Volume - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about volume measurement with simple explanations, formulas, and practice activities
What is Volume?
Volume is the amount of space that a three-dimensional object takes up. It tells us how much space is inside a shape like a box, ball, or can.
We measure volume using cubic units. Just like we use inches or centimeters to measure length, we use cubic centimeters (cm³), cubic inches (in³), or liters to measure volume.
Think of volume as how much water a container can hold. A small cup has less volume than a large bucket because it can hold less water.
Volume is different from area: area measures flat surfaces (2D), while volume measures space inside objects (3D).
Key Concept
Volume = Length × Width × Height for rectangular prisms. This formula helps us calculate how much space is inside box-like objects.
Measuring Volume
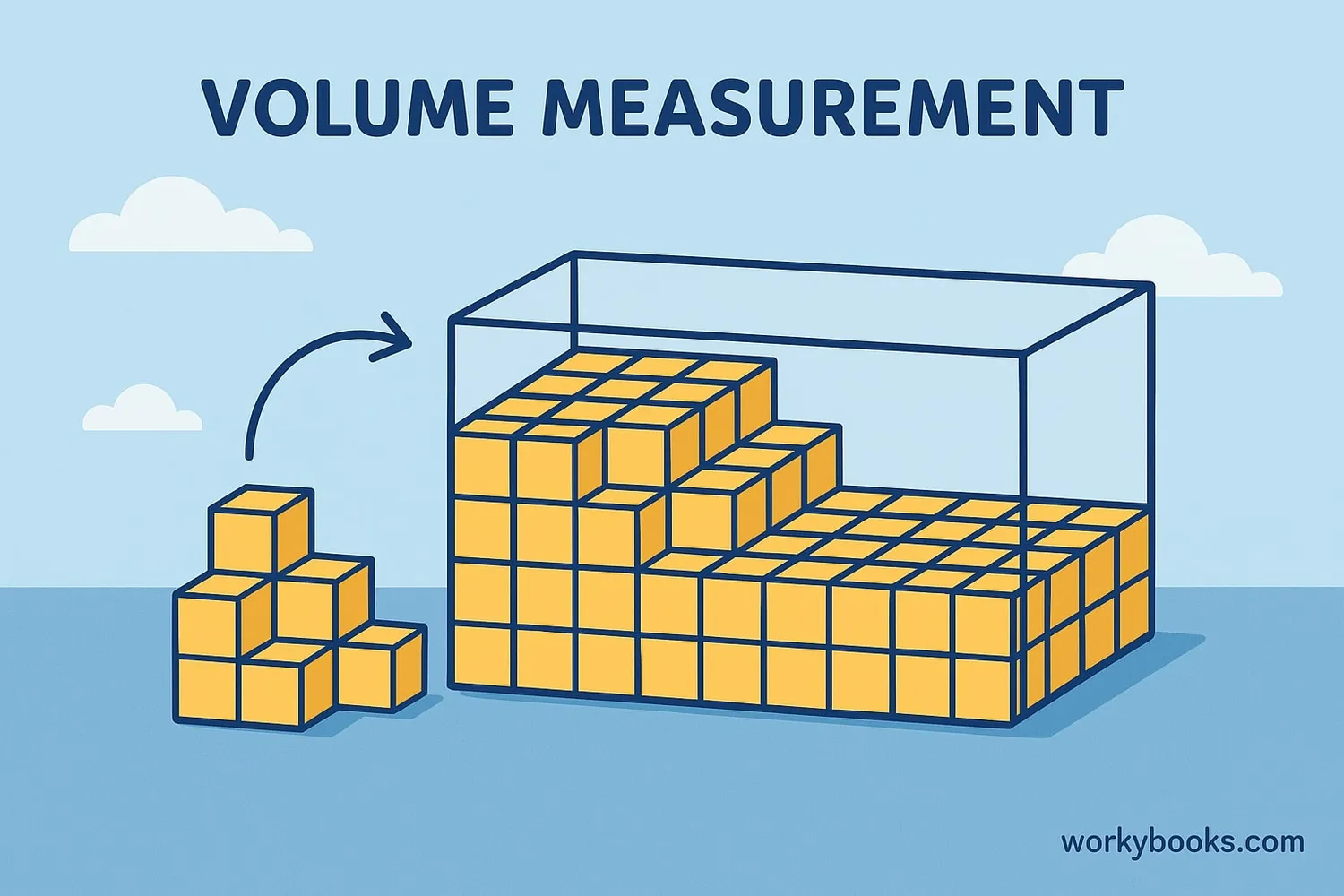
There are two main ways to measure volume:
1. Using Unit Cubes: We can fill a shape with small cubes of the same size. The number of cubes that fit inside tells us the volume.
2. Using Formulas: For regular shapes, we can use mathematical formulas to calculate volume.
We measure volume in cubic units. Some common units include:
- Cubic centimeters (cm³)
- Cubic meters (m³)
- Cubic inches (in³)
- Liters (L) and milliliters (mL) for liquids
When we measure volume with unit cubes, we count how many cubes fit in one layer, then multiply by how many layers tall the object is.
Remember
1 milliliter (mL) = 1 cubic centimeter (cm³). This relationship helps us connect liquid measurements to space measurements.
Volume Formulas
Cube
s = side length
Rectangular Prism
l = length, w = width, h = height
Cylinder
r = radius, h = height
Sphere
r = radius
To use these formulas:
1. Identify the shape of the object
2. Measure the required dimensions (side length, radius, height)
3. Plug the measurements into the formula
4. Calculate the volume
Remember that π (pi) is approximately 3.14. For cylinders and spheres, we multiply by π because these shapes have curved surfaces.
Volume Examples

Let's practice volume calculation with real-world examples:
Example 1: Cube-Shaped Box
A small jewelry box measures 5 cm on each side. What is its volume?
Solution: V = s³ = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125 cm³
Example 2: Rectangular Fish Tank
A fish tank is 30 cm long, 20 cm wide, and 25 cm high. How much water can it hold?
Solution: V = l × w × h = 30 × 20 × 25 = 15,000 cm³ or 15 liters
Example 3: Soda Can
A soda can has a radius of 3 cm and height of 12 cm. What is its volume?
Solution: V = πr²h = 3.14 × 3² × 12 ≈ 3.14 × 9 × 12 ≈ 339 cm³
Example 4: Basketball
A basketball has a radius of 12 cm. What is its volume?
Solution: V = ⁴⁄₃πr³ = ⁴⁄₃ × 3.14 × 12³ ≈ ⁴⁄₃ × 3.14 × 1728 ≈ 7,234 cm³
Practice Tip
Look for rectangular prisms around you - books, boxes, rooms. Measure their dimensions and calculate their volume!
Volume Practice Quiz
Test your volume knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about volume:
Volume Trivia
Discover interesting facts about volume and measurement:
Ancient Volume Measurement
The ancient Egyptians measured volume using units called "hekat" (about 4.8 liters). They developed complex formulas to calculate volumes of granaries and pyramids.
Archimedes' Principle
The famous scientist Archimedes discovered how to measure volume while taking a bath. He realized that the volume of water displaced equals the volume of the submerged object.
Largest Volume on Earth
The Pacific Ocean has the largest volume of any single feature on Earth - about 710 million cubic kilometers! That's enough to fill 280 billion Olympic-sized swimming pools.
Smallest Measured Volume
Scientists can measure volumes as small as a cubic femtometer (10⁻⁴⁵ m³). That's one million times smaller than a proton!





