Geometry Base - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about geometric bases in 2D and 3D shapes with visual examples and practice activities
What is a Geometric Base?
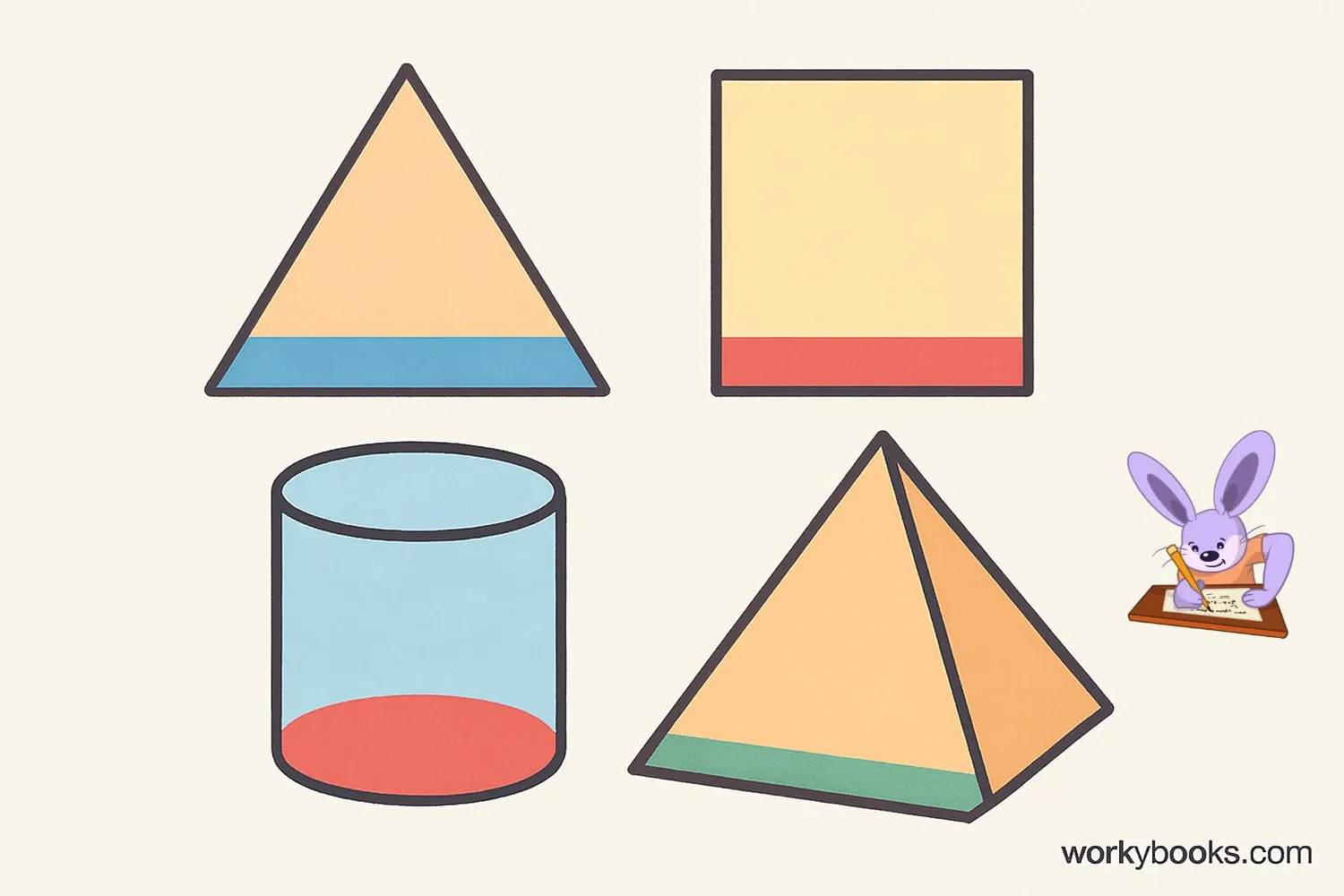
In geometry, a base is the side or face of a geometric figure that serves as a reference for measurements. Think of it as the foundation of a shape that helps us calculate area and volume.
Bases are important because:
- They provide a reference point for measuring height
- They help us calculate area and volume
- They define the shape's orientation in space
In 2D shapes, the base is usually the bottom side, but it can be any side we choose. In 3D shapes, the base is the face on which the shape stands.
Key Concept
The base is like the foundation of a building - it supports the shape and gives us a starting point for measurements.
Bases in 2D Shapes
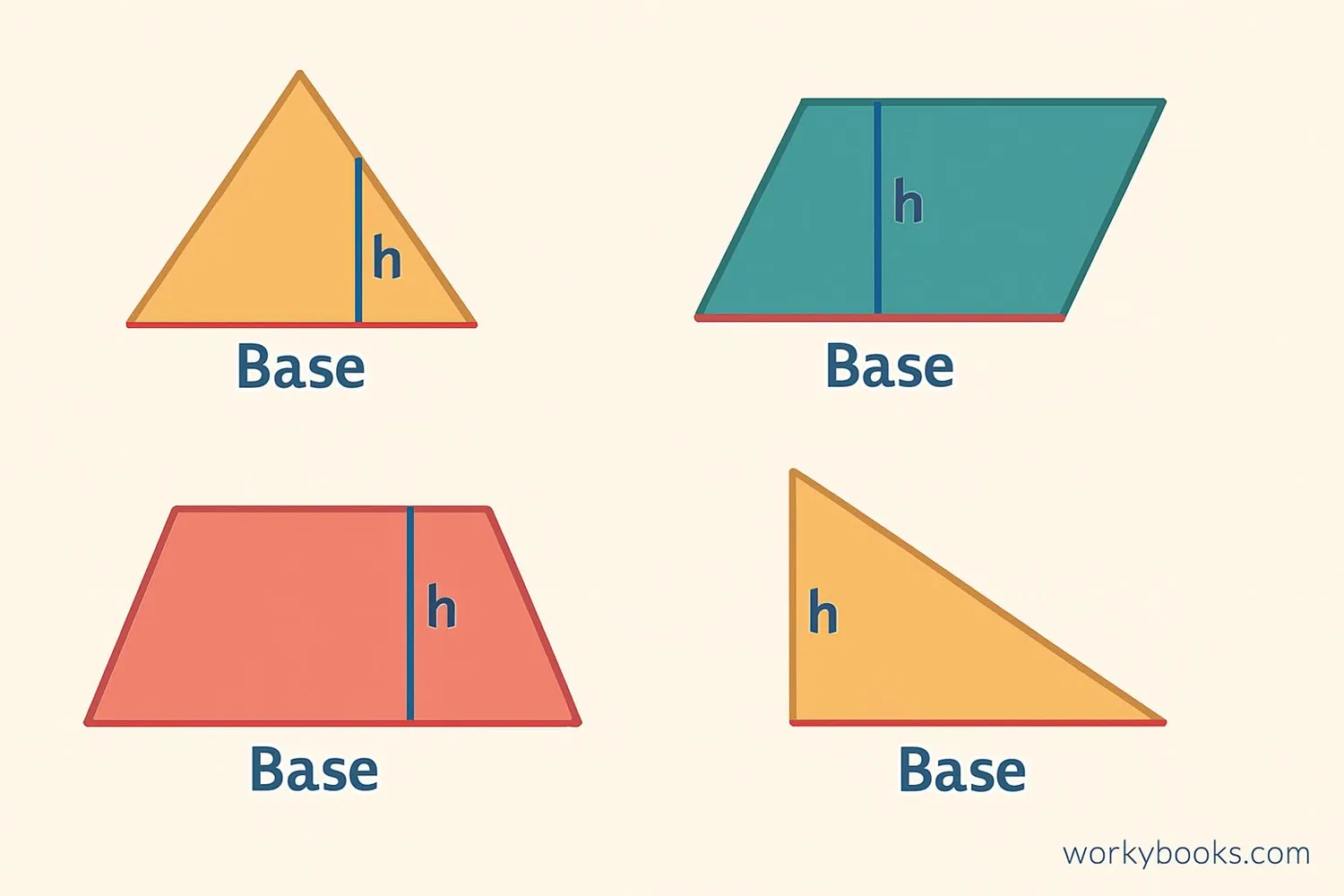
Triangle
Any side can be the base. The height is always perpendicular to the base.
Parallelogram
Usually the bottom side, but any side can be the base. Opposite sides are parallel.
Trapezoid
Has two parallel sides called bases (base1 and base2). The height is perpendicular to both.
Bases in 3D Shapes
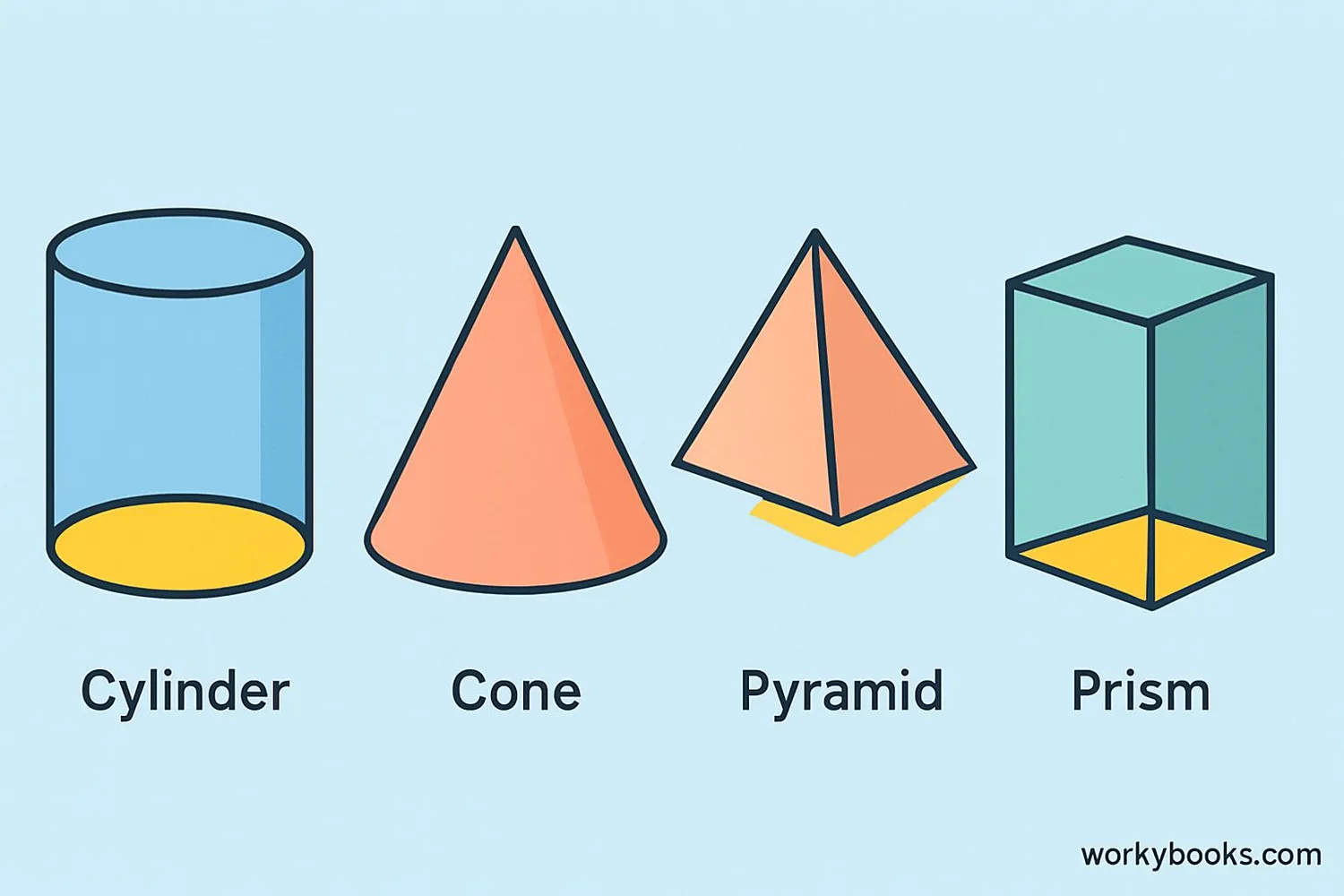
Cylinder
Has two circular bases that are parallel and congruent.
Cone
Has one circular base. The apex is directly above the center of the base.
Pyramid
Has one polygonal base. Triangular faces meet at the apex.
Prism
Has two parallel and congruent polygonal bases. Lateral faces are parallelograms.
Formulas Involving Bases
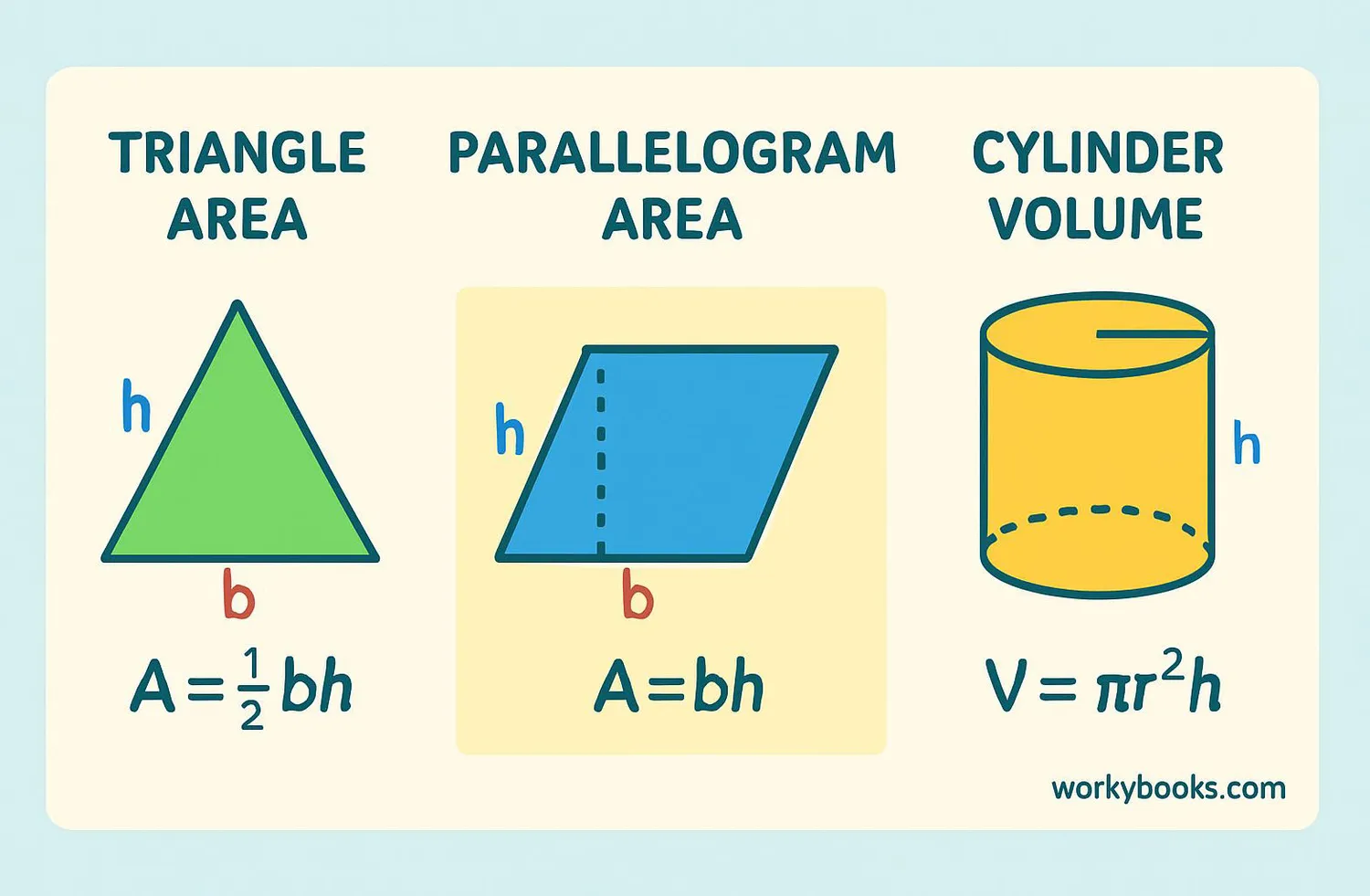
Bases are used in many geometric formulas. Here are the most important ones:
Area Formulas
Volume Formulas
Remember
The height is always perpendicular to the base. It's the shortest distance from the base to the opposite vertex or face.
Real-World Examples
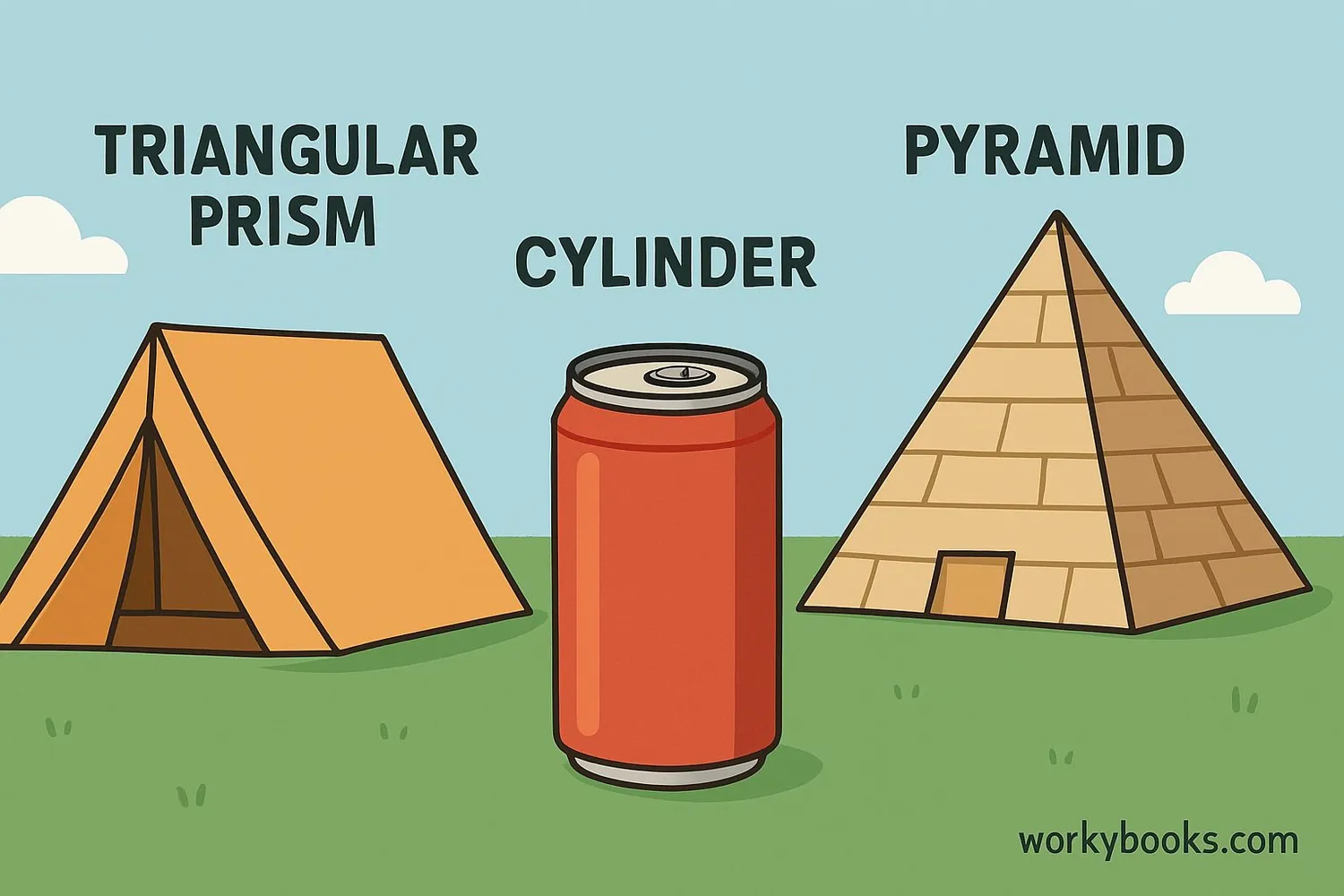
Let's see bases in action with some real-world examples:
Example 1: A triangular tent has a base of 2.5 meters and height of 2 meters. What's its area?
Solution: Area = ½ × base × height = ½ × 2.5 × 2 = 2.5 m²
Example 2: A cylindrical water tank has a base radius of 1.2 meters and height of 3 meters. What's its volume?
Solution: Volume = π × r² × h = 3.14 × (1.2)² × 3 ≈ 13.56 m³
Example 3: A rectangular swimming pool is 8m long, 4m wide, and 2m deep. What's its volume?
Solution: Base area = 8 × 4 = 32 m², Volume = base area × height = 32 × 2 = 64 m³
Example 4: A pyramid monument has a square base 15m on each side and height 20m. What's its volume?
Solution: Base area = 15 × 15 = 225 m², Volume = (base area × height) ÷ 3 = (225 × 20) ÷ 3 = 1500 m³
Measurement Tip
When solving problems, always identify the base first before applying formulas.
Base Knowledge Quiz
Test your understanding of geometric bases with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about geometric bases:
Geometry Trivia
Discover interesting facts about geometric bases:
Ancient Geometry
The concept of a geometric base dates back to ancient Egypt, where surveyors used ropes to create right angles for measuring fields after Nile floods. This "rope-stretching" was essential for their geometry.
Pyramid Precision
The Great Pyramid of Giza has a nearly perfect square base. The difference in length between its sides is less than 0.05% - an amazing feat of ancient engineering.
Space Shapes
Many spacecraft components are cylindrical because this shape with circular bases distributes pressure evenly and is structurally strong while using minimal materials.
Largest Prism
The largest man-made prism is the Luxor Hotel in Las Vegas. Its pyramid shape has a square base measuring 183 meters on each side and stands 110 meters tall.





