Parallelepiped - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding 3D Shapes and Geometry
What is a Parallelepiped?
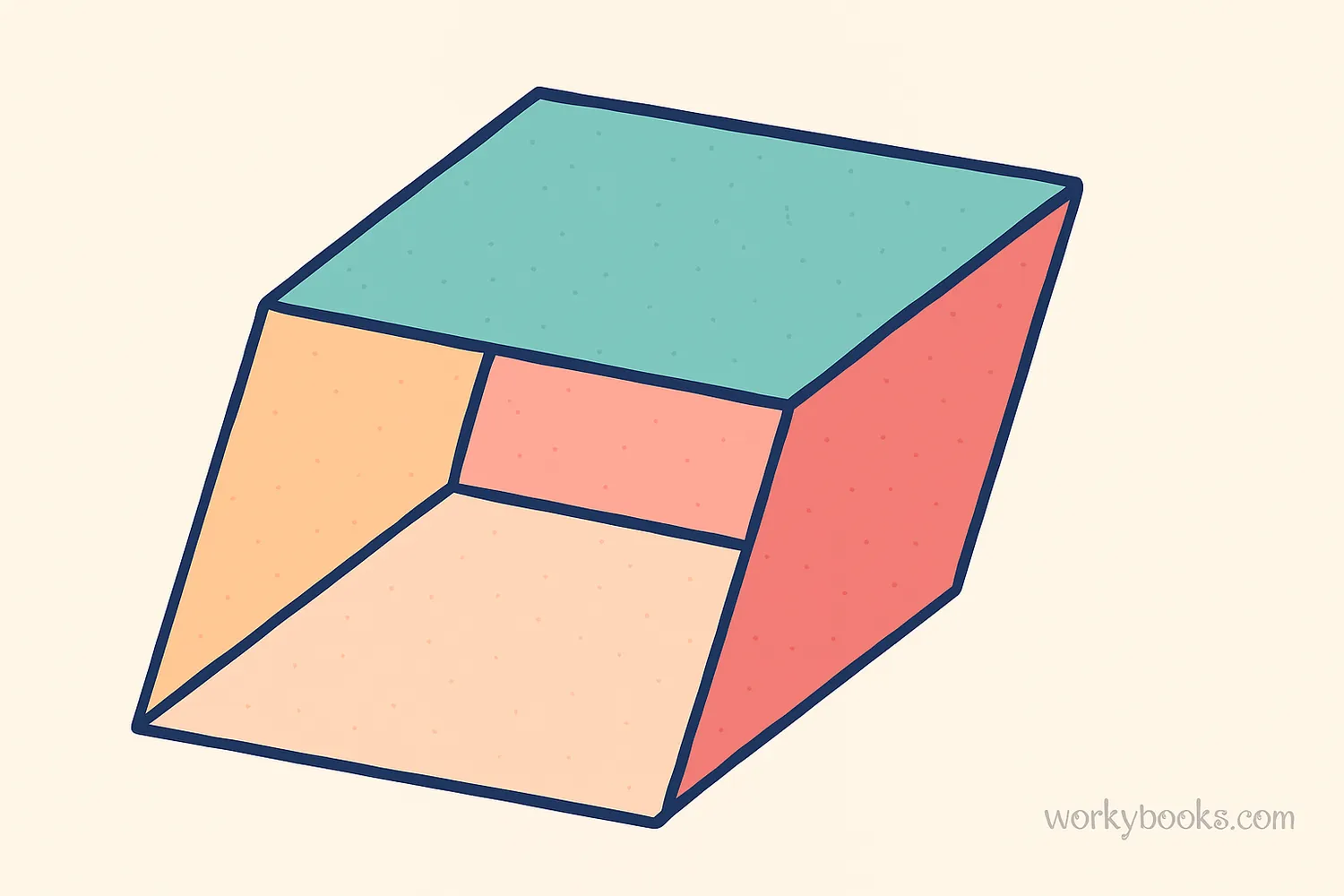
A parallelepiped is a 3-dimensional shape that looks like a slanted box! Think of it as a special kind of prism where all six faces are parallelograms.
The word "parallelepiped" might sound complicated, but it's just a combination of "parallelogram" (a slanted rectangle) and "piped" (meaning it has depth). It's like a box that's been pushed from the side, making all its faces slanted.
Math Tip!
Remember: All faces of a parallelepiped are parallelograms. This means opposite sides are parallel and equal in length.
Properties of a Parallelepiped
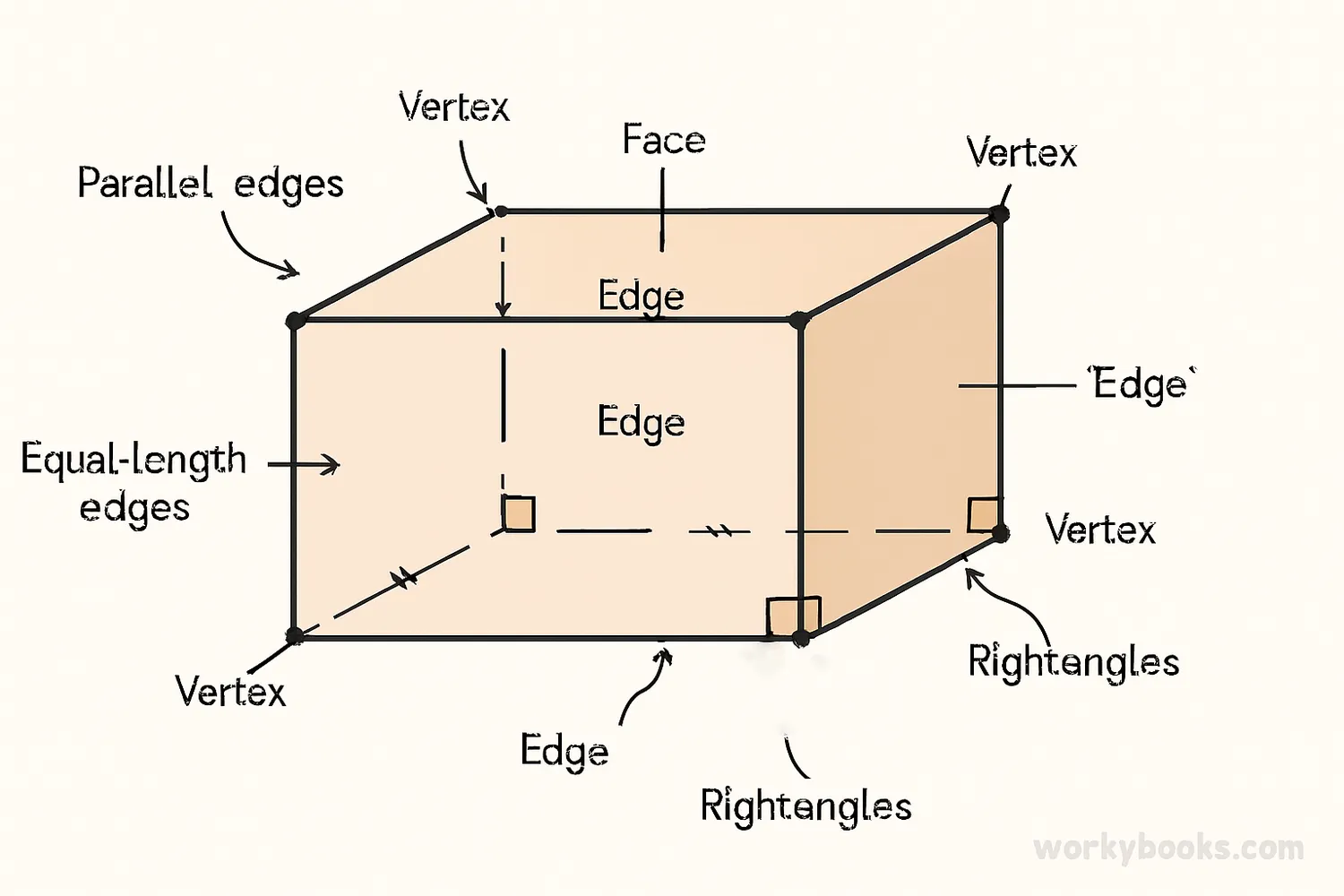
Parallelepipeds have special properties that make them unique among 3D shapes:
Faces
6 faces, all parallelograms
Edges
12 edges, parallel in groups of 4
Vertices
8 corners where edges meet
Opposite Faces
Parallel and congruent
Diagonals
4 space diagonals that meet at center
One important property is that opposite faces are parallel and identical in size and shape. This is why it's called a parallelepiped - all its faces are parallelograms arranged in parallel pairs.
Types of Parallelepipeds
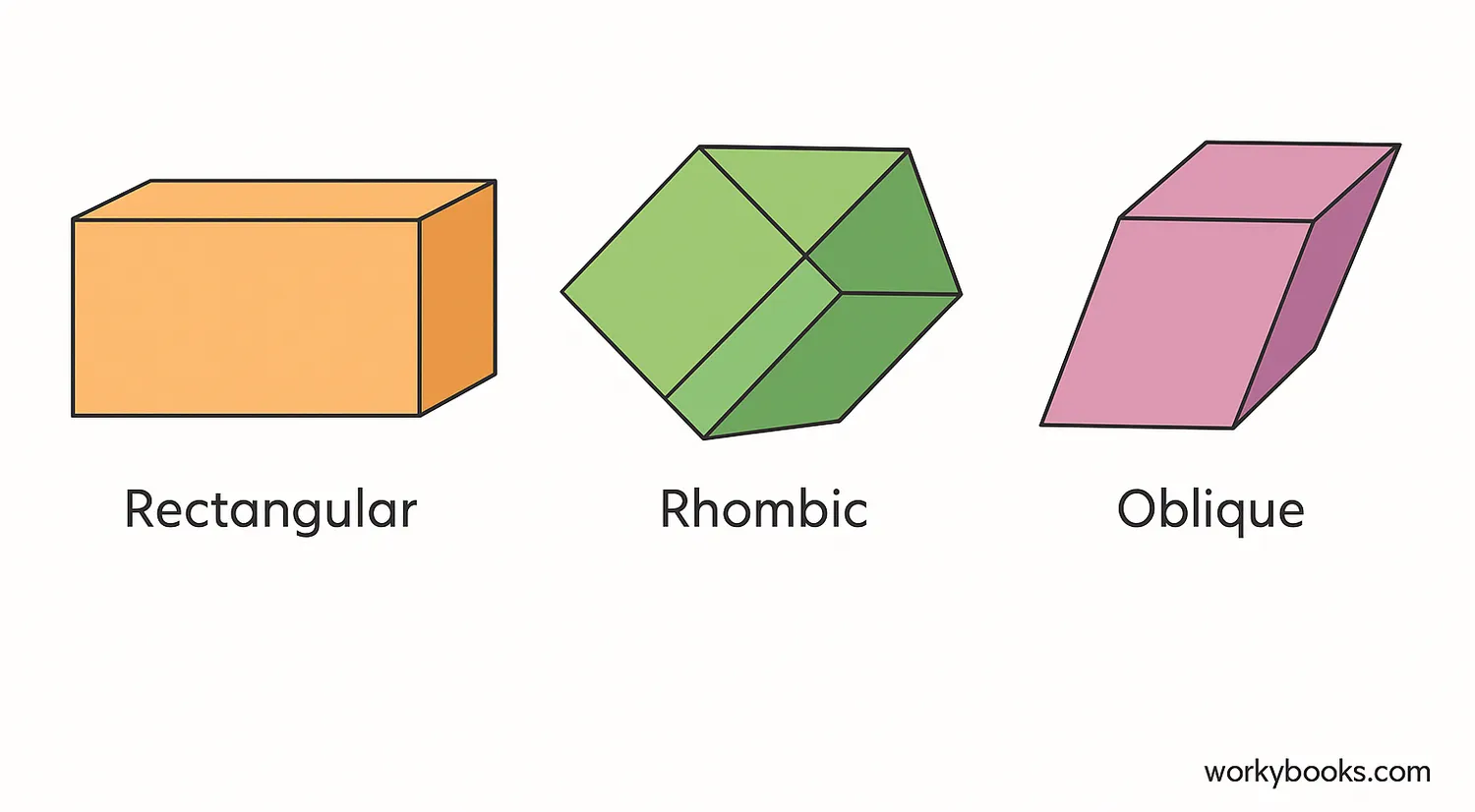
There are different types of parallelepipeds based on their angles and face shapes:
Rectangular Parallelepiped
All angles are right angles (90°). This is just a rectangular box!
Rhombic Parallelepiped
All faces are rhombuses (diamond shapes with equal sides)
Oblique Parallelepiped
Faces are not perpendicular to base - it's clearly slanted
The most common type is the rectangular parallelepiped, which is what we usually call a "box" or "rectangular prism." A cube is a special rectangular parallelepiped where all edges are equal!
Volume of a Parallelepiped
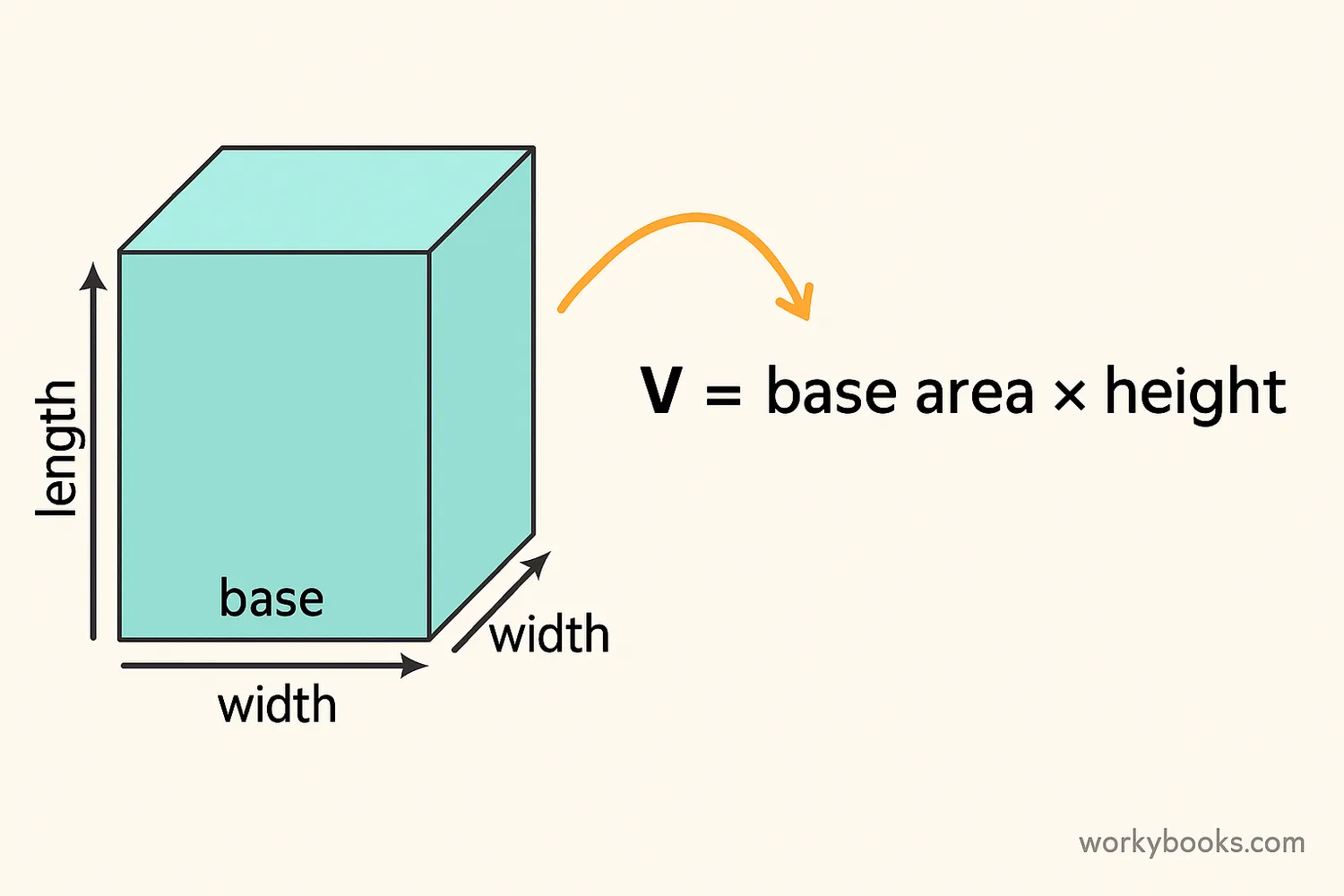
To find the volume of a parallelepiped, we use this simple formula:
For a rectangular parallelepiped (a box), the formula becomes:
The volume tells us how much space is inside the shape. Think of it as how many unit cubes would fit inside the parallelepiped.
Example Calculation
If a rectangular parallelepiped has length = 5 cm, width = 3 cm, and height = 4 cm, then its volume is 5 × 3 × 4 = 60 cubic centimeters.
Examples of Parallelepipeds

Parallelepipeds are all around us! Here are some common examples:
Boxes
Cardboard boxes, gift boxes, and storage containers
Books
Most books are rectangular parallelepipeds
Bricks
Building bricks are perfect examples
Buildings
Many buildings have parallelepiped shapes
Suitcases
Travel suitcases are often parallelepipeds
Ice Cubes
Ice cube trays make parallelepiped-shaped ice
Next time you look around, try to spot parallelepipeds in your environment. You'll be surprised how common they are!
Parallelepiped Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about parallelepipeds.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about parallelepipeds:
Math Facts About Parallelepipeds
Discover some fascinating facts about parallelepipeds and geometry!
Word Origin
The word "parallelepiped" comes from Greek words: "parallelos" (parallel) + "epipedon" (plane surface). It literally means "having parallel planes."
Crystal Shapes
Many crystals in nature form parallelepiped shapes! For example, salt crystals are often perfect cubes, which are special parallelepipeds.
In Architecture
Parallelepipeds are fundamental in architecture. Many famous buildings, like the UN Headquarters in New York, use parallelepiped shapes in their design.
Mathematical Property
The volume of a parallelepiped can be calculated using vectors! If three edges meeting at a corner are represented as vectors, the volume equals the absolute value of their scalar triple product.





