Point of Concurrency - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover where lines meet in geometry and how these special points help us understand shapes!
What is a Point of Concurrency?
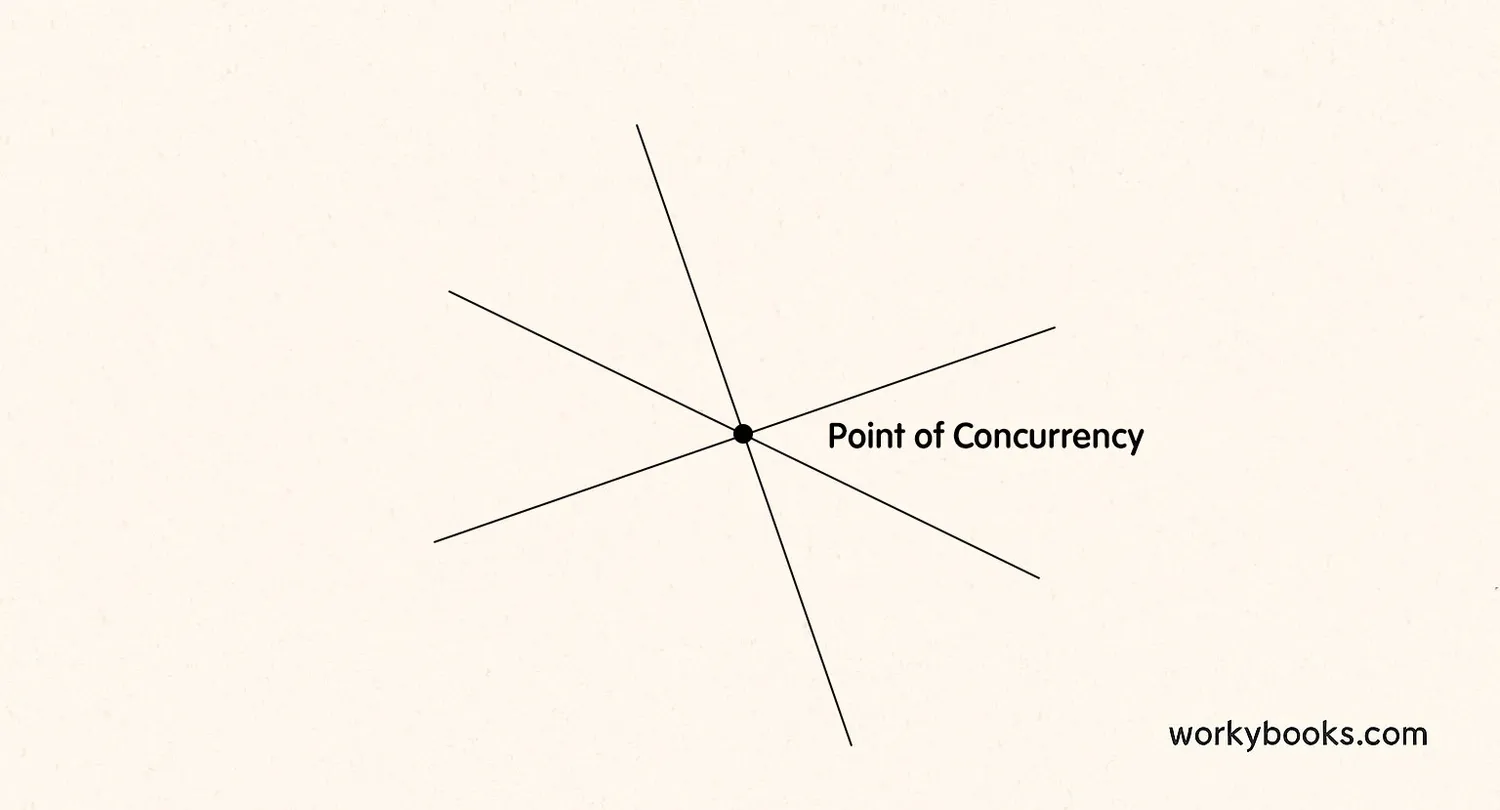
A point of concurrency is a special point where three or more lines intersect or meet. Think of it like a meeting place for lines! In geometry, when lines have something in common and cross at the exact same spot, we call that spot a point of concurrency.
The word "concurrency" comes from "con-" meaning together and "current" meaning flowing or running. So it's like lines running together to meet at one point!
Math Fact!
For lines to be concurrent, they must all pass through exactly the same point. If even one line doesn't pass through that point, they're not concurrent!
Types of Points of Concurrency
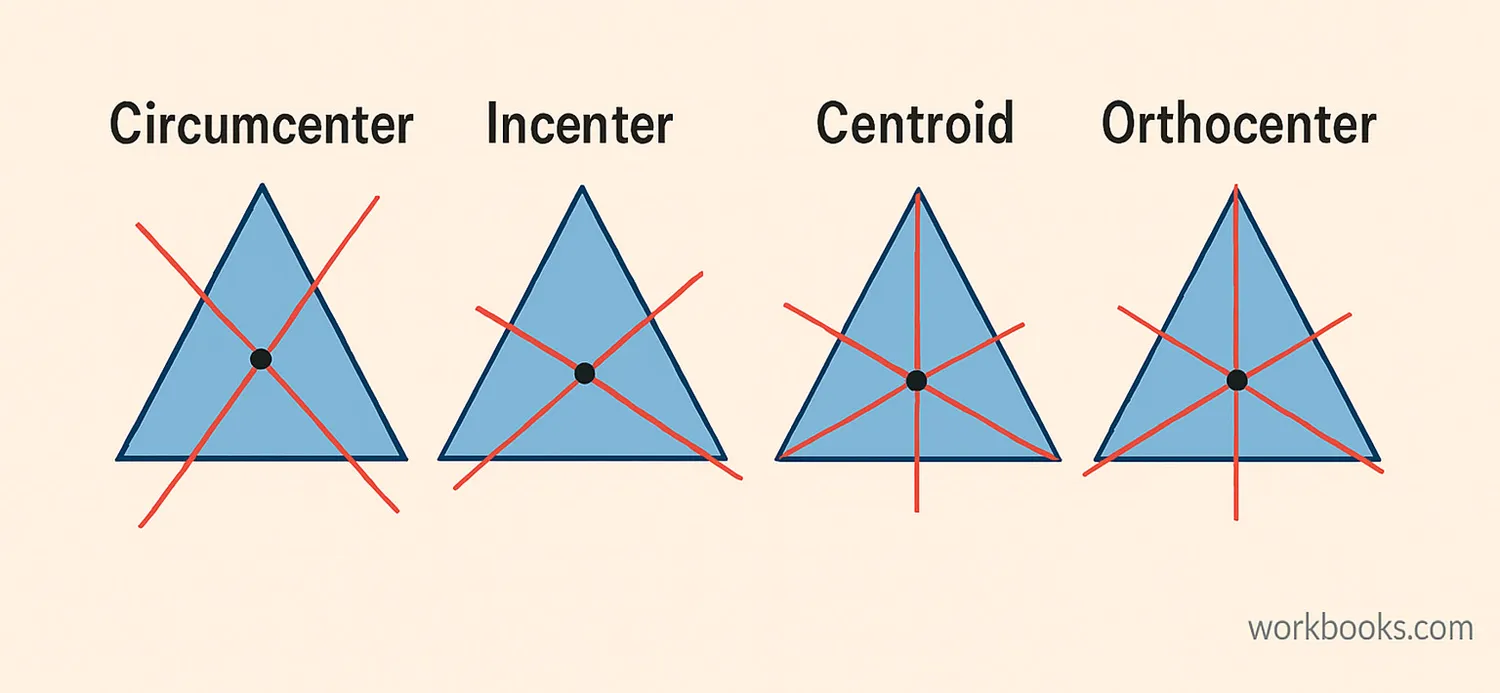
In triangles, there are four special types of points of concurrency. Each one is created by different kinds of lines meeting at a point:
Centroid
Where the three medians of a triangle meet. The median is a line from a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
The centroid is the center of gravity of a triangle!
Circumcenter
Where the perpendicular bisectors of the three sides meet. A perpendicular bisector is a line that cuts another line in half at a 90-degree angle.
The circumcenter is the center of a circle that passes through all three vertices!
Incenter
Where the three angle bisectors of a triangle meet. An angle bisector is a line that divides an angle into two equal parts.
The incenter is the center of a circle that fits perfectly inside the triangle!
Orthocenter
Where the three altitudes of a triangle meet. An altitude is a line from a vertex that is perpendicular to the opposite side.
In some triangles, the orthocenter falls outside the triangle!
Each of these points has special properties and uses in geometry. Architects and engineers use these points when designing structures to make them strong and balanced!
Examples in Real Life
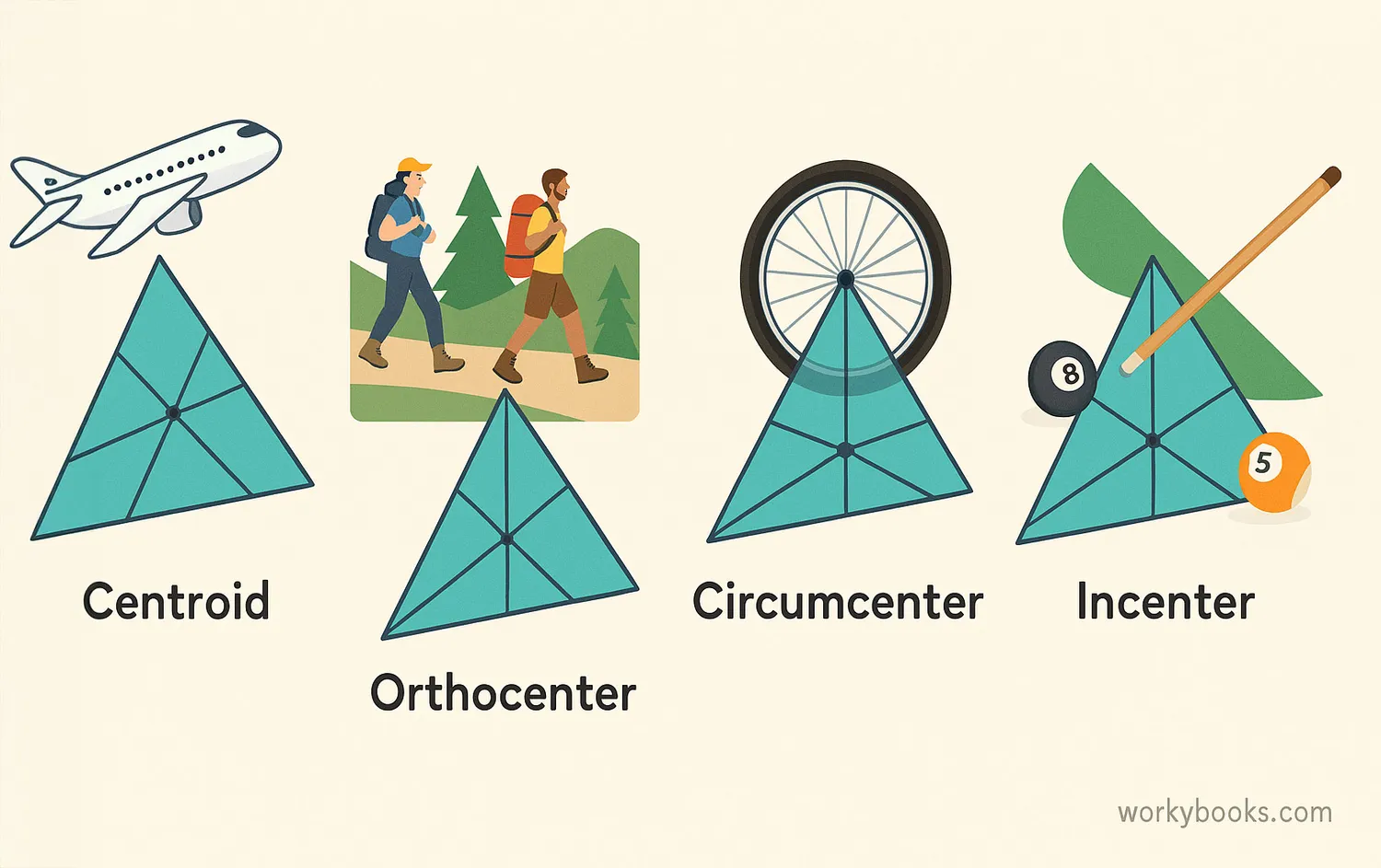
Points of concurrency aren't just math concepts—they appear in many real-world objects and situations:
Pizza Slices
If you draw lines from the tips of each slice to the center, they all meet at one point—the center of the pizza!
Bicycle Wheels
The spokes of a bicycle wheel all connect to the center hub, creating a point of concurrency.
Navigation
When ships or planes use multiple navigation lines to find their position, where those lines cross is a point of concurrency.
Architecture
Architects use points of concurrency to design stable structures and find balance points.
Next time you see a bicycle wheel or eat a slice of pizza, remember—you're looking at geometry in action! Points of concurrency help make these objects work properly and look balanced.
Geometry Quiz
Test your knowledge about points of concurrency with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about points of concurrency:
Math Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about points of concurrency and geometry!
The Magical Euler Line
In most triangles, the centroid, circumcenter, and orthocenter all lie on a straight line called the Euler Line, named after the famous mathematician Leonhard Euler.
Perfect Balance
If you cut a triangle from cardboard, the centroid is exactly where you could balance it on the tip of your pencil! This point is the center of gravity of the triangle.
Navigation Trick
Before GPS, sailors used the concept of concurrency to navigate. They would take bearings to three landmarks, and where those bearing lines converged was their location!
Ancient Architecture
The ancient Egyptians might have used points of concurrency when building pyramids to ensure they were symmetrical and stable, though they didn't have the mathematical terms we use today.





