Homozygous Traits - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how genes work and why traits appear the way they do!
What is Homozygous?
Homozygous is a genetics term that describes when an organism has two identical alleles for a particular gene. Alleles are different versions of the same gene.
Think of genes as instructions for traits like eye color or hair texture. Each gene comes in different versions (alleles). When an organism has two of the same allele for a gene, we say it is homozygous for that trait.
For example, if you inherit the blue eye allele from both parents, you would be homozygous for blue eyes. This means you'll definitely have blue eyes because there's no different allele to change the outcome.
Genetics Fact!
The word "homozygous" comes from Greek words: "homo" meaning same, and "zygous" meaning paired. So it literally means "same pair"!
Homozygous Dominant vs. Homozygous Recessive
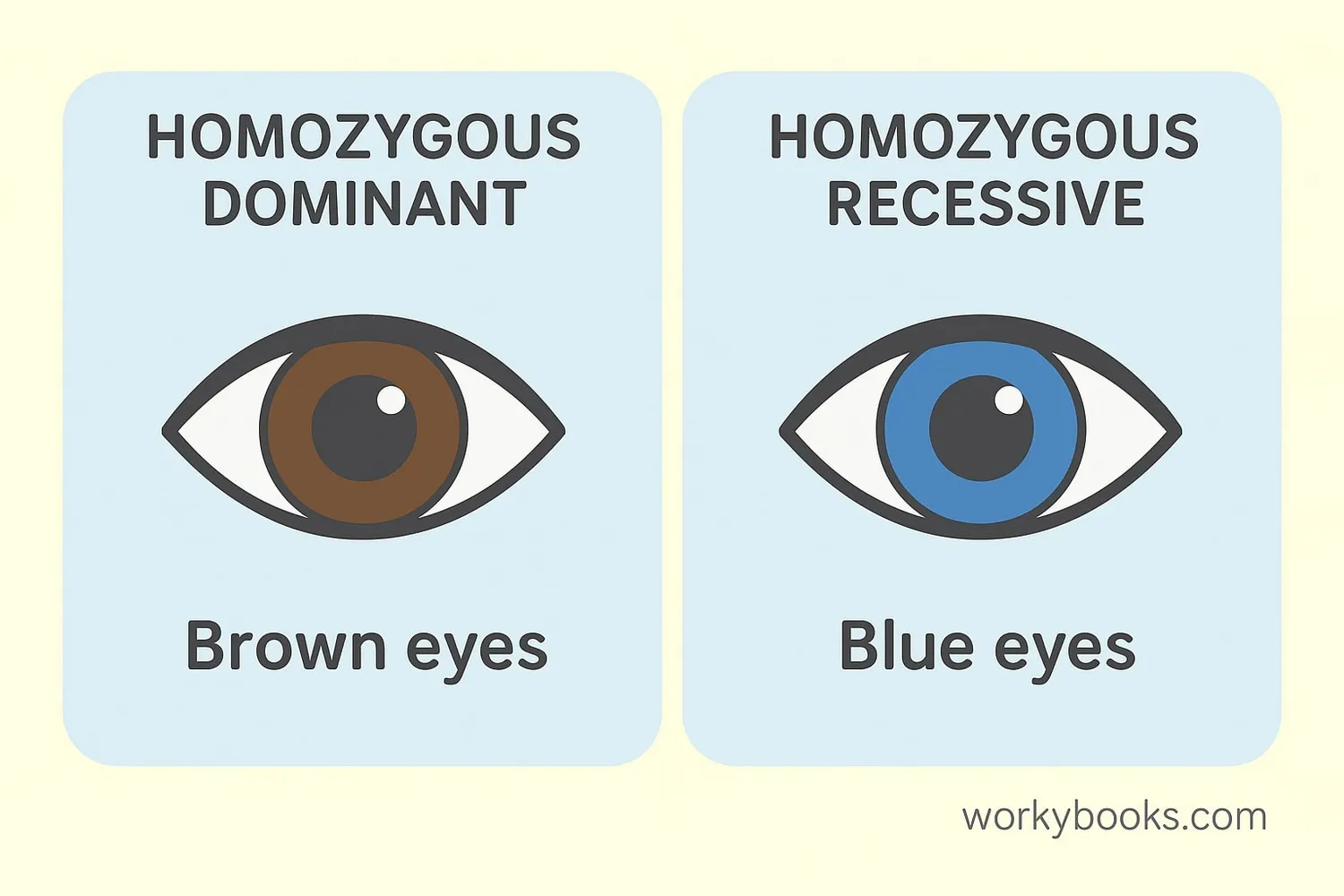
There are two types of homozygous traits:
Homozygous Dominant
Two dominant alleles (e.g., BB for brown eyes)
Shows the dominant trait
Homozygous Recessive
Two recessive alleles (e.g., bb for blue eyes)
Shows the recessive trait
Punnett Square Example
In this Punnett square, both parents are heterozygous (Bb) for brown eyes. The bb combination is homozygous recessive and will result in blue eyes.
Genetic Power!
Homozygous organisms are "true breeding" - they will always pass the same allele to their offspring for that trait!
Examples of Homozygous Traits
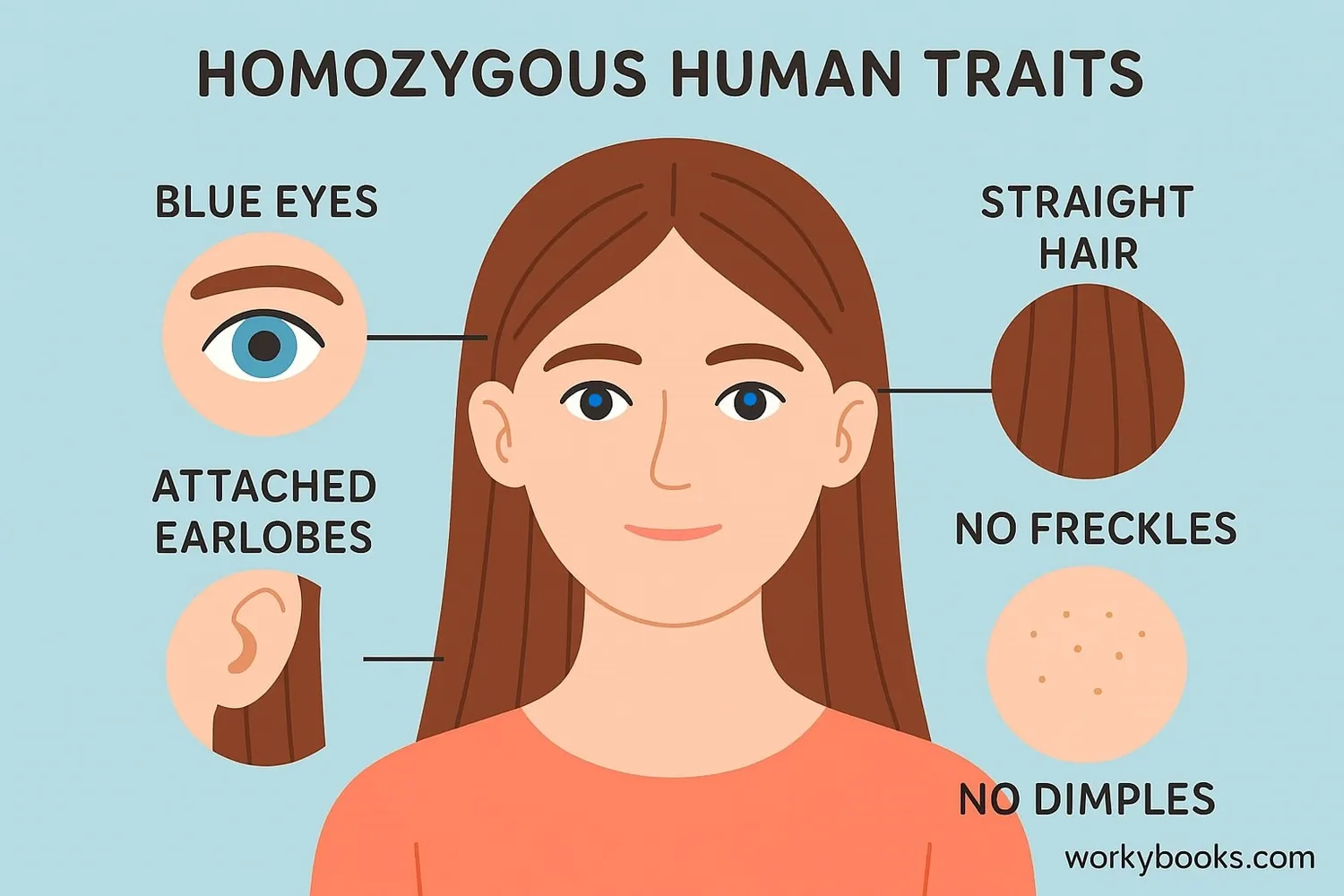
Many human traits can be homozygous. Here are some common examples:
| Trait | Homozygous Dominant | Homozygous Recessive |
|---|---|---|
| Eye Color | Brown eyes (BB) | Blue eyes (bb) |
| Hair Type | Curly hair (CC) | Straight hair (cc) |
| Freckles | Has freckles (FF) | No freckles (ff) |
| Earlobes | Free earlobes (EE) | Attached earlobes (ee) |
| Dimples | Has dimples (DD) | No dimples (dd) |
Remember that homozygous traits are always expressed physically because there's no different allele to influence the outcome. This makes homozygous organisms very predictable in their traits!
Why Homozygous Traits Matter
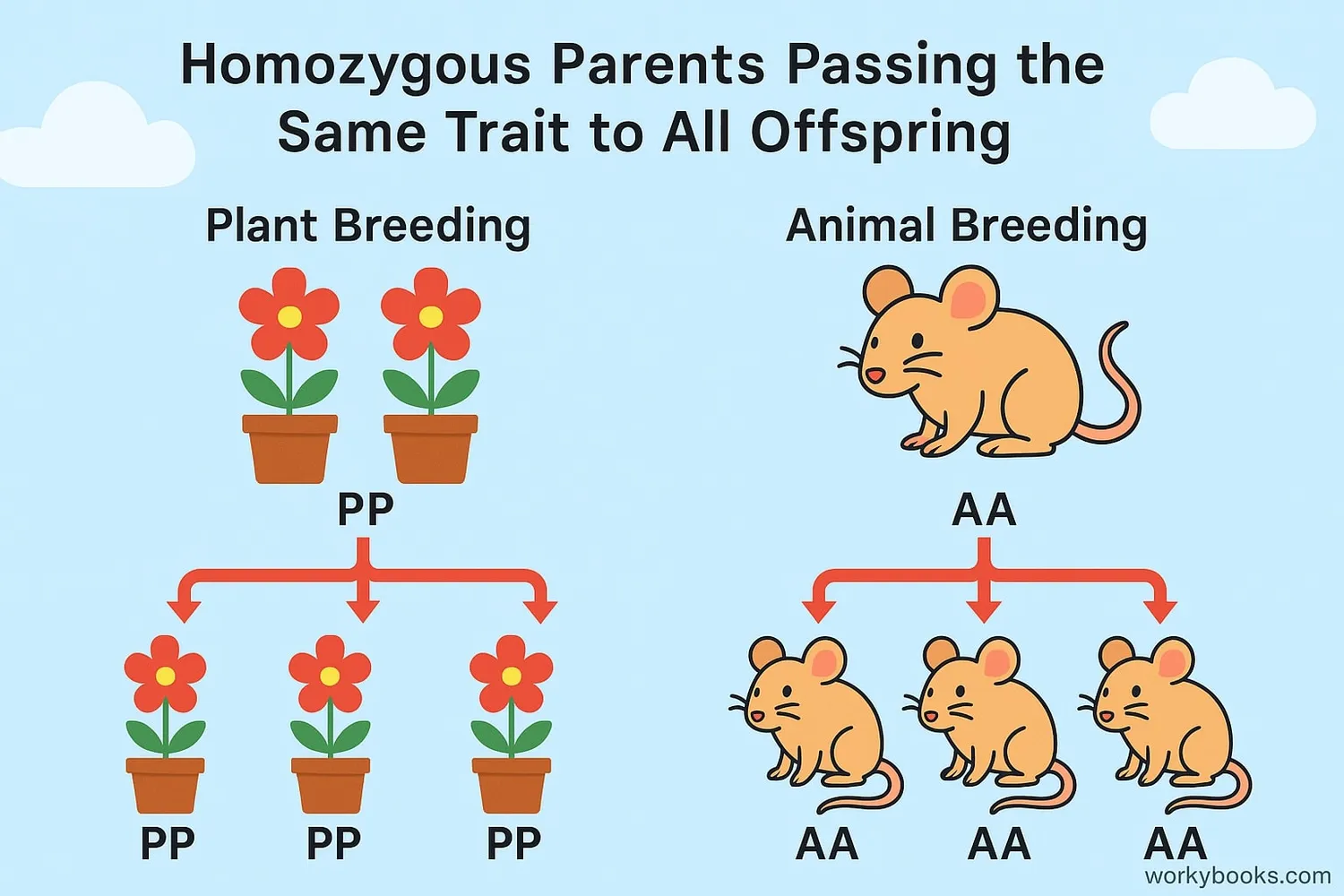
Homozygous traits are important in genetics for several reasons:
True Breeding
Organisms with homozygous traits always pass the same version to their offspring
Predictability
Scientists can predict inheritance patterns more easily
Genetic Research
Homozygous lines help study gene functions
In agriculture and breeding:
• Farmers breed homozygous plants for consistent crops
• Animal breeders use homozygous animals to maintain desirable traits
• Scientists create homozygous organisms to study genetic diseases
Understanding homozygous traits helps us understand why we look the way we do and how traits are passed through families!
Genetics Quiz
Test your knowledge about homozygous traits with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about homozygous traits:
Genetics Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about homozygous traits and genetics!
Plant Breeding
Many food crops like wheat and corn are homozygous for important traits, ensuring consistent size, color, and ripening time!
Purebred Animals
Purebred dogs are often homozygous for traits like coat color and size, which is why they look so similar within a breed!
Blue Eyes
All people with blue eyes are homozygous recessive for eye color! This trait originated from a single common ancestor 6,000-10,000 years ago.
Genetic Research
Scientists use homozygous lab mice to study diseases because their identical genes make experiments more reliable and repeatable.




