Zero - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the power of zero in mathematics with easy explanations and activities
What is Zero?
Zero is a special number that represents "nothing" or "no quantity." It's the starting point for counting and a placeholder in our number system.
Zero is a whole number and an integer. It's neither positive nor negative. When we count objects, if there are none, we say there are zero objects. For example:
• If you have 3 apples and eat all 3, you have zero apples left.
• If a basket is empty, it contains zero fruits.
• The temperature can be zero degrees, which is very cold!
Zero helps us understand that "nothing" is a quantity we can measure and work with mathematically.
Key Concept
Zero is the only integer that is neither positive nor negative. It serves as the boundary between positive and negative numbers.
Zero on the Number Line
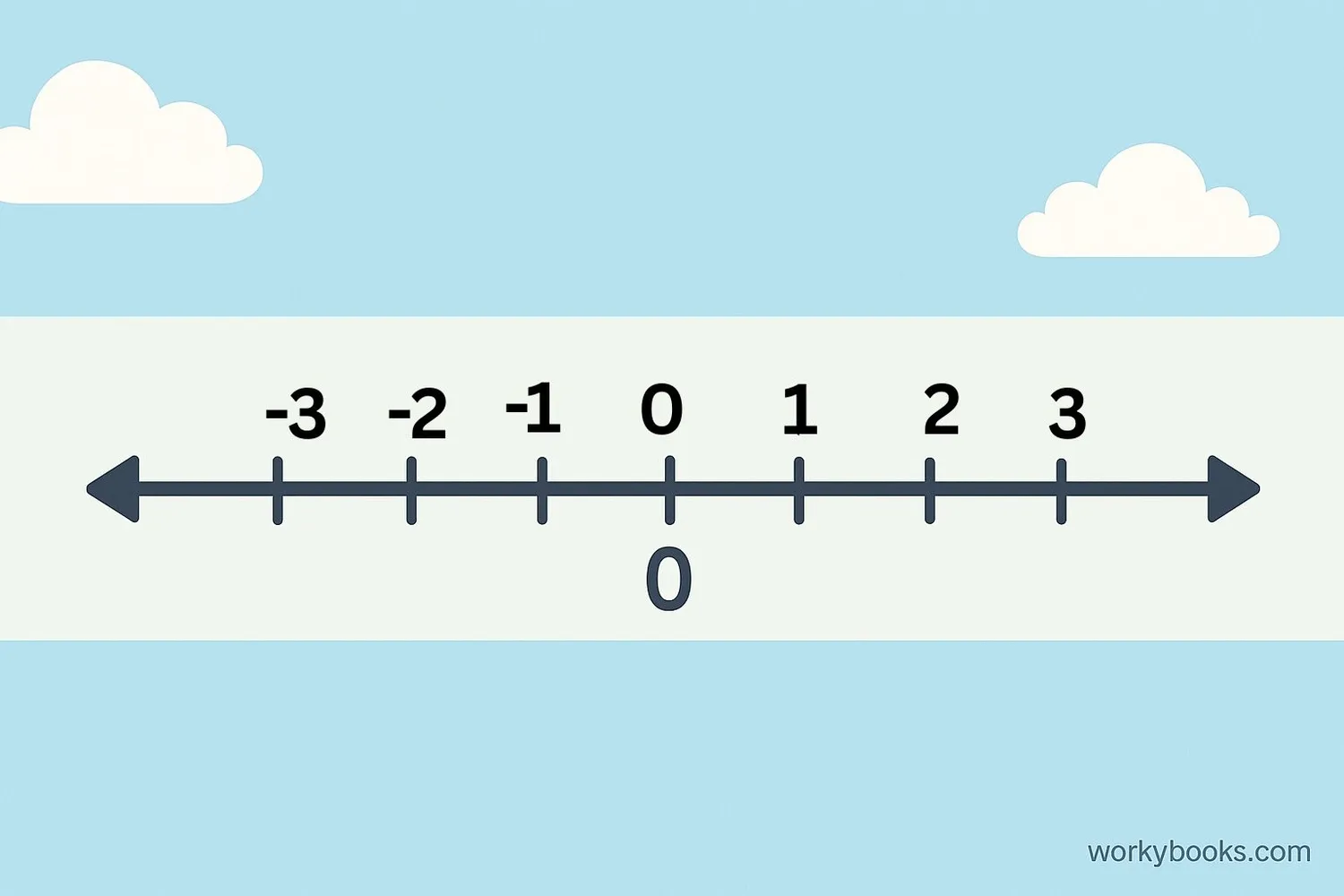
The number line is a straight line where numbers are placed at equal intervals. Zero is exactly in the middle of the number line, separating positive numbers (to the right) from negative numbers (to the left).
Here's a simple number line:
Important facts about zero on the number line:
• Zero is the reference point for all numbers
• The distance from zero to a number is called its absolute value
• Zero has an absolute value of zero
• Numbers to the right of zero are positive
• Numbers to the left of zero are negative
Remember
Zero is neither positive nor negative. It is the boundary between positive and negative numbers.
Zero in Place Value
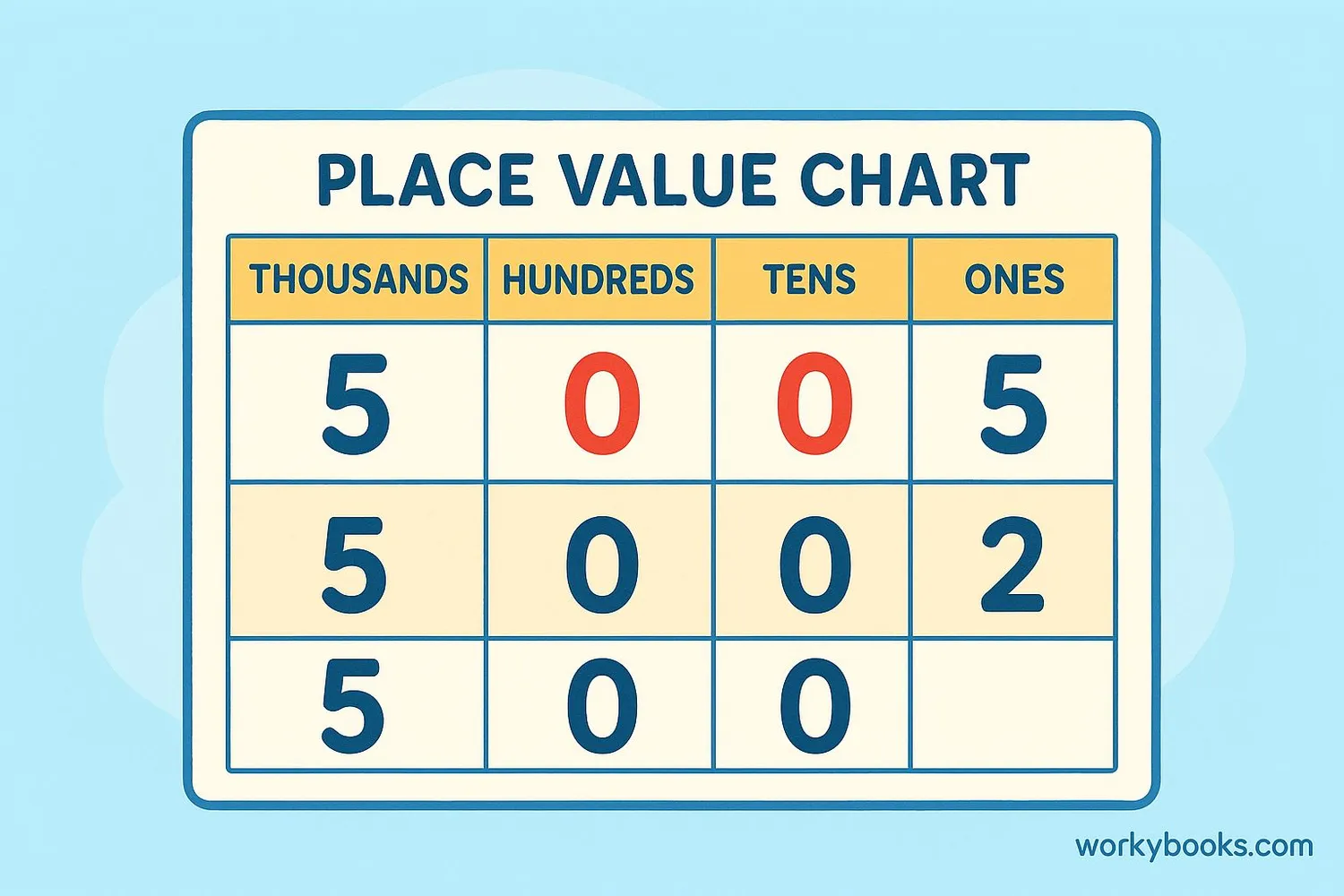
In our number system, zero plays a crucial role as a placeholder. It helps us write numbers correctly by showing that a particular place has no value.
For example:
• In the number 205, the zero tells us there are no tens
• In 5002, the zeros show there are no hundreds or tens
• Without zero, 205 would look like 25, which is a completely different number!
This is why zero is essential in our base-10 number system. It allows us to represent large numbers efficiently.
Place Value Example
The zeros show that there are no hundreds and no tens in this number.
Place Value Tip
Zeros at the beginning of a number (like 005) don't change the value, but zeros in the middle or end are important placeholders.
Zero in Mathematical Operations
Zero has special properties when we use it in mathematical operations:
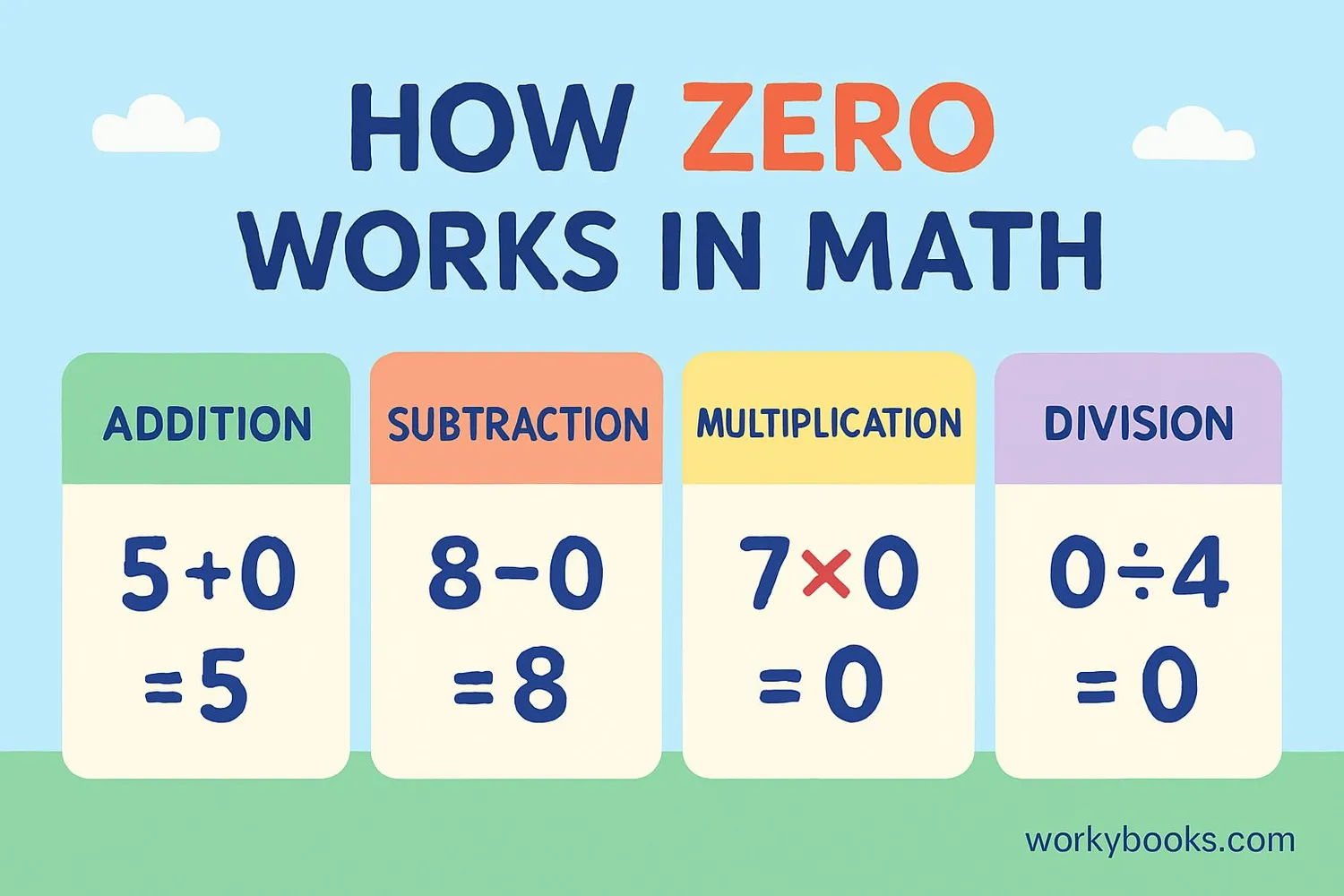
Addition: When you add zero to any number, the number stays the same.
Example: 7 + 0 = 7
Subtraction: When you subtract zero from a number, the number stays the same. When you subtract a number from itself, you get zero.
Example: 9 - 0 = 9 and 5 - 5 = 0
Multiplication: When you multiply any number by zero, you get zero.
Example: 6 × 0 = 0
Division: You can divide zero by any number (except zero), and you get zero. But you cannot divide a number by zero - it's undefined!
Example: 0 ÷ 4 = 0 but 4 ÷ 0 is undefined
Important Rule
Division by zero is impossible. You can't split something into zero groups!
Zero Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about zero with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about zero:
Zero Trivia
Discover interesting facts about zero:
Historical Importance
The ancient Mayans independently developed the concept of zero around 350 CE. Their zero symbol looked like a shell and was used in their sophisticated calendar system.
Roman Numerals
The Romans didn't have a symbol for zero. This made their number system less efficient for mathematics and calculations compared to systems that included zero.
Zero Gravity
In space, astronauts experience "zero gravity" or microgravity. This doesn't mean there's no gravity - it means they're in free fall around the Earth, creating the sensation of weightlessness.
Mathematical Properties
Zero is the only number that can't be represented in Roman numerals. It's also the only integer that's neither prime nor composite.





