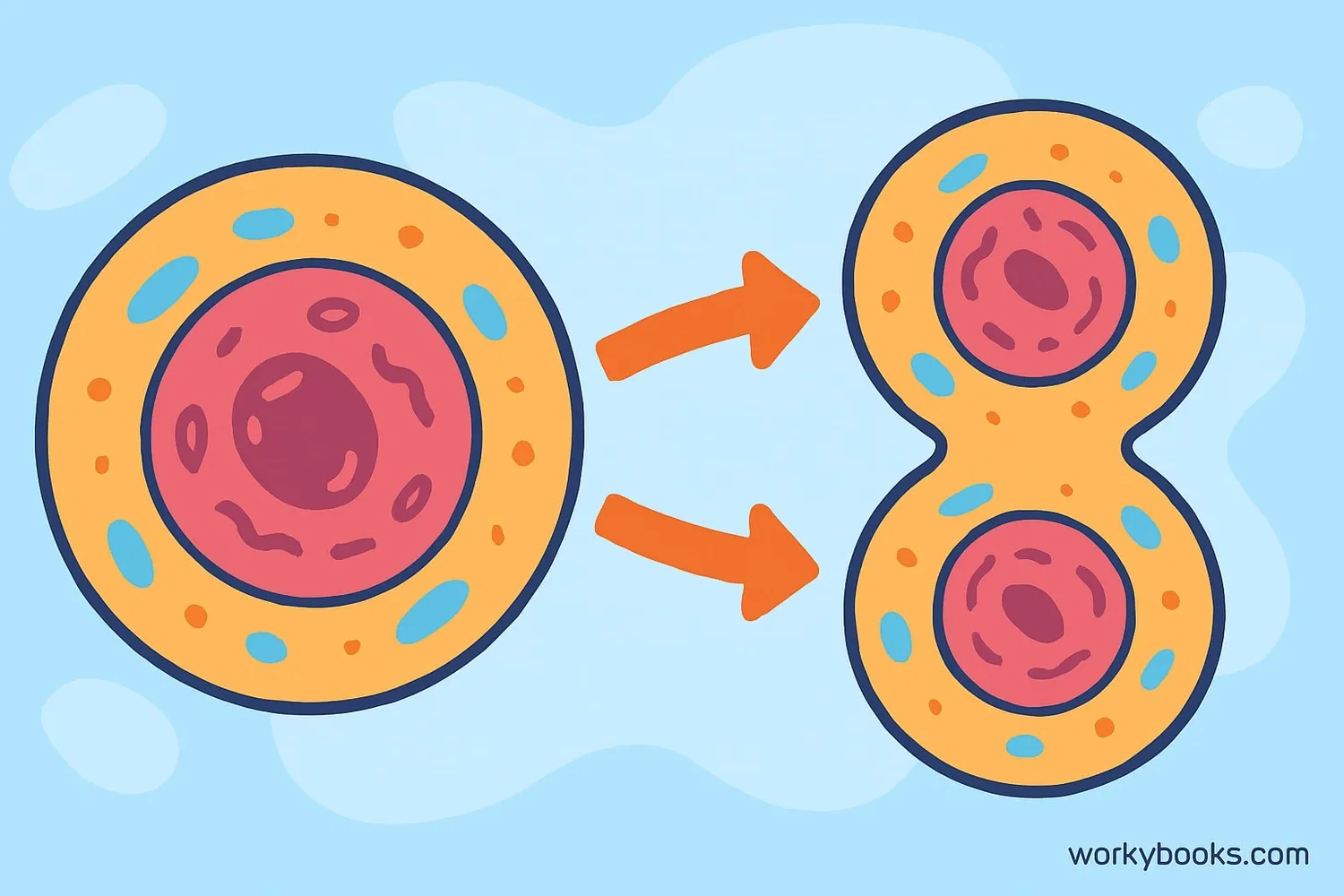
Cell division is how one cell becomes two new cells! It's the amazing process where cells make copies of themselves. All living things—from tiny bacteria to giant trees—depend on cell division to grow, repair injuries, and replace old cells.
Think of your body as a city made of trillions of tiny building blocks called cells. Just like a city needs builders to create new buildings, your body needs cell division to create new cells for growth and repair.
Did You Know?
Your body creates about 300 million new cells every minute through cell division!
The Cell Cycle
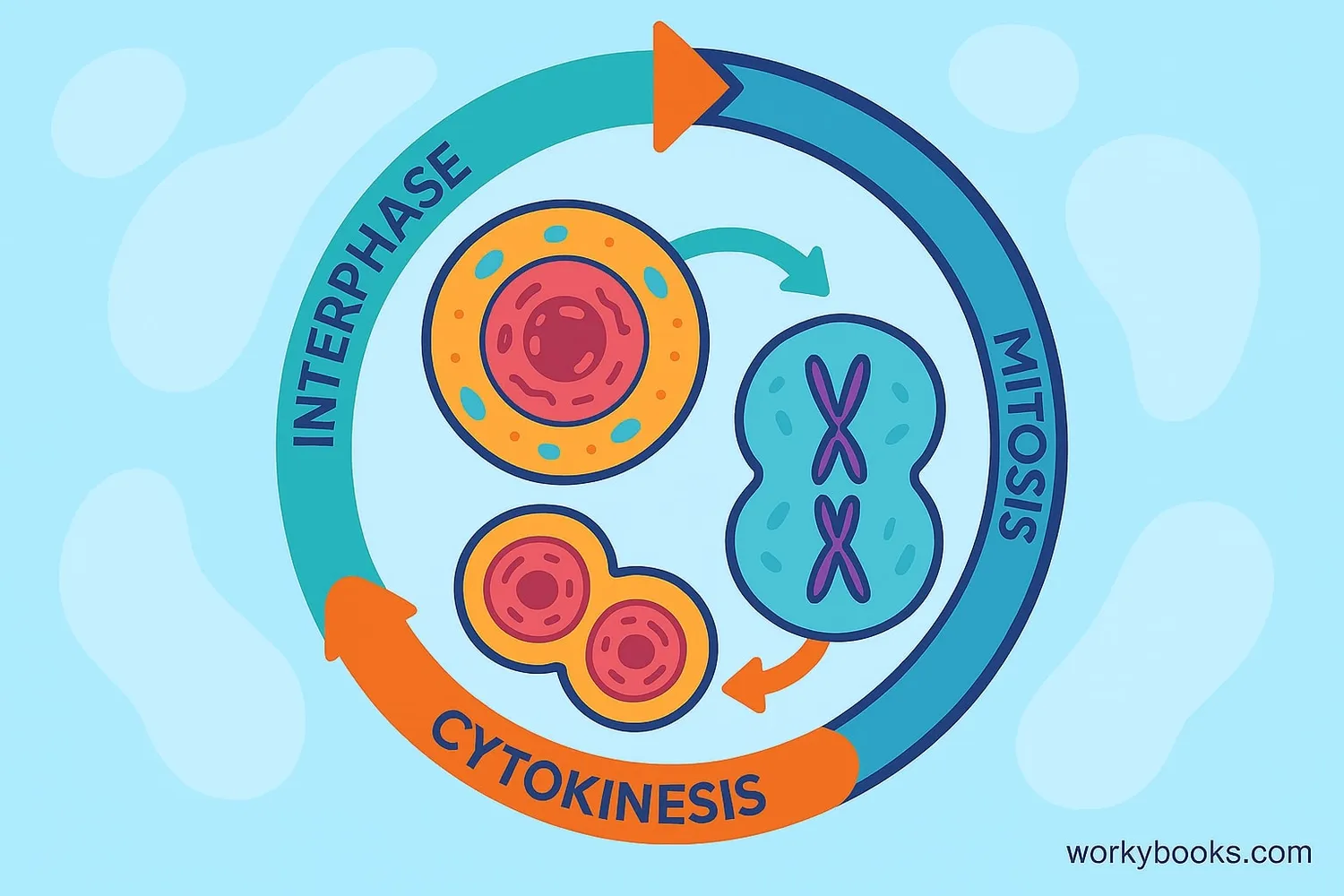
The cell cycle is like a cell's life story from birth to division. It has three main phases:
Interphase
The cell grows and copies its DNA
Mitosis
The nucleus divides into two identical nuclei
Cytokinesis
The cell splits into two new daughter cells
Most of a cell's life is spent in interphase—about 90% of the time! During this phase, the cell:
• Grows to full size
• Makes copies of its organelles
• Duplicates its DNA
• Prepares for division
The Stages of Mitosis
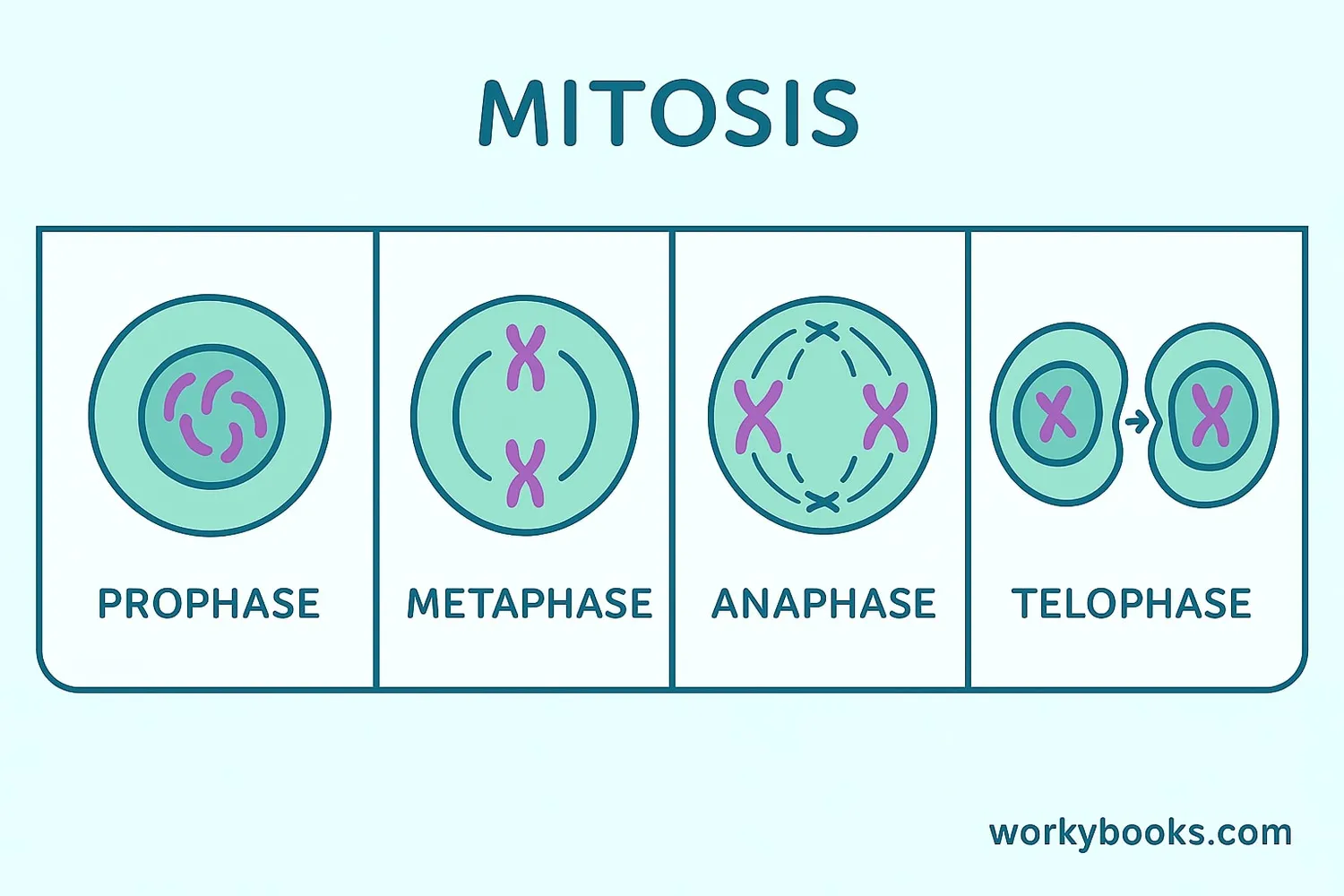
Mitosis is the amazing process where a cell's nucleus divides to create two identical nuclei. It happens in four stages:
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible and the nucleus breaks down
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
Chromosome pairs separate and move to opposite ends
Telophase
Two new nuclei form around the chromosomes
After mitosis comes cytokinesis, where the cell membrane pinches in (in animal cells) or a cell plate forms (in plant cells) to create two separate daughter cells. Each new cell has the exact same genetic material as the original cell!
Remember the Order!
Use this phrase to remember mitosis stages: "People Meet And Talk" (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase)
Understanding Meiosis
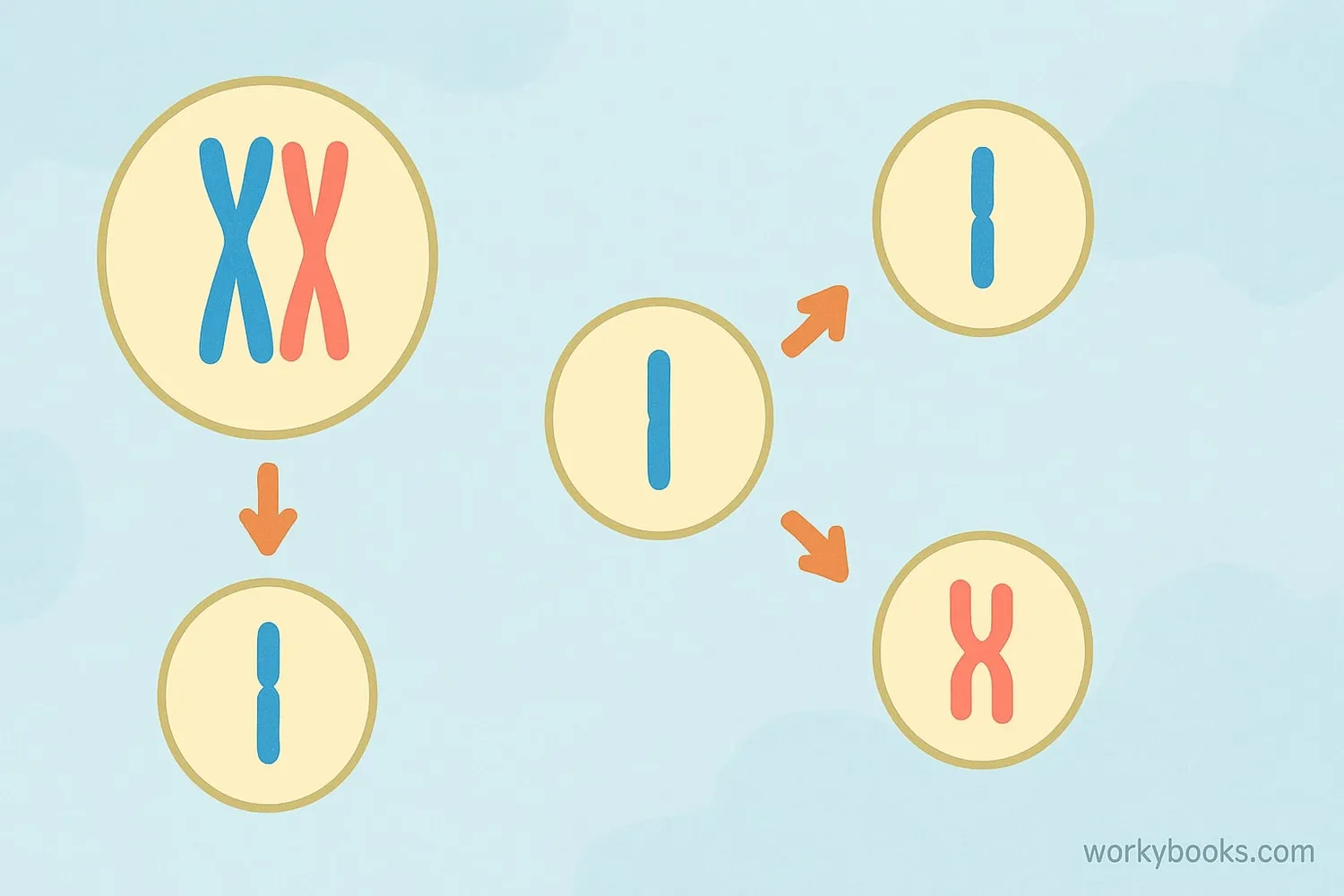
Meiosis is a special type of cell division that creates sex cells (sperm and egg cells). While mitosis makes identical cells, meiosis makes unique cells with half the usual number of chromosomes.
Here's how meiosis is different from mitosis:
Two Divisions
Meiosis has two division phases (Meiosis I and II)
Half Chromosomes
Produces cells with half the chromosomes
Genetic Variety
Creates unique combinations of DNA
Meiosis is why children look like a mix of their parents! When sperm and egg cells combine during fertilization, they create a new cell with a complete set of chromosomes—half from mom and half from dad.
Why Cell Division Matters
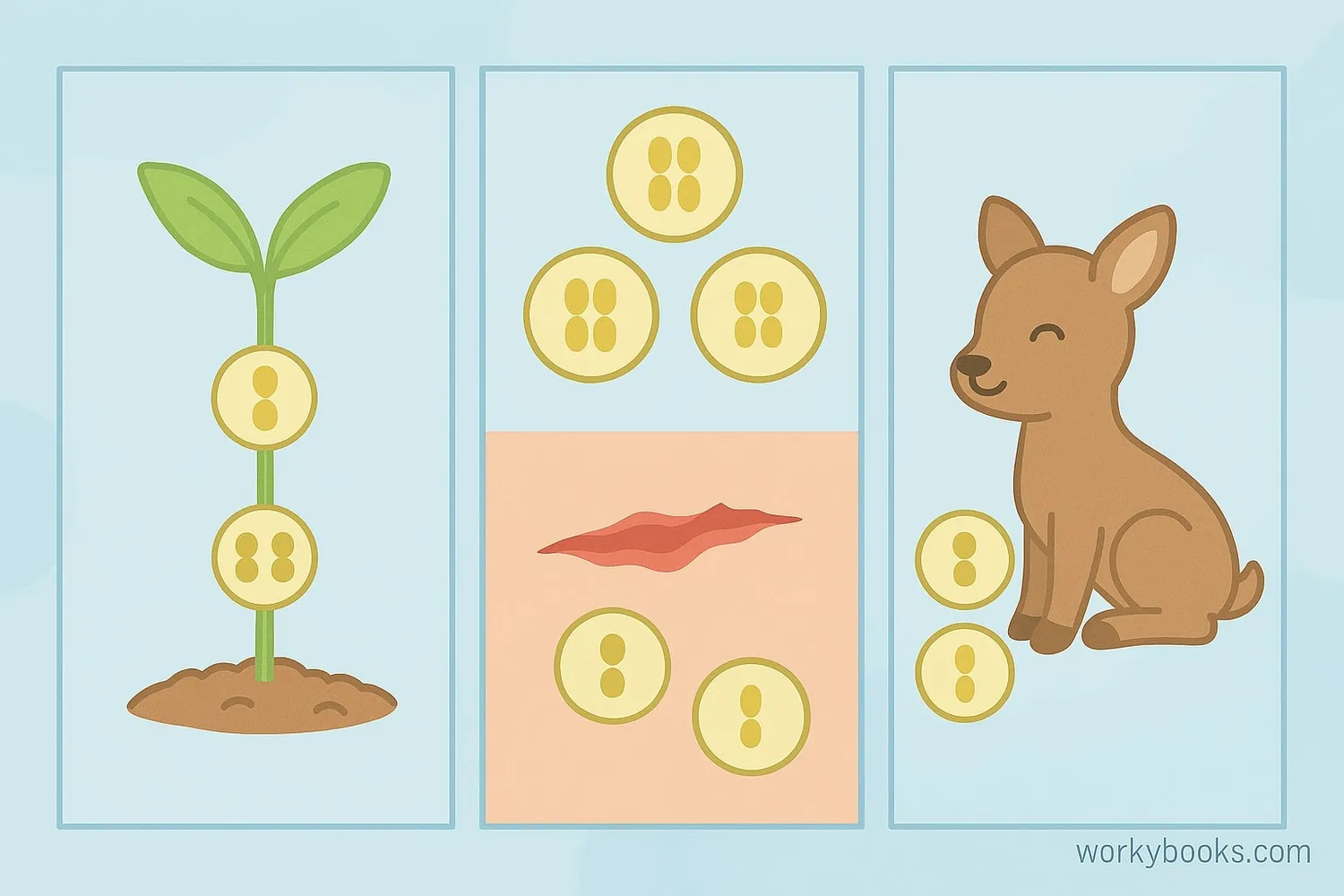
Cell division is essential for all living things! Here's why it's so important:
Growth
Allows organisms to grow from a single cell to trillions
Repair
Replaces damaged or dead cells to heal injuries
Reproduction
Creates sperm and egg cells for making offspring
Without cell division:
• Babies couldn't grow into adults
• Paper cuts would never heal
• Plants couldn't grow new leaves
• Species couldn't reproduce
Every time you grow taller, heal a scraped knee, or even replace old skin cells, you're experiencing cell division in action!
Cell Division Quiz
Test your knowledge about cell division with this interactive quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about cell division:
Amazing Cell Division Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about cell division!
Size Matters
If all the cells from just one human were lined up, they would stretch around Earth's equator more than 200 times!
Division Speed
Embryo cells can divide every 20 minutes! That's why a fertilized egg grows into a baby with trillions of cells in just 9 months.
Cell Lifespans
Your stomach lining cells live only 2 days, while some of your brain cells last your entire lifetime. Red blood cells live about 4 months!
Historical Discovery
Scientists first observed cell division in 1835, but it took until 1882 to name the process "mitosis" from the Greek word for thread (referring to chromosomes).




