Vertebrate - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover animals with backbones through examples, facts, and classification
What are Vertebrates?
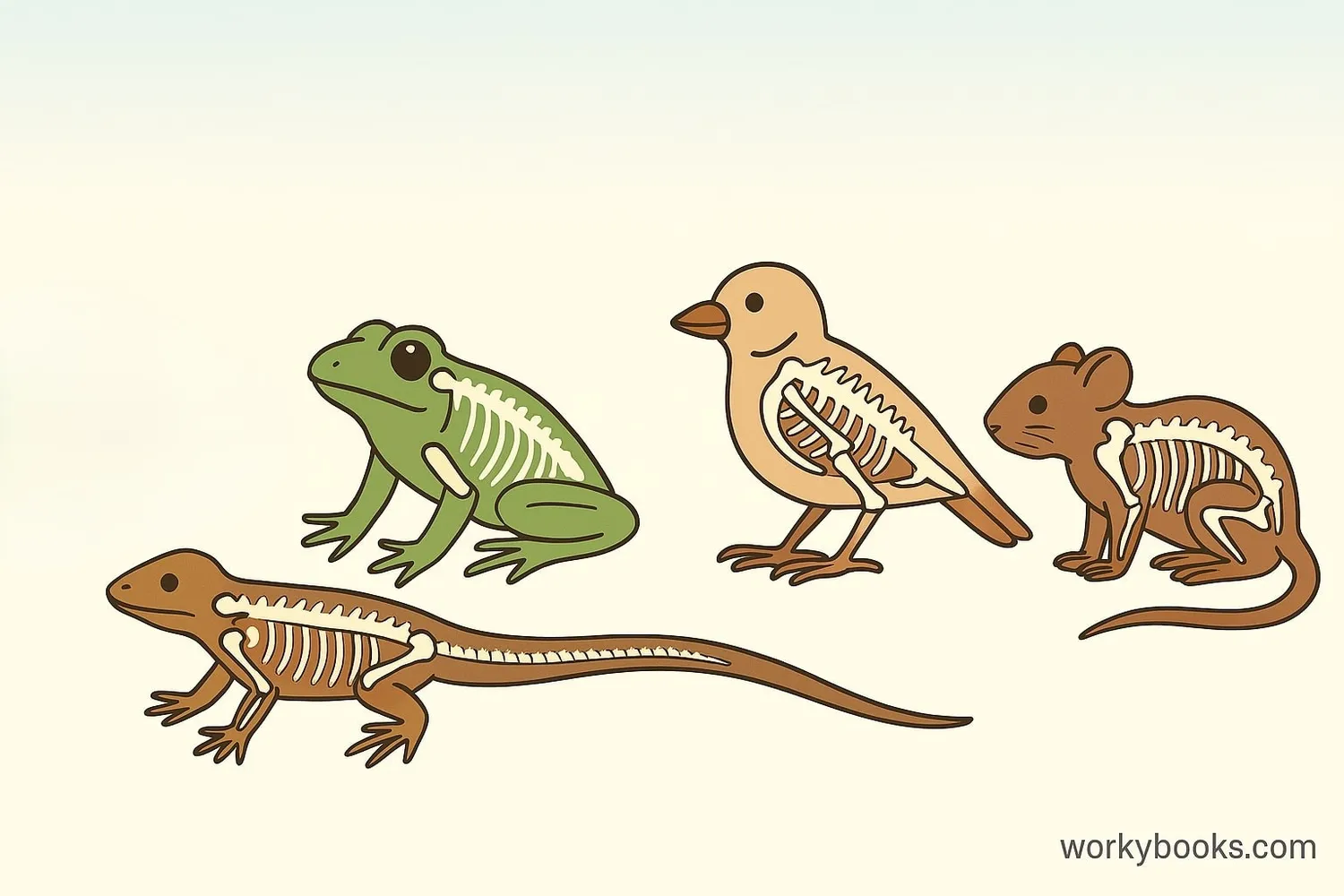
Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone or spinal column. This backbone is made up of small bones called vertebrae that protect the spinal cord - an important part of the nervous system.
Vertebrates make up only about 5% of all animal species, but they include most of the animals we're familiar with - like fish, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals (including humans!).
The backbone gives vertebrates their body structure and support, allowing them to grow larger than invertebrates and move in more complex ways. All vertebrates have an internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage.
Did You Know?
The first vertebrates appeared on Earth about 500 million years ago during the Cambrian Period!
Key Characteristics of Vertebrates
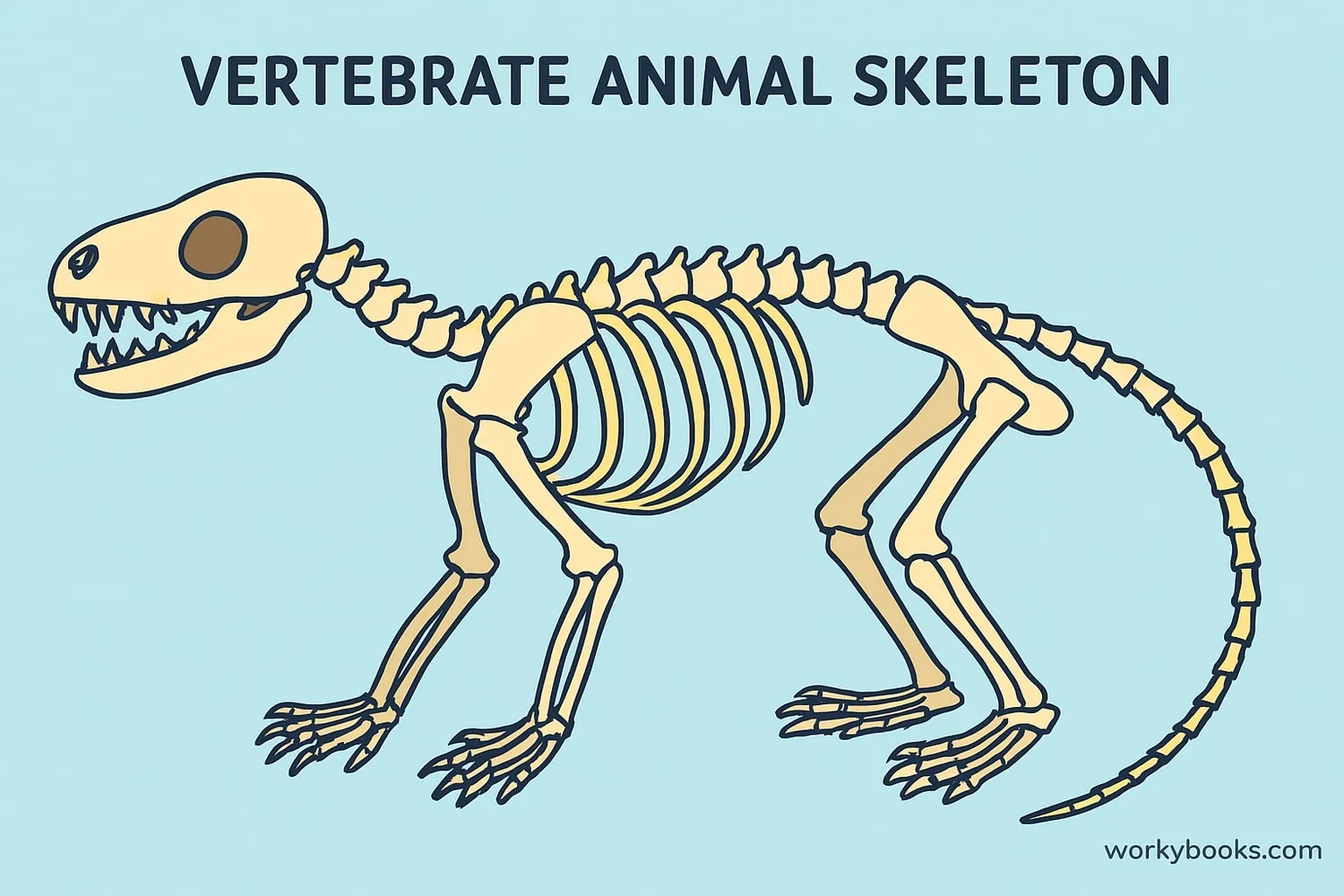
While vertebrates come in many shapes and sizes, they all share these important characteristics:
Backbone
A series of bones (vertebrae) that protect the spinal cord
Internal Skeleton
Made of bone or cartilage that supports the body
Skull
Protects the brain and sensory organs
Complex Nervous System
Includes a brain and spinal cord
Bilateral Symmetry
Body plan with mirror-image left and right sides
Vertebrates also have advanced organ systems including:
• Closed circulatory system with a heart
• Respiratory system with lungs or gills
• Digestive system with specialized organs
• Endocrine system for hormone regulation
Classification of Vertebrates
Scientists classify vertebrates into five main groups based on their characteristics:
Fish
Live in water, breathe through gills, have scales and fins. Examples: Goldfish, sharks, salmon.

Amphibians
Live both in water and on land, moist skin, lay eggs in water. Examples: Frogs, toads, salamanders.
Reptiles
Dry, scaly skin, lay eggs on land. Examples: Snakes, lizards, turtles, crocodiles.
Birds
Feathers, wings, lay hard-shelled eggs. Examples: Eagles, penguins, sparrows, ostriches.
Mammals
Hair or fur, produce milk for young. Examples: Humans, dogs, whales, bats.
Evolutionary Fact
All vertebrates evolved from fish! Amphibians evolved from fish, reptiles from amphibians, and both birds and mammals from reptiles.
Vertebrates vs Invertebrates
The animal kingdom is divided into vertebrates (with backbones) and invertebrates (without backbones). While vertebrates are more familiar to us, invertebrates make up about 95% of all animal species!
| Feature | Vertebrates | Invertebrates |
|---|---|---|
| Backbone | Yes | No |
| Size | Generally larger | Generally smaller |
| Nervous System | Complex with brain and spinal cord | Simple or no nervous system |
| Examples | Humans, dogs, birds, fish | Insects, spiders, worms, jellyfish |
| Species Diversity | About 65,000 species | Over 1 million species |
While vertebrates have internal skeletons, many invertebrates have other types of support structures:
• Exoskeletons (like insects and crustaceans)
• Hydrostatic skeletons (like worms and jellyfish)
• No skeleton at all (like octopuses)
Vertebrate Quiz
Test your knowledge about vertebrates with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about vertebrates:
Vertebrate Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about vertebrates:
Ancient Vertebrates
The first vertebrates were jawless fish that appeared over 500 million years ago. They were small, rarely longer than a few centimeters.
Bird Bones
Many bird bones are hollow to make them lighter for flight. Despite this, bird skeletons are actually stronger than mammal bones of similar size.
Mammal Diversity
There are about 5,500 mammal species, but rodents make up about 40% of all mammal species. Bats make up about 20% of mammal species!
Fish Abundance
Fish are the most diverse group of vertebrates, with over 33,000 known species. That's more than all other vertebrate groups combined!




