Enlargement - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about geometric enlargement and biological growth with visual examples and practice activities
What is Enlargement?
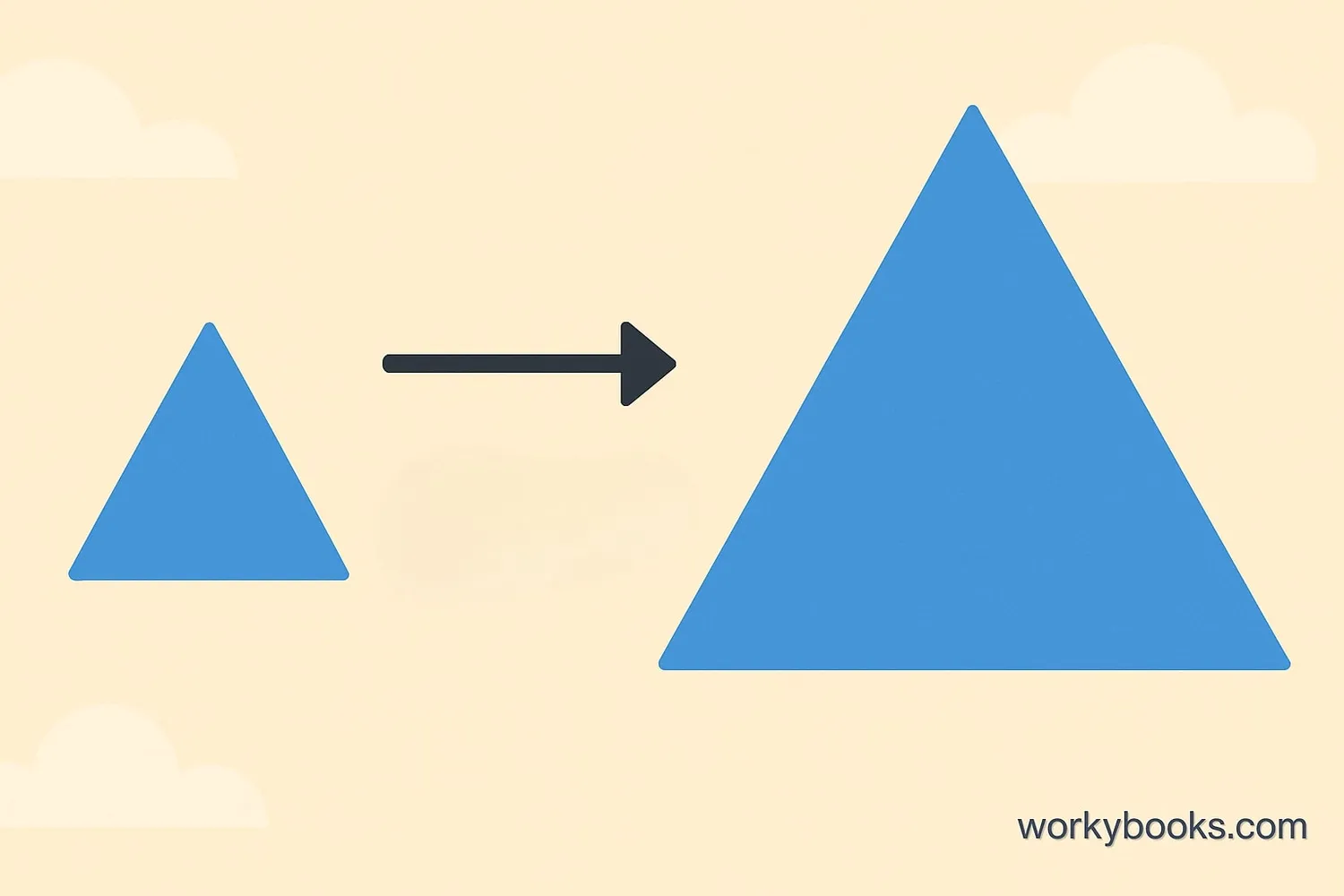
Enlargement is when we make something bigger while keeping its shape exactly the same. In mathematics, enlargement is a type of transformation that changes the size of a shape but keeps its proportions.
When we enlarge a shape:
- All angles stay the same
- All sides become longer by the same scale factor
- The shape becomes larger but looks similar to the original
In biology, enlargement refers to growth - when living things like plants, animals, or cells get bigger. Both types of enlargement follow mathematical principles!
Key Concept
Enlargement creates a similar shape that is proportionally larger than the original.
Understanding Scale Factor
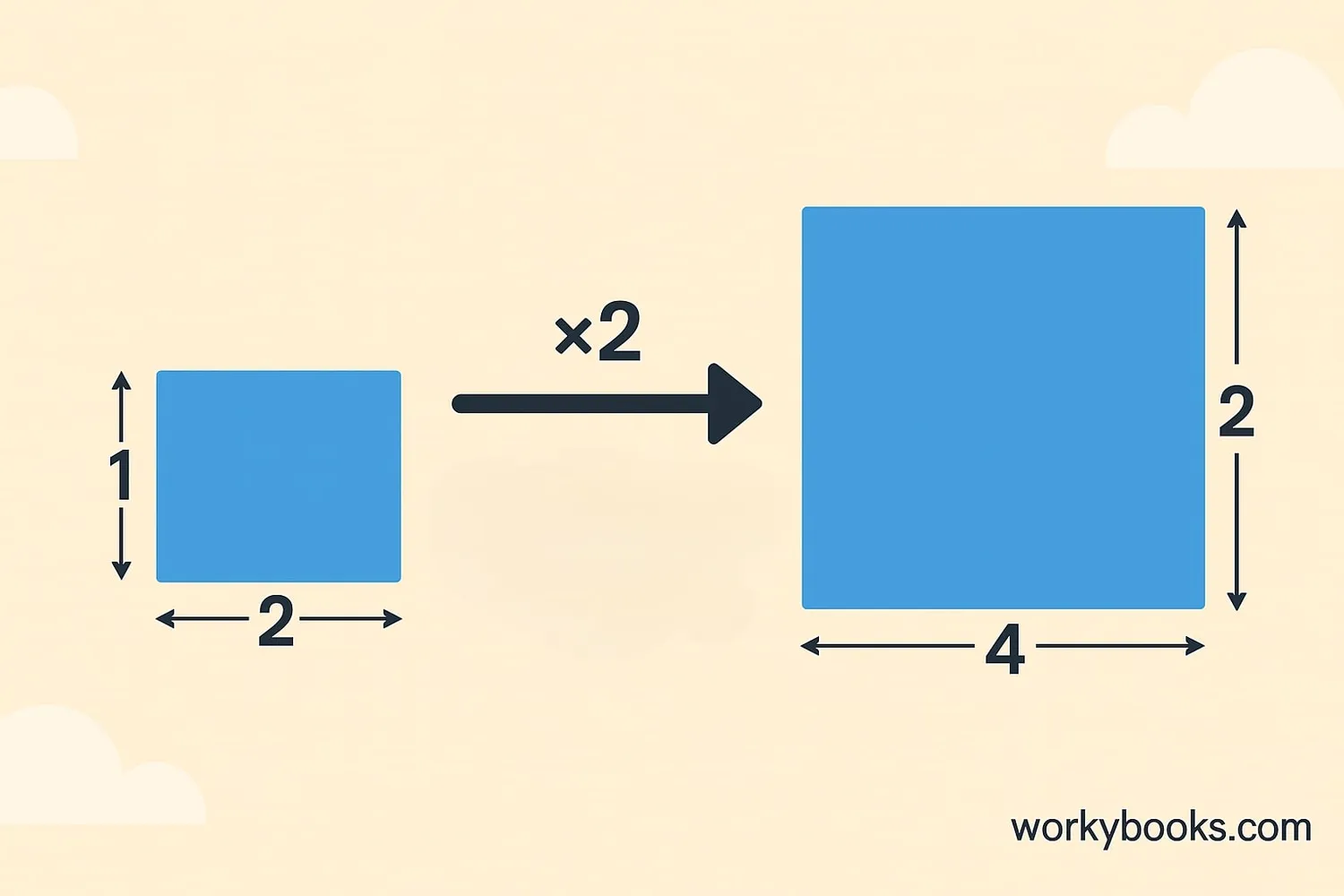
The scale factor tells us how many times larger the new shape is compared to the original. It's the number we multiply all the original lengths by to get the enlarged shape.
Scale Factor Formula
If the scale factor is greater than 1, the shape gets larger. If it's less than 1, the shape gets smaller (this is called a reduction).
Step 1: Original side length = 2cm
Step 2: Multiply by scale factor: 2 × 3 = 6cm
Step 3: The enlarged square has sides of 6cm
The area of the new shape will be the scale factor squared times the original area (3² = 9 times larger in this example).
Remember
Scale factor applies to all dimensions equally. This keeps the shape proportional to the original.
Center of Enlargement
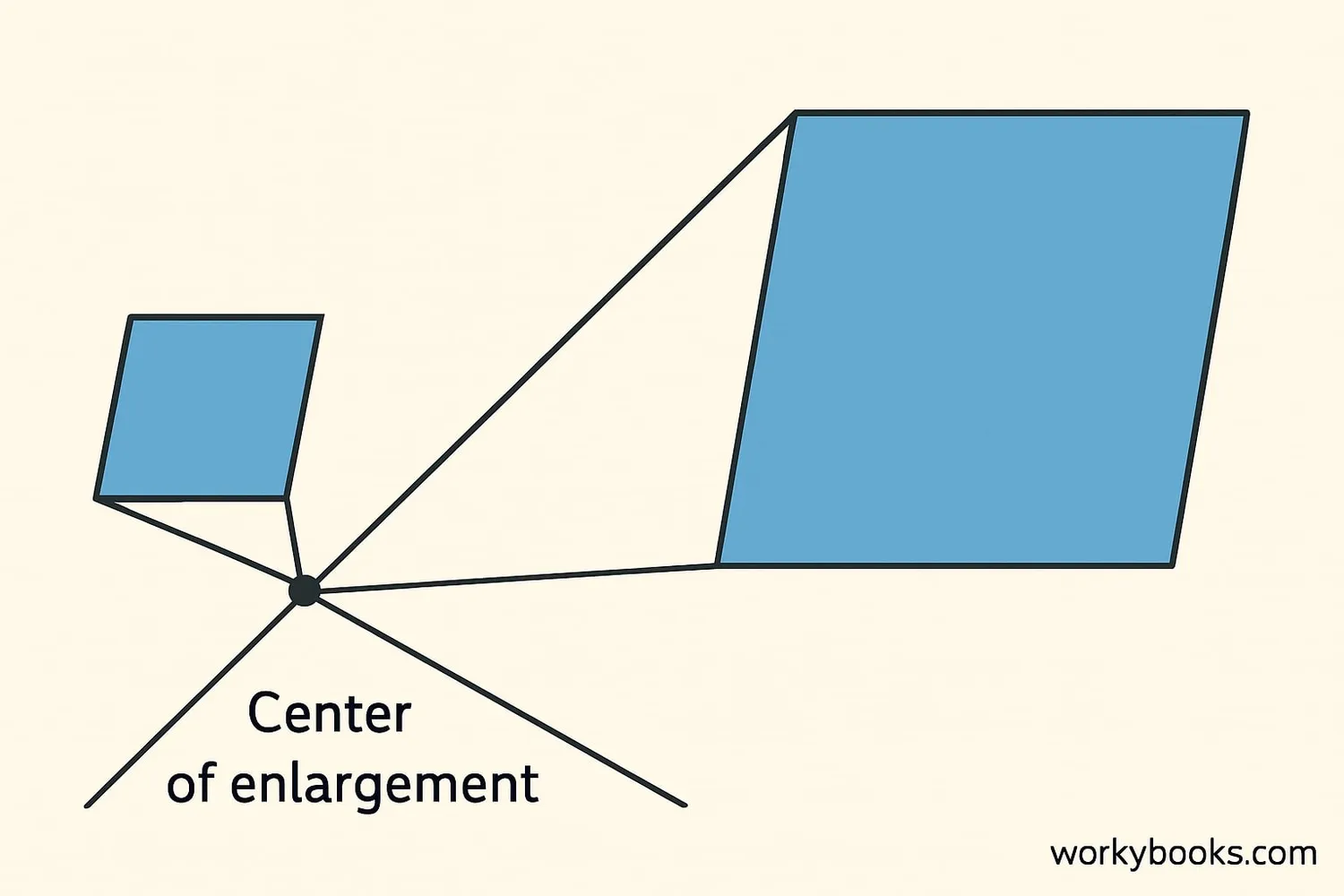
The center of enlargement is a fixed point that tells us where the enlargement starts from. All points on the shape move directly away from this center point when we enlarge the shape.
How to find the center of enlargement:
- Draw straight lines through matching points on the original and enlarged shapes
- Find where these lines meet - this is the center of enlargement
The distance from the center of enlargement to any point on the new shape is equal to the scale factor multiplied by the distance from the center to the corresponding point on the original shape.
Example: If the scale factor is 2, points on the enlarged shape will be twice as far from the center as the original points.
Important Note
The center of enlargement can be inside, outside, or even on the shape itself.
Biological Enlargement: Growth
Cell Growth
Cells grow by increasing in size through a process called hypertrophy. They absorb nutrients and water, getting larger until they divide.
Organism Growth
Plants and animals grow through cell proliferation (making more cells) and cell enlargement. Growth hormones regulate this process.
In biology, enlargement refers to the growth of living things. Biological growth follows mathematical patterns similar to geometric enlargement:
Similarities:
- Proportional growth: Body parts grow in proportion to each other
- Scale factors: Different parts may grow at different rates
- Conservation of shape: Organisms maintain their basic form as they grow
Differences:
- Biological growth is three-dimensional
- Different body parts may have different growth rates
- Growth is regulated by hormones and genetics
Understanding enlargement helps scientists study how organisms develop from a single cell to a full-grown plant or animal.
Growth Fact
Human cells can increase their size up to 100 times before dividing to create new cells.
Real-World Examples
Enlargement concepts appear in many areas of our daily lives:
Geometry Examples:
- Photography: Zoom lenses create enlargements of distant objects
- Maps: Scale factors convert real distances to map distances
- Architecture: Blueprints use scale factors to represent buildings
- Digital images: Enlarging photos while maintaining proportions
Biology Examples:
- Plant growth: From seed to mature plant
- Human development: Growth from infant to adult
- Cell division: Cells grow before dividing
- Tissue repair: Cells enlarge to heal wounds
Understanding enlargement helps us design better technology, study living organisms, and create accurate representations of our world.
Real-World Connection
Movie special effects use enlargement principles when creating giant creatures or miniature sets.
Enlargement Practice Quiz
Test your knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about enlargement:
Enlargement Trivia
Discover interesting facts about enlargement and growth:
Ancient Enlargement
The concept of geometric enlargement dates back to ancient Greece. Mathematician Euclid described principles of similarity in his book "Elements" around 300 BC.
Giant Pumpkins
The world's heaviest pumpkin weighed over 2,700 pounds! Growers achieve this enormous enlargement through careful control of growth factors.
Photo Enlargement
The first photographic enlargers were developed in the 1850s. Before that, all photos were "contact prints" the same size as the negative.
Cell Growth Speed
Some bacteria can double in size every 20 minutes under ideal conditions. That's like a human baby growing to adult size in just 3 days!





