Chemical Equations - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how scientists write and balance chemical reactions!
What is a Chemical Equation?
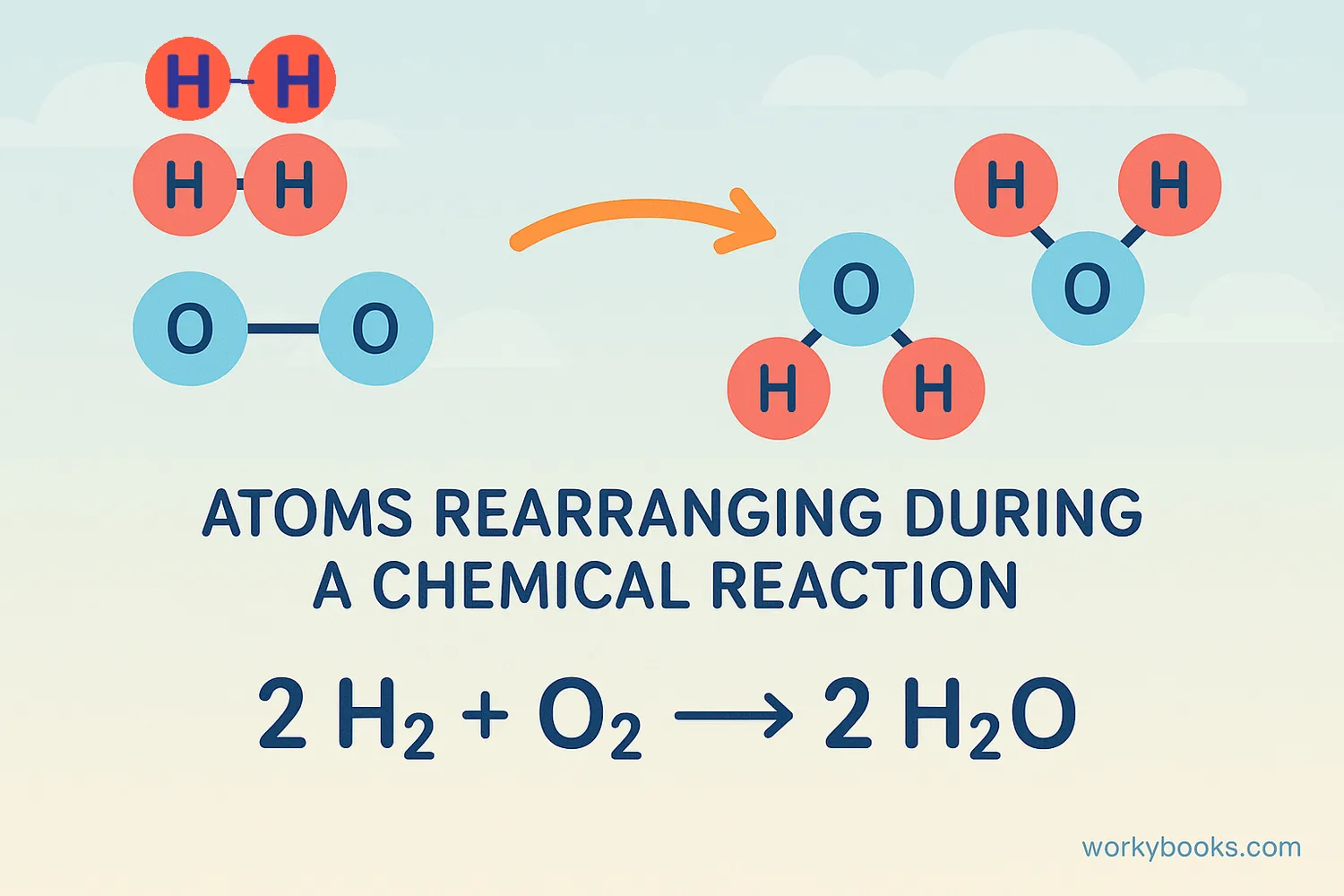
A chemical equation is like a recipe for chemistry! It's a special way scientists write down what happens during a chemical reaction. Chemical equations show which substances you start with (reactants) and what new substances you end up with (products).
Think of it like baking cookies: You start with flour, sugar, and eggs (reactants), and after mixing and baking, you get cookies (products)! Chemical equations use symbols and formulas to show these changes in a precise, scientific way.
Science Fact!
The first chemical equations were developed in the 1600s, but the modern system we use today was created in the 1800s by Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius.
Parts of a Chemical Equation
Every chemical equation has three main parts:
Reactants
The starting substances (on the left side)
Arrow
Means "yields" or "produces"
Products
The new substances formed (on the right side)
Here's an example showing each part:
Symbol Key
+ means "and" or "reacts with" | → means "yields" or "produces" | (s) = solid | (l) = liquid | (g) = gas | (aq) = dissolved in water
Writing Chemical Equations
Writing chemical equations follows specific steps to make sure they're accurate and easy to understand:
Identify Reactants
What substances are you starting with?
Identify Products
What new substances are formed?
Write Formulas
Use correct chemical formulas
Add Coefficients
Place numbers to balance atoms
Add State Symbols
(s), (l), (g), or (aq)
Example: When hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas, they form water. The equation is:
Practice Writing
Try writing the equation for photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide and water produce glucose and oxygen.
Balancing Chemical Equations
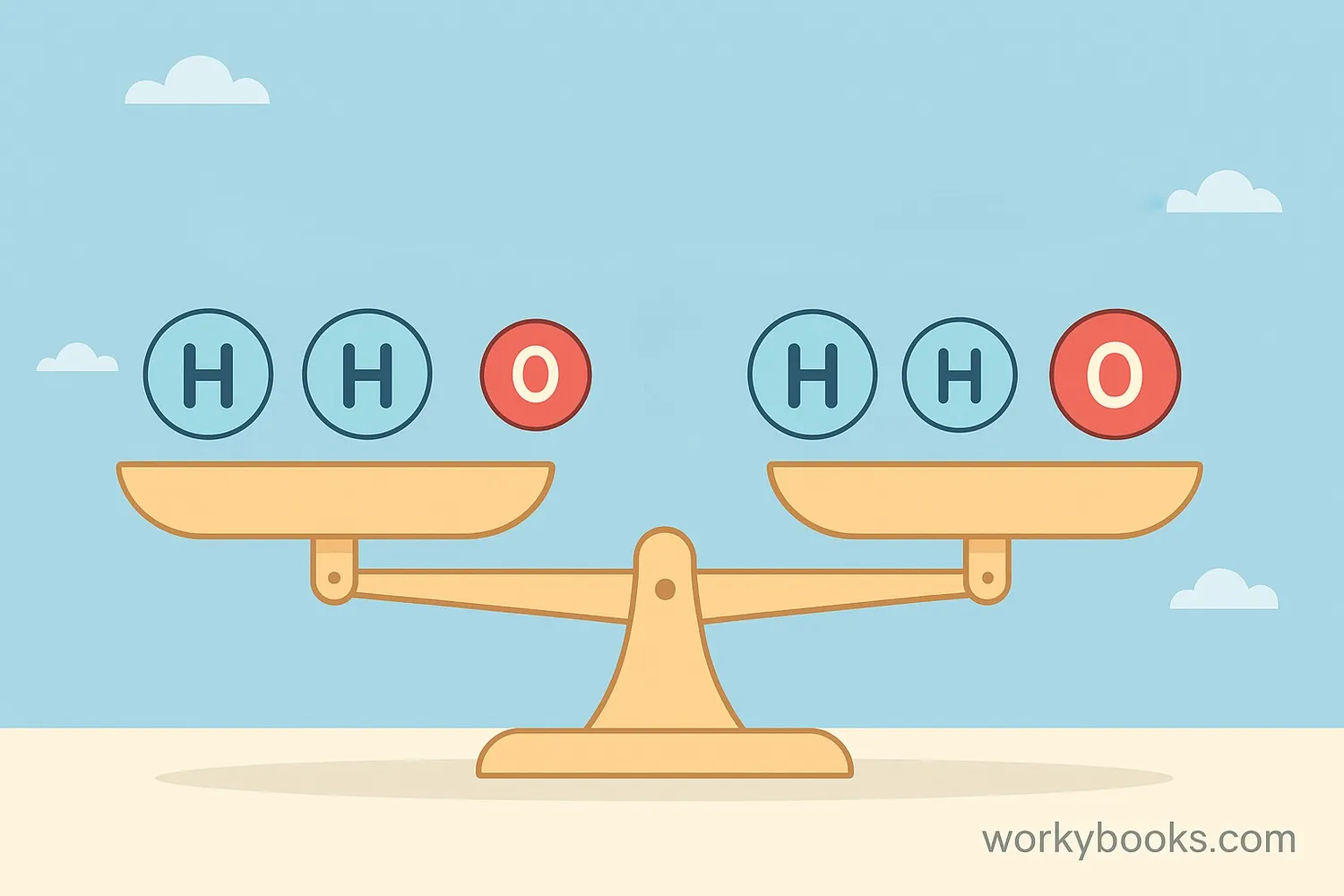
Balancing equations is like solving a puzzle! It makes sure that no atoms are created or destroyed during a reaction (Law of Conservation of Mass). We use coefficients (numbers in front) to balance the atoms on both sides.
Count Atoms
List atoms on both sides
Start with Complex Molecules
Balance them first
Use Coefficients
Add numbers in front of formulas
Never Change Subscripts
That would change the substance!
Check All Atoms
Ensure equal numbers on both sides
Example: Let's balance the equation for water formation:
Balancing Trick
Balance oxygen and hydrogen last since they often appear in multiple compounds!
Types of Chemical Equations
Chemical equations can represent different types of reactions:
Synthesis
A + B → AB (Combining substances)
Decomposition
AB → A + B (Breaking down)
Single Replacement
A + BC → AC + B (Swapping elements)
Double Replacement
AB + CD → AD + CB (Swapping partners)
Combustion
Fuel + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O (Burning)
Photosynthesis Example: This essential life process is a complex chemical reaction:
Reaction Insight
Photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration! Together they form the carbon cycle that sustains life on Earth.
Chemical Equations Quiz
Test your knowledge with this chemical equations quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about chemical equations:
Chemical Equations Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about chemical equations!
Ancient Equations
The first known chemical equations were written by ancient Egyptian alchemists around 2000 BCE! They used symbols for metals and minerals in their formulas.
Space Chemistry
NASA scientists use chemical equations to create rocket fuel! The space shuttle main engines used: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O + energy, producing enough power to lift 4.5 million pounds!
Record Equation
The longest chemical equation ever written has over 1,000 atoms on each side! It describes a complex biochemical process in human cells.
Life Equation
Your body performs about 37 billion billion (3.7×10¹⁹) chemical reactions every second! That's more reactions per second than there are stars in the observable universe!





