Cylinder - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about 3D shapes with simple explanations, visual examples, and practice activities
What is a Cylinder?
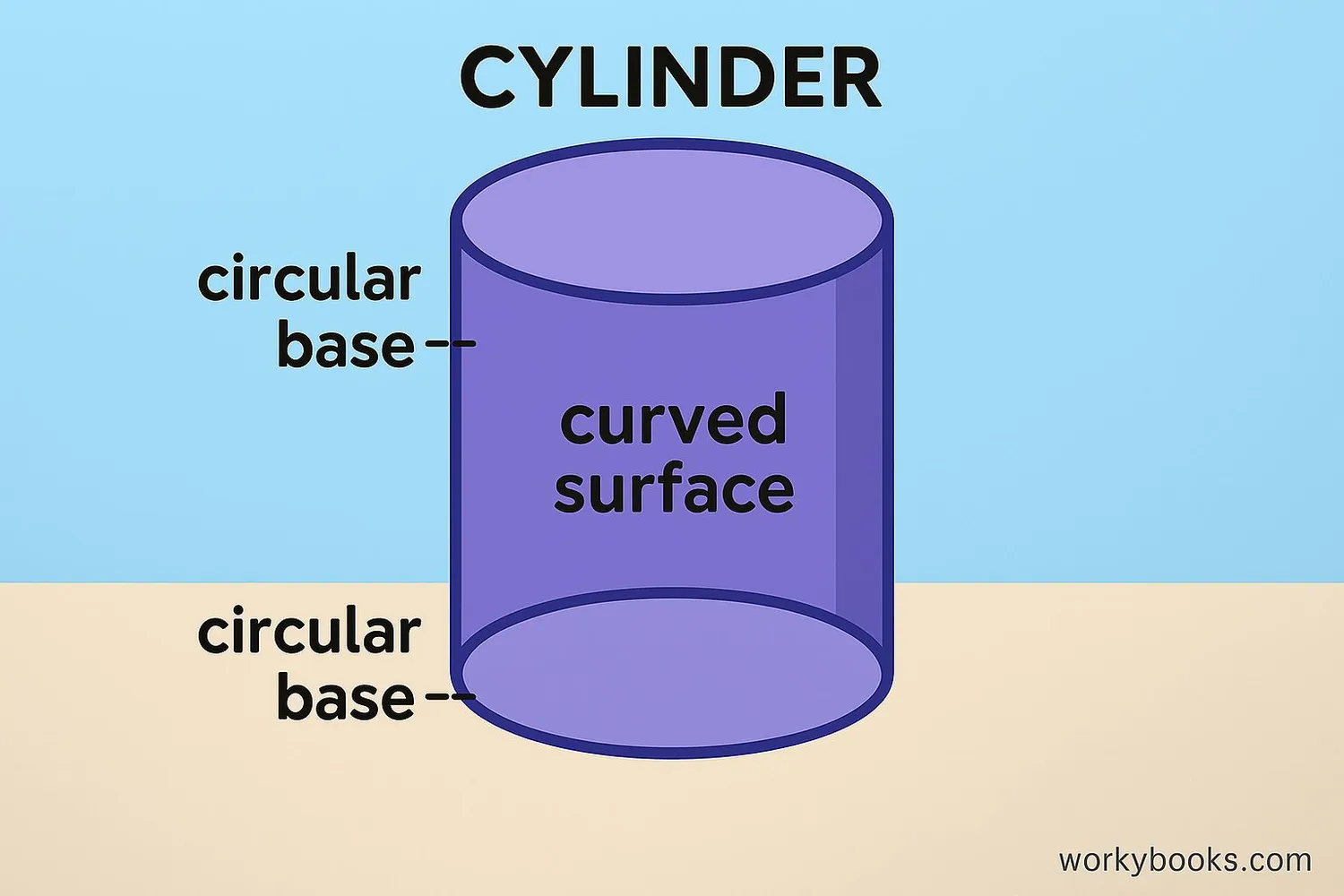
A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two identical circular bases connected by a curved surface. It's like a can or a tube shape.
Cylinders are all around us in everyday life. Some examples include soda cans, paper towel rolls, and water bottles. They're important in geometry because they help us understand volume and surface area of 3D objects.
The cylinder has three main parts:
- Two circular bases - the flat, round surfaces at the top and bottom
- Curved surface - the side that connects the two bases
- Height - the distance between the two bases
Key Concept
A cylinder is a 3D shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface at a fixed distance (height).
Properties of Cylinders
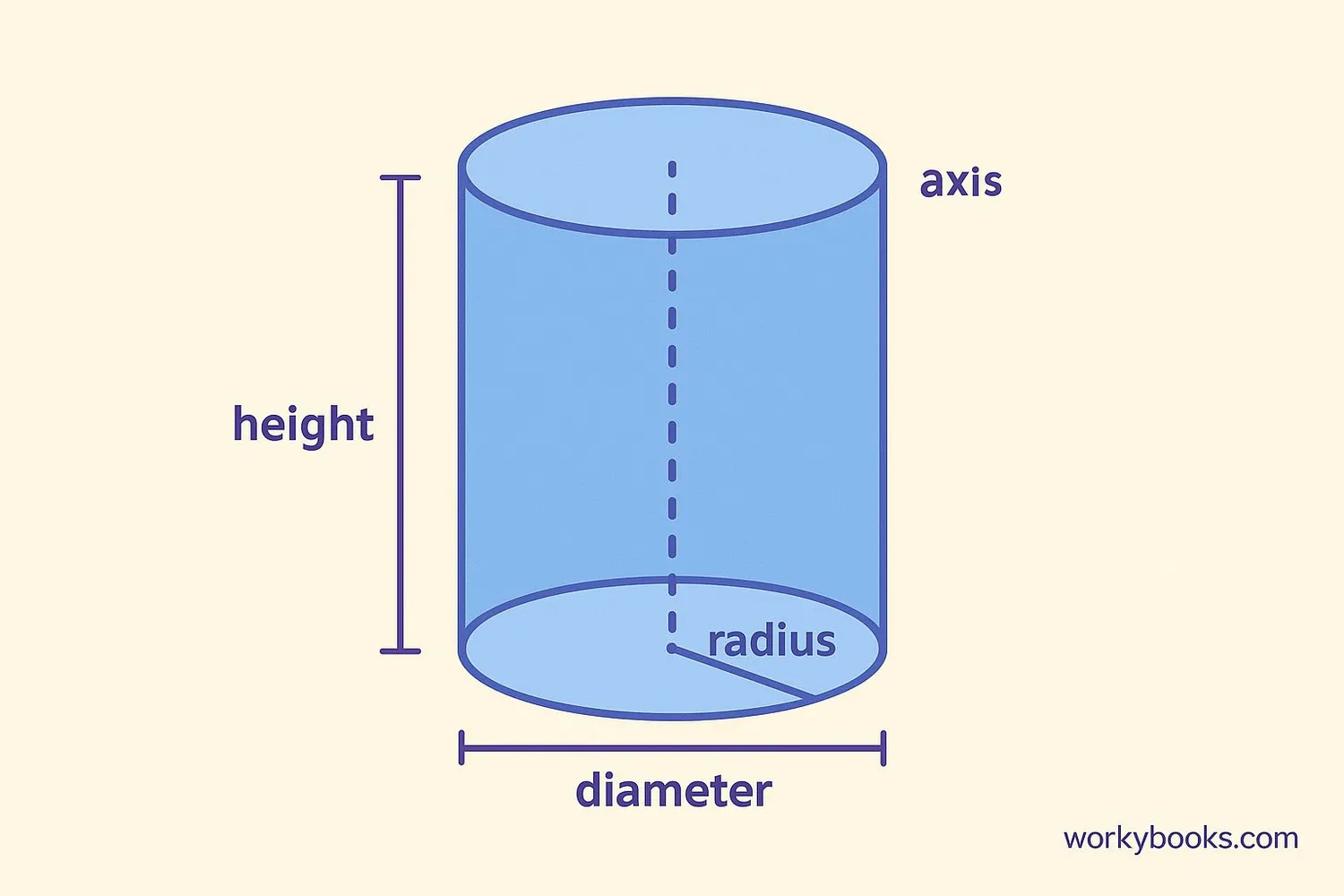
Cylinders have special properties that help us recognize and measure them:
- Two identical circular bases - The top and bottom are perfect circles of the same size
- Curved lateral surface - When unrolled, this becomes a rectangle
- Height (h) - The perpendicular distance between the bases
- Radius (r) - The distance from the center to the edge of the circular base
- Diameter (d) - Twice the radius, the distance across the circular base
- Axis - The straight line connecting the centers of the two bases
- No vertices - Unlike other 3D shapes, cylinders don't have corners
Did You Know?
If you unroll the curved surface of a cylinder, it becomes a perfect rectangle! This helps us calculate its surface area.
Cylinder Formulas
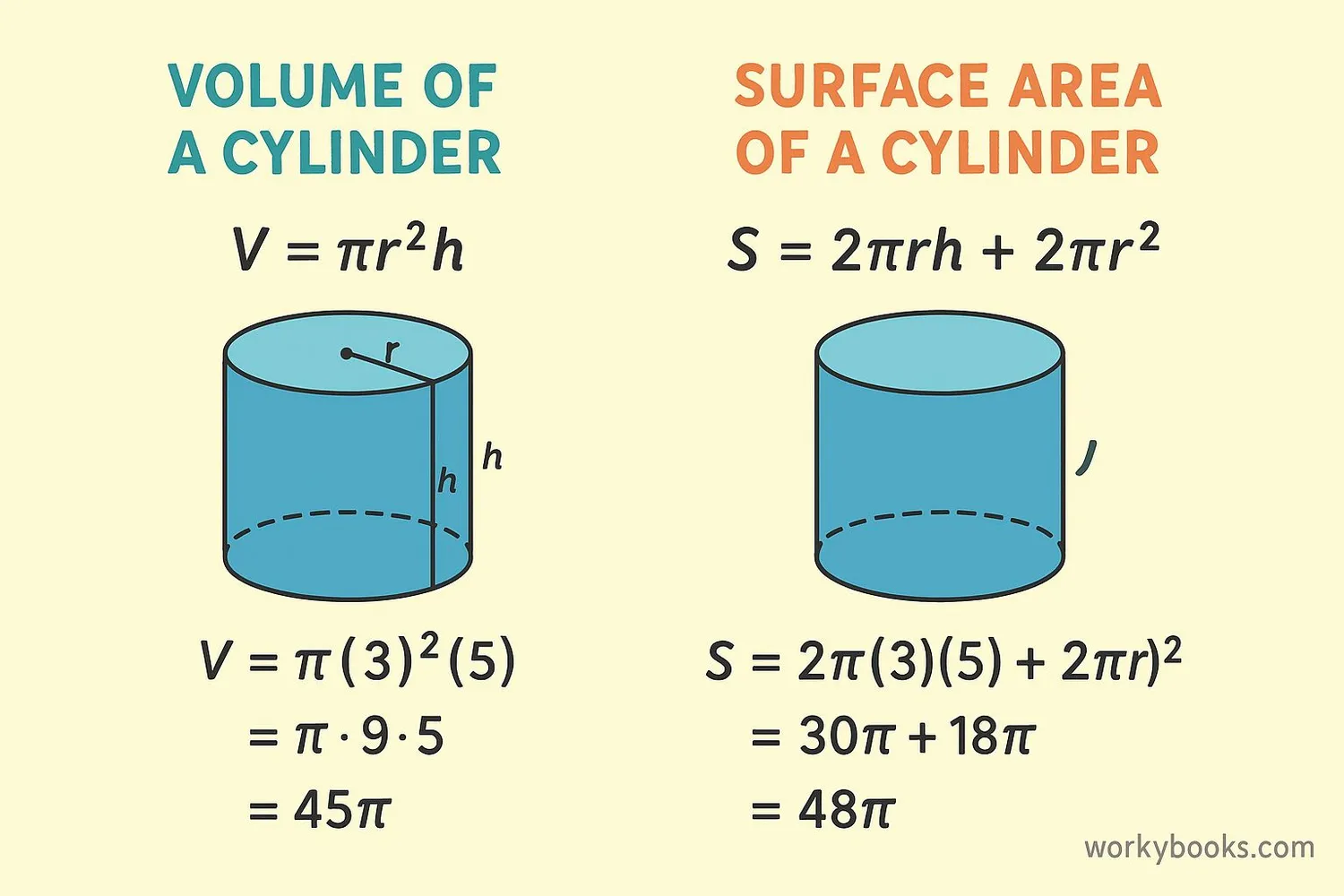
We use special formulas to calculate the volume and surface area of cylinders:
Volume of a Cylinder
Volume equals pi (≈3.14) times radius squared times height
Total Surface Area
Area equals 2 times pi times radius times (height plus radius)
Example: Let's calculate the volume of a cylinder with radius 3 cm and height 5 cm
Step 1: Square the radius → 3 × 3 = 9
Step 2: Multiply by π → 9 × 3.14 ≈ 28.26
Step 3: Multiply by height → 28.26 × 5 = 141.3 cm³
So the volume is approximately 141.3 cubic centimeters.
Remember
Volume is measured in cubic units (like cm³), while surface area is measured in square units (like cm²).
Types of Cylinders
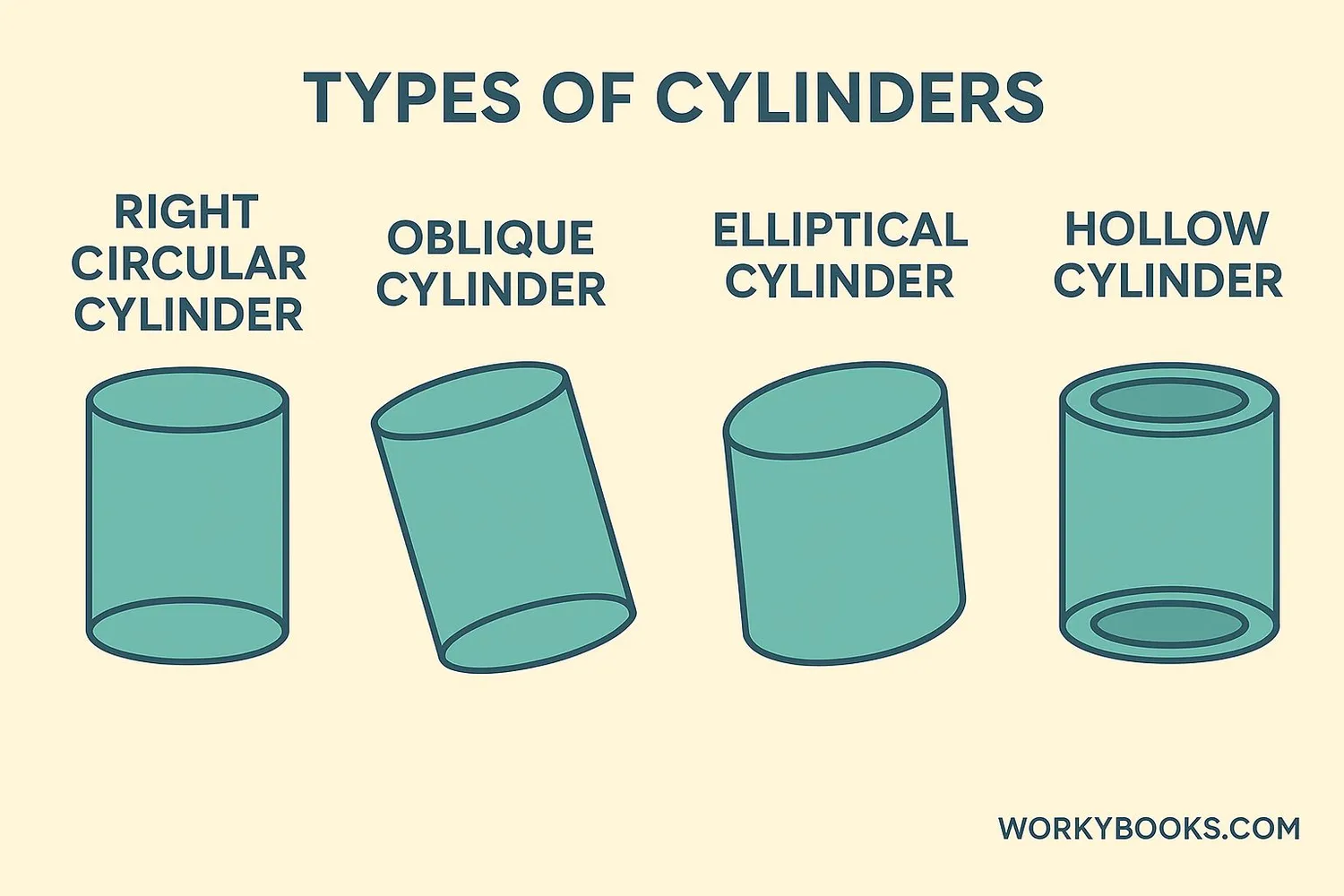
There are several types of cylinders used in mathematics and real-world applications:
1. Right Circular Cylinder
The most common type where the axis is perpendicular to the bases. All our formulas work for this type.
2. Oblique Cylinder
The sides lean over - the axis is not perpendicular to the bases. It looks like a tilted can.
3. Elliptical Cylinder
Has oval-shaped (elliptical) bases instead of circular ones. Some pipes use this shape.
4. Hollow Cylinder
Like a tube with thickness - it has an inner and outer cylinder. Water pipes are often hollow cylinders.
Real-World Connection
Hydraulic cylinders in machines are usually right circular cylinders, while some architectural columns might be oblique cylinders.
Real-World Cylinder Examples
Cylinders are everywhere in our daily lives! Here are some common examples:
- Food containers - Soup cans, oatmeal containers, potato chip tubes
- Household items - Candles, batteries, paper towel rolls, drinking glasses
- Building materials - Pipes, columns, some types of bricks
- Transportation - Car engine cylinders, airplane fuselages, rocket bodies
- Nature - Some tree trunks, stalactites in caves, certain plant stems
Activity: Look around your home or classroom. How many cylindrical objects can you find? Try to estimate their height and radius!
Engineering Fact
Cylinders are strong shapes that can hold pressure well, which is why they're used in engines, hydraulic systems, and storage tanks.
Cylinder Quiz
Test your knowledge about cylinders with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about cylinders:
Cylinder Trivia
Discover interesting facts about cylinders:
Ancient Cylinders
The ancient Egyptians used cylindrical stone rollers to move heavy blocks when building pyramids. These early cylinders helped them transport massive stones across the desert.
Hydraulic Power
Hydraulic cylinders can generate tremendous force. The largest hydraulic cylinders can lift over 1,000 tons! They work by using pressurized fluid to move a piston inside the cylinder.
Rocket Shapes
Most rockets are cylindrical because this shape is strong and aerodynamic. The Saturn V rocket that took astronauts to the moon was over 110 meters (363 feet) tall - that's taller than a 36-story building!
Tallest Cylinder
The tallest cylindrical structure in the world is the KVLY-TV mast in North Dakota, USA. It stands 629 meters (2,063 feet) tall - that's about 1.7 times taller than the Eiffel Tower!





