Dilation in Geometry - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about geometric transformations, scale factors, and how shapes change size without changing form
What is Dilation in Geometry?
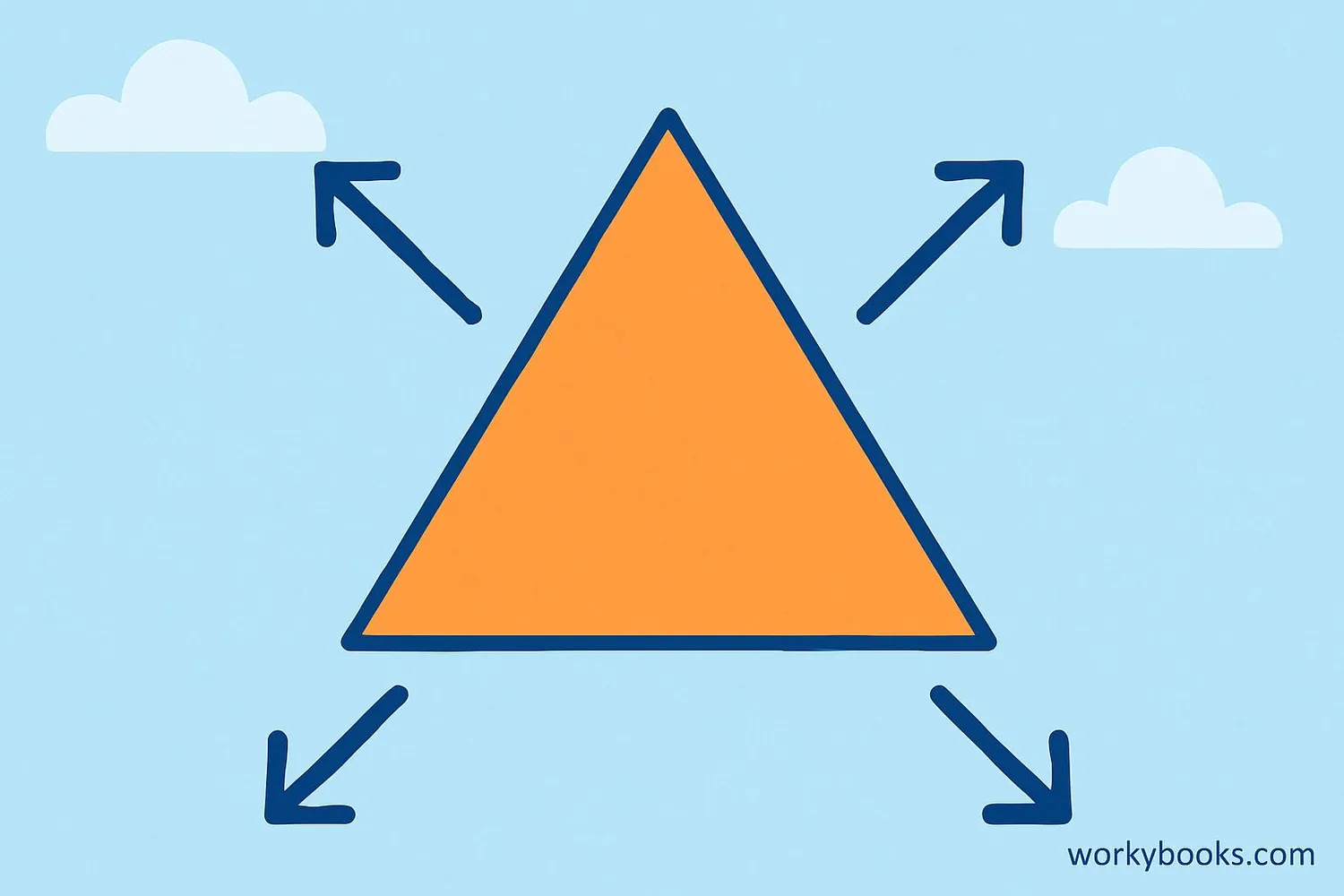
Dilation is a geometric transformation that changes the size of a shape without changing its form. It's like using a magnifying glass on a shape - it gets larger but keeps the same proportions.
In mathematics, dilation is a type of similarity transformation. This means that the original shape (called the pre-image) and the transformed shape (called the image) have the same shape but different sizes.
Dilation requires two important elements:
- Scale factor: A number that determines how much the shape will grow or shrink
- Center of dilation: The fixed point from which the shape expands or contracts
Key Concept
Dilation preserves angles and proportions but changes size. All corresponding angles remain equal, and all sides change by the same scale factor.
Understanding Scale Factor
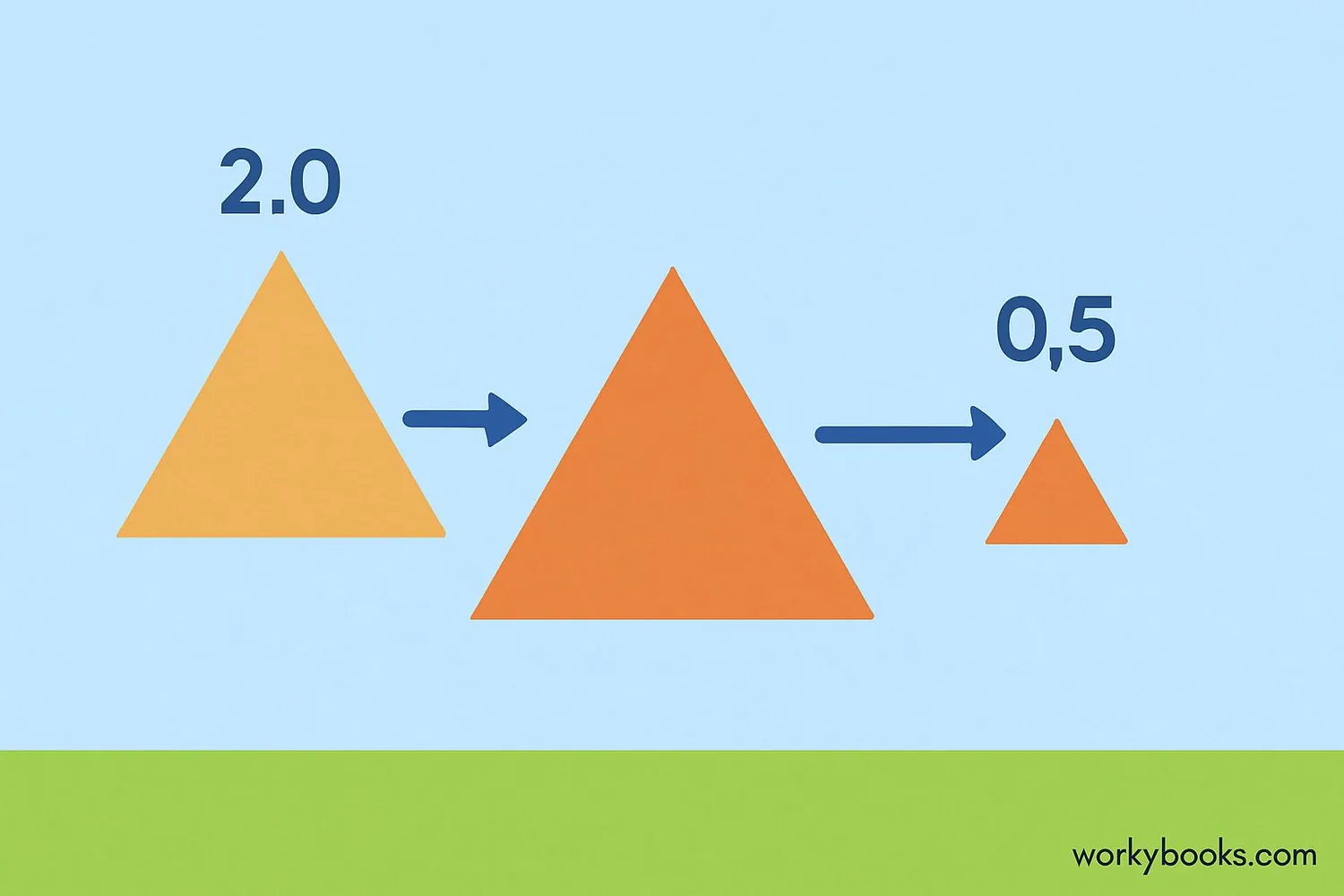
The scale factor is the number that tells us how much larger or smaller the image will be compared to the original shape. It's the ratio of any length in the image to the corresponding length in the original shape.
Scale Factor Formula
Enlargement: When the scale factor is greater than 1 (e.g., 2, 3, 1.5). The image is larger than the original shape.
Reduction: When the scale factor is between 0 and 1 (e.g., 0.5, 0.75). The image is smaller than the original shape.
Important: A scale factor of 1 means the image is the same size as the original.
Remember
Negative scale factors are possible and create an image on the opposite side of the center of dilation, but we usually focus on positive scale factors in basic geometry.
Center of Dilation
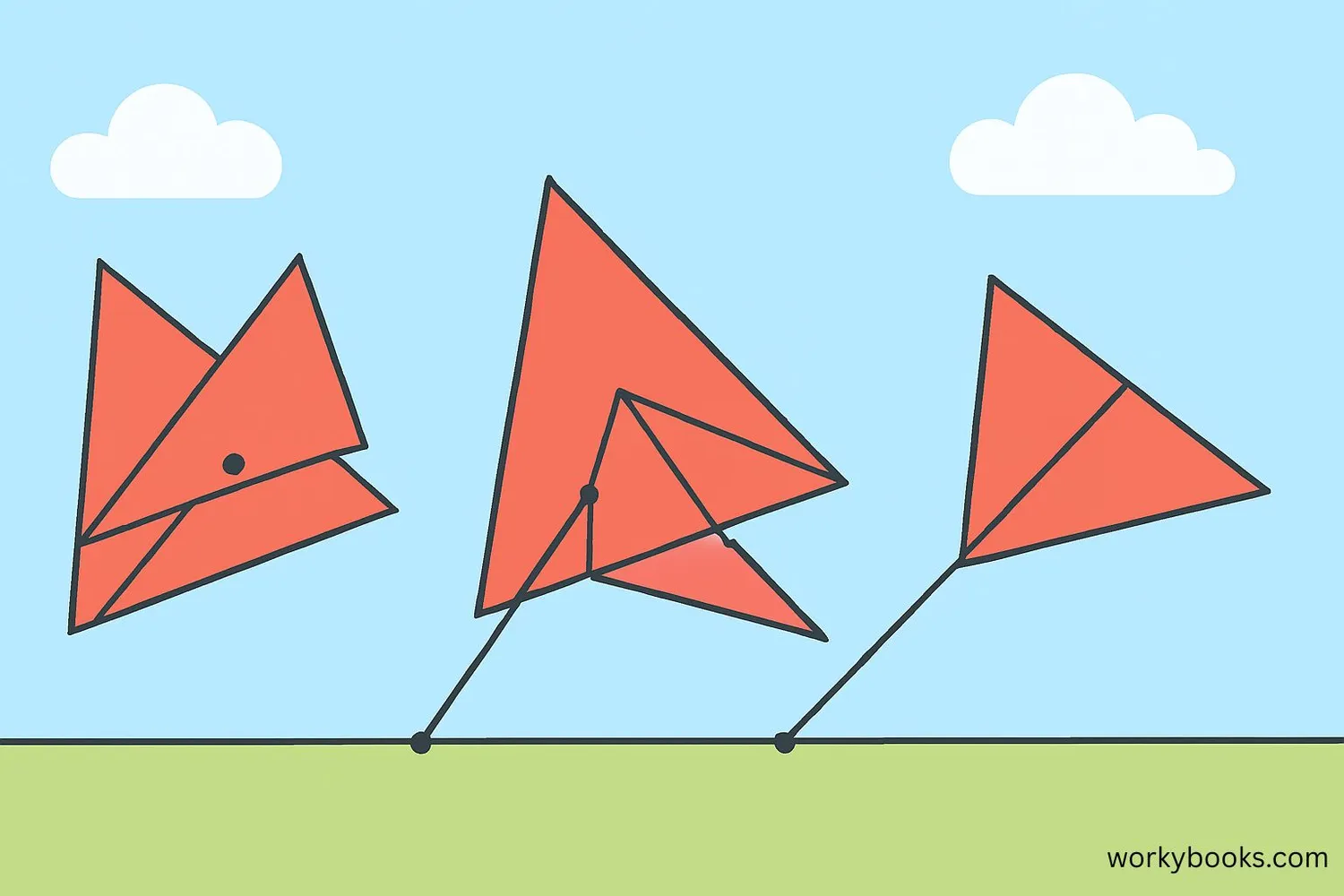
The center of dilation is the fixed point from which the dilation occurs. Every point in the shape moves along a straight line that passes through this center point.
The center can be located in different positions relative to the shape:
Inside the shape: The image grows outward from the center point.
On the shape: The point on the shape remains fixed while other points move.
Outside the shape: The entire shape moves away from or toward the center point as it changes size.
To find the image of a point after dilation:
- Draw a line from the center of dilation through the point
- Measure the distance from the center to the point
- Multiply that distance by the scale factor
- Mark the new point along the same line at the calculated distance
Visual Tip
Imagine stretching a rubber band from the center of dilation to each point of the shape. When you dilate, you're just making those rubber bands longer or shorter.
Properties of Dilation
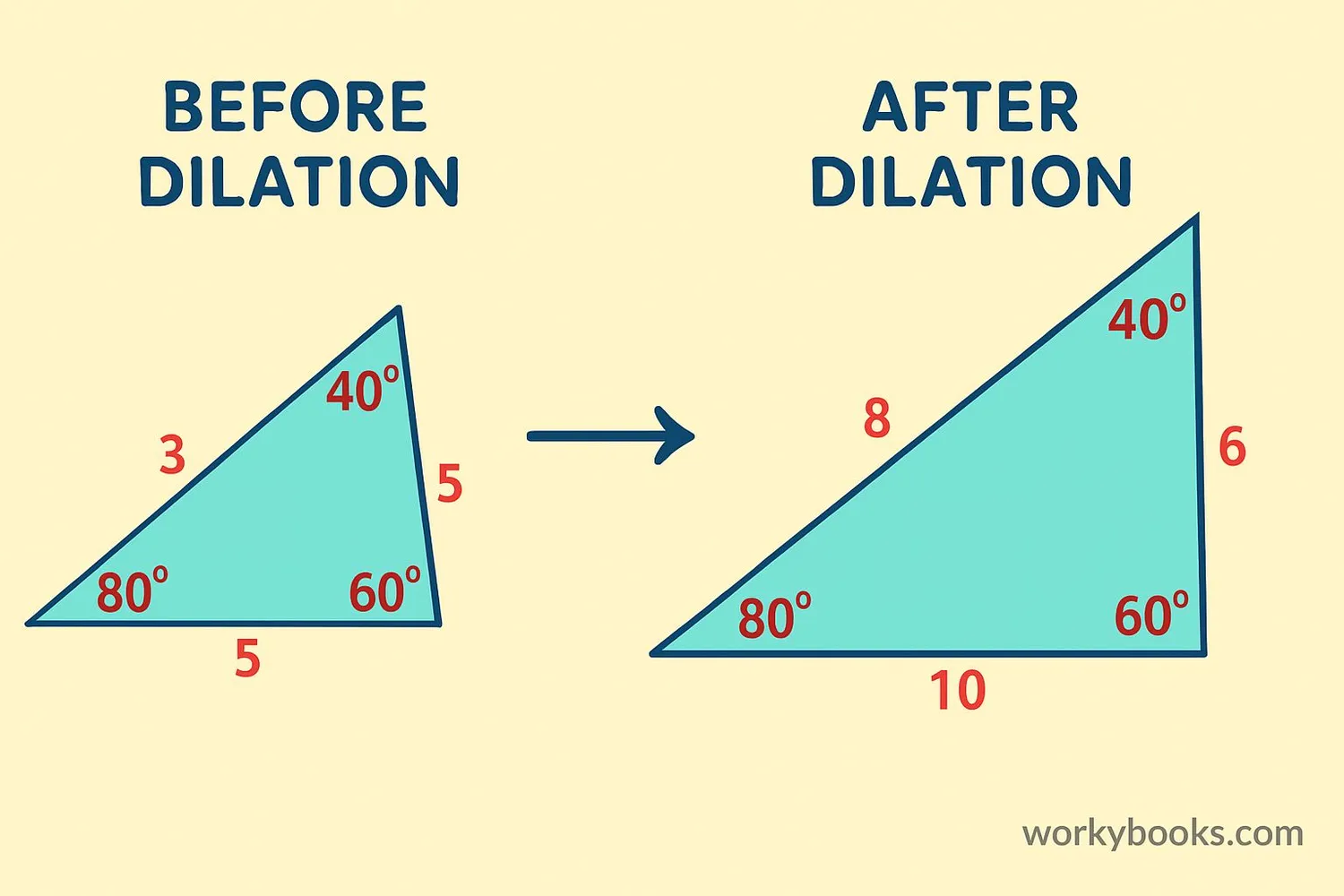
Dilation has special properties that make it different from other transformations:
Proportional Sides
All corresponding sides of the pre-image and image are proportional, with the ratio equal to the scale factor.
Angle Preservation
Corresponding angles of the pre-image and image are equal. Dilation preserves angle measures.
Parallel Lines
Lines that were parallel before dilation remain parallel after dilation.
Collinear Points
Points that were on a straight line remain collinear after dilation.
Important Note
Unlike rotation or reflection, dilation is not a rigid transformation because it changes the size of the shape. However, it is a similarity transformation.
Real-World Examples
Dilation isn't just a math concept - we see it all around us in daily life:
Photocopy Enlargement
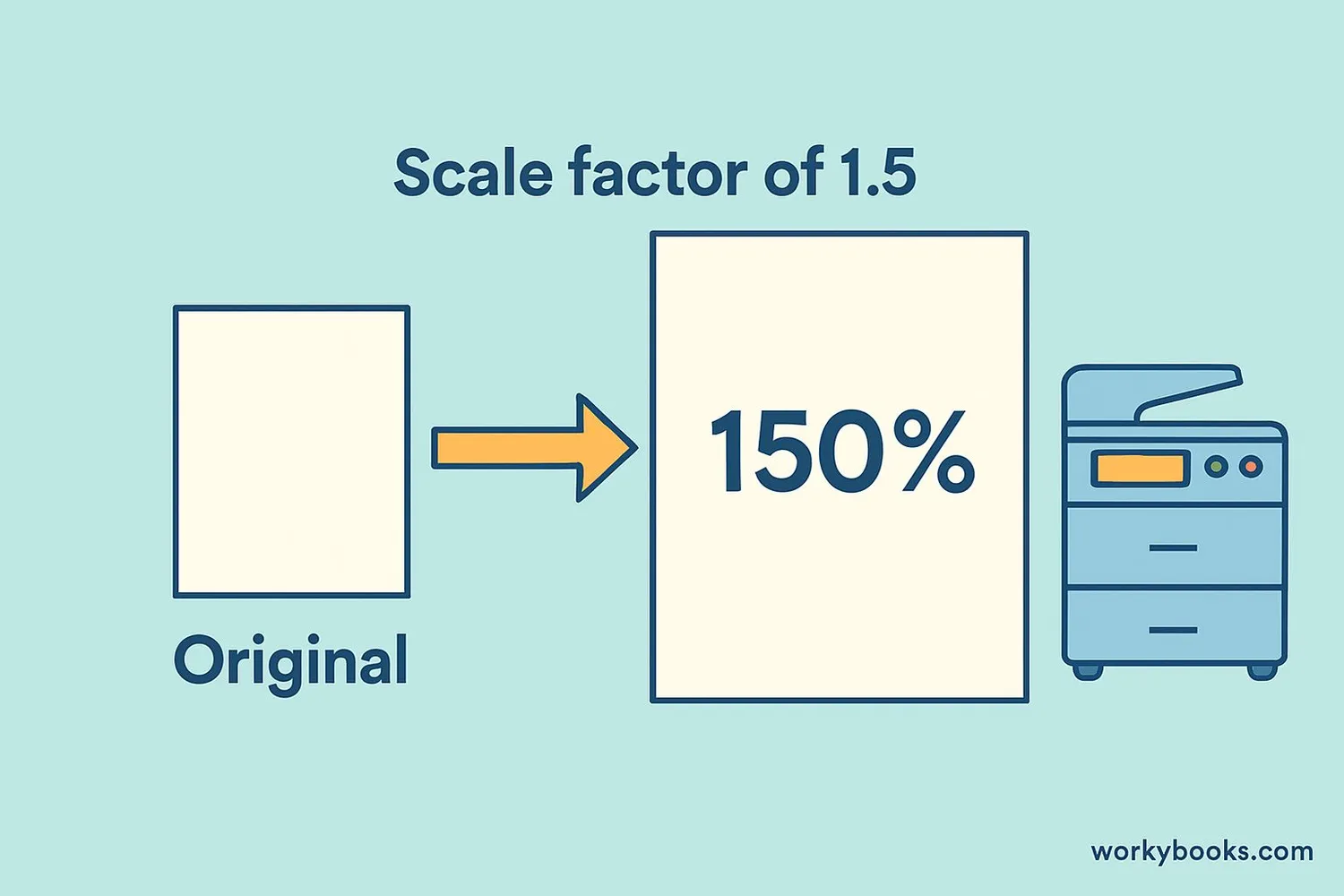
When you make a photocopy at 150% size, you're applying a scale factor of 1.5 to the original document.
Map Scaling
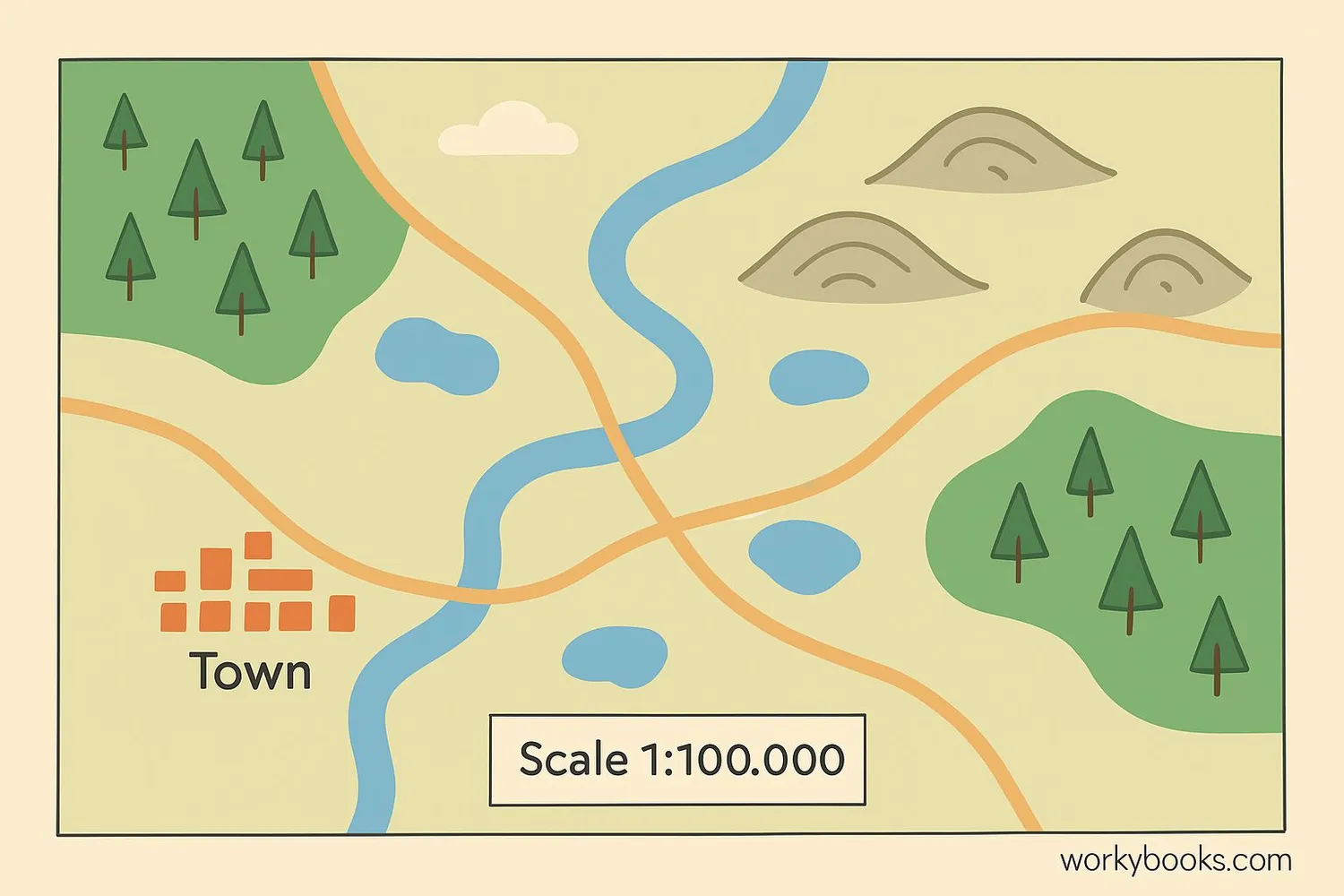
Maps use scale factors to represent large areas. A 1:100,000 scale map means 1cm on the map equals 1km in real life (scale factor 1/100,000).
Shadow Puppets

When you move your hand closer to a light source, your shadow on the wall enlarges - a dilation with the light source as the center.
Try This
Place a small object close to a flashlight and observe its shadow. Move the object closer to the light to see enlargement (scale factor >1) or farther away to see reduction (scale factor <1).
Dilation Practice Quiz
Test your understanding of dilation with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about dilation:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about dilation and geometry:
Art and Dilation
Artists have used dilation principles for centuries! When creating perspective drawings, objects farther away appear smaller - essentially a reduction dilation.
Nature's Dilations
Many natural patterns show dilation properties. Snowflakes often have similar structures at different scales, and fern leaves demonstrate self-similarity through dilation.
Digital Imaging
When you zoom in or out on a digital image, your device uses mathematical dilation algorithms to resize the picture while trying to preserve details.
Astronomy Applications
Astronomers use dilation concepts when studying star formations. They often compare images at different scales to understand cosmic structures.





