Migration - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover nature's incredible journeys across land, sea, and sky
What is Migration?
Migration is the seasonal movement of animals from one place to another. Many species travel long distances to find better living conditions, food sources, or breeding grounds. This incredible journey happens across land, sea, and sky!
Think of migration as nature's way of solving problems. When winter comes and food becomes scarce, animals don't just stay and suffer - they travel to places with better conditions. Some migrations cover thousands of miles, while others are shorter but equally important for survival.
Seasonal Movement
Animals move based on changing seasons
Long Distances
Some travel thousands of miles
Return Journey
Most return to their original home
Group Behavior
Animals often travel together
Migration Fact!
The Arctic Tern holds the record for the longest migration - flying about 44,000 miles each year between the Arctic and Antarctica!
Migration Patterns

Animals follow various migration patterns based on their species and needs. Some travel in straight lines while others follow coastlines or mountain ranges. Here are the main types:
Latitudinal
North-south movement (most common)
Altitudinal
Moving up/down mountains with seasons
Longitudinal
East-west movement across continents
Different animals have unique migration routes:
Birds: Fly along "flyways" - highways in the sky! Many birds migrate at night using stars for navigation.
Marine Animals: Whales travel from cold feeding grounds to warm breeding areas. Sea turtles return to the beach where they were born.
Land Mammals: Wildebeest in Africa make the "Great Migration" following rain patterns.
Why Animals Migrate
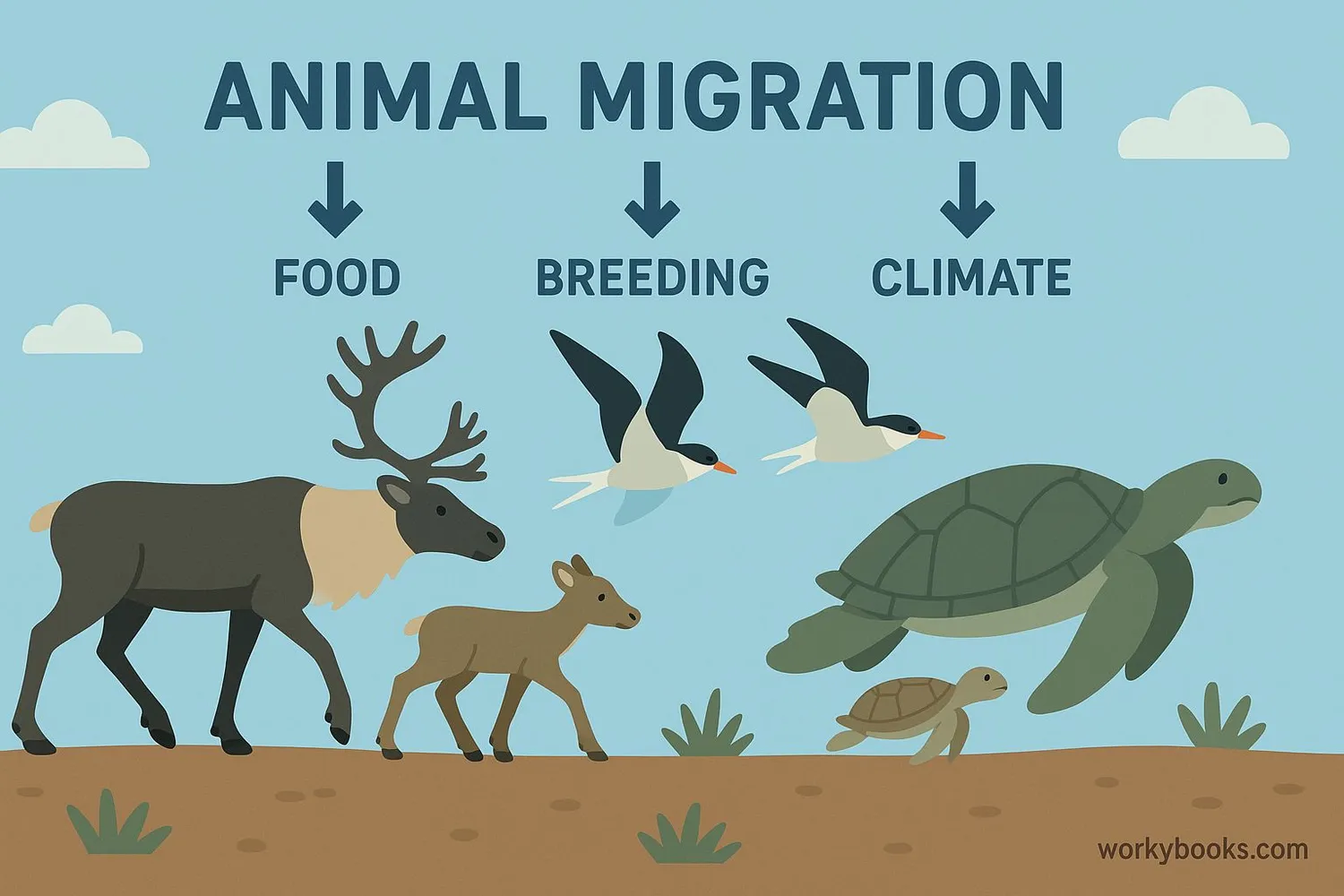
Animals migrate for three main reasons: to find food, to reproduce in better conditions, and to escape harsh weather. These journeys are essential for their survival!
Food
Moving to areas with abundant food sources
Breeding
Finding safe places to raise young
Climate
Escaping extreme temperatures
Food Migration Example: Gray whales travel 10,000-14,000 miles round trip between feeding grounds in the Arctic and breeding lagoons in Mexico.
Breeding Migration Example: Salmon swim hundreds of miles upstream to lay eggs in the exact spot where they were born.
Climate Migration Example: Monarch butterflies travel up to 3,000 miles to escape cold winters, with multiple generations completing the journey.
Migration Challenges

Migration is full of challenges and dangers. Animals face many obstacles during their incredible journeys:
Predators
Vulnerable to attack during travel
Human Obstacles
Cities, roads, fences, and pollution
Habitat Loss
Disappearing resting and feeding areas
Conservation efforts are helping protect migration routes:
• Wildlife corridors connect habitats
• Protected areas along migration routes
• International agreements to protect migratory species
• Reducing light pollution that confuses birds
• Building wildlife crossings over highways
By understanding migration challenges, we can help protect these incredible journeys for future generations!
Migration Quiz
Test your migration knowledge with this interactive quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about migration:
Migration Trivia
Discover amazing facts about animal migration:
Natural Navigation
Some birds can detect the Earth's magnetic field using special proteins in their eyes, creating a visual compass that helps them navigate during migration.
Group Migration
Wildebeest in Africa participate in the "Great Migration" where over 1.5 million animals travel together across the Serengeti in search of fresh grass.
Tiny Travelers
The Monarch butterfly migration spans 3-4 generations! No single butterfly completes the entire round trip from Canada to Mexico and back.
High Flyers
Bar-headed geese migrate over the Himalayas at altitudes up to 29,500 feet - higher than Mount Everest! They've evolved special blood to survive with less oxygen.





