Classification of Matter - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how scientists organize and categorize all the different types of matter around us!
What is Matter?

Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Everything you can see, touch, or feel is made of matter - from the air you breathe to the ground you walk on!
Scientists classify matter based on its composition (what it's made of) and properties (its characteristics). Understanding how matter is organized helps scientists predict how different materials will behave and interact with each other.
Matter Fact!
Over 99% of the visible universe is made of matter! The rest is made of something called dark matter and dark energy.
States of Matter
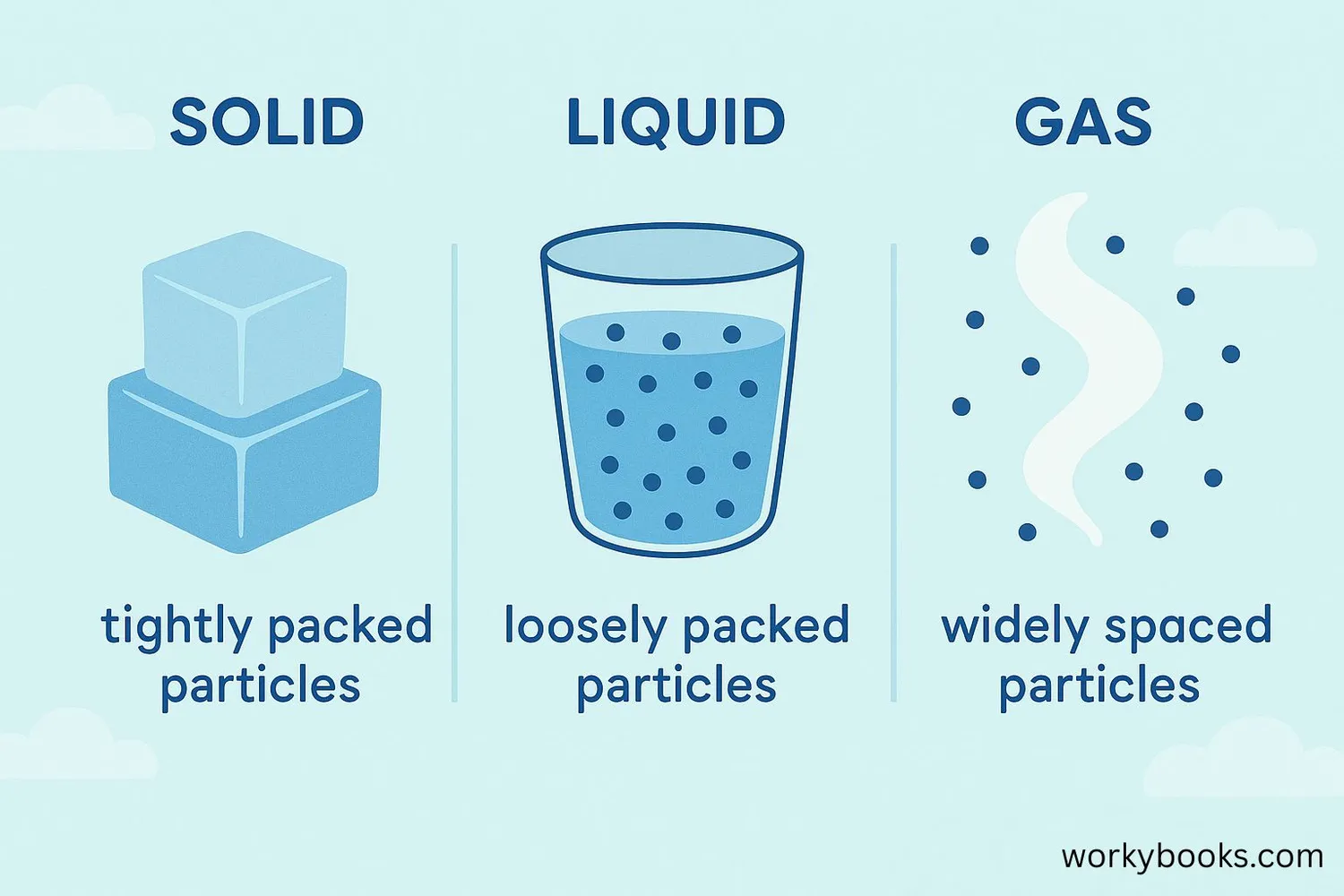
Matter exists in different forms called states. The three most common states are:
Solid
Has definite shape and volume. Particles are tightly packed and vibrate in place.
Liquid
Has definite volume but takes the shape of its container. Particles can slide past each other.
Gas
No definite shape or volume. Particles move freely and spread out to fill their container.
Matter can change from one state to another through processes like melting, freezing, evaporation, and condensation. These changes are physical changes because the substance itself doesn't change - just its form.
Plasma - The Fourth State
There's actually a fourth state called plasma! It's what stars are made of and is the most common state of matter in the universe.
Pure Substances vs Mixtures
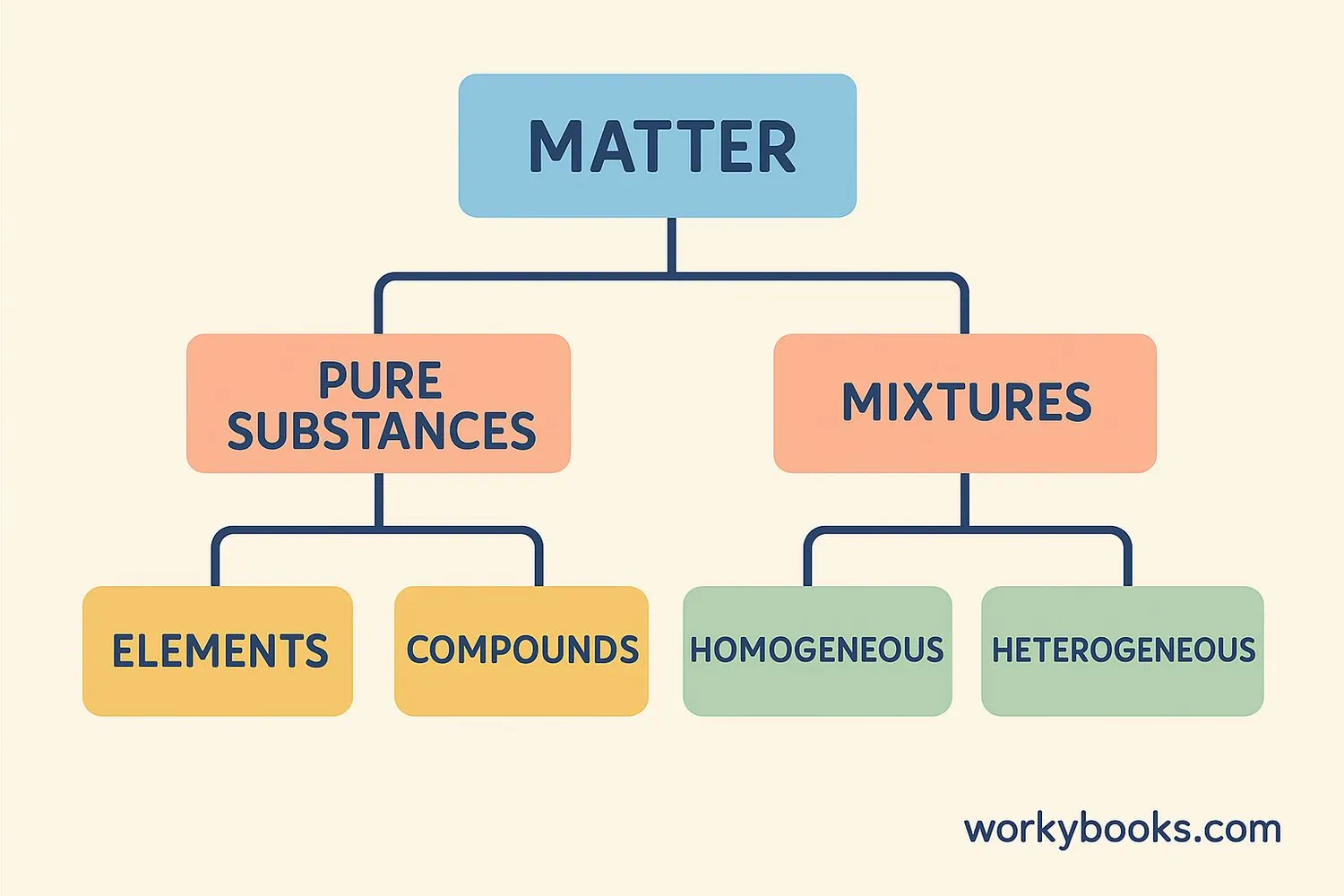
One of the main ways scientists classify matter is by whether it's a pure substance or a mixture:
Pure Substances
Have a fixed composition and the same properties throughout. Examples: pure water, gold, oxygen gas.
Mixtures
Contain two or more substances physically combined. Examples: salad, air, salt water.
Mixtures can be further classified as:
Homogeneous mixtures (also called solutions) have the same composition throughout. You can't see the different parts. Examples: air, salt water, brass.
Heterogeneous mixtures have visibly different parts. Examples: trail mix, salad, oil and water.
Elements and Compounds
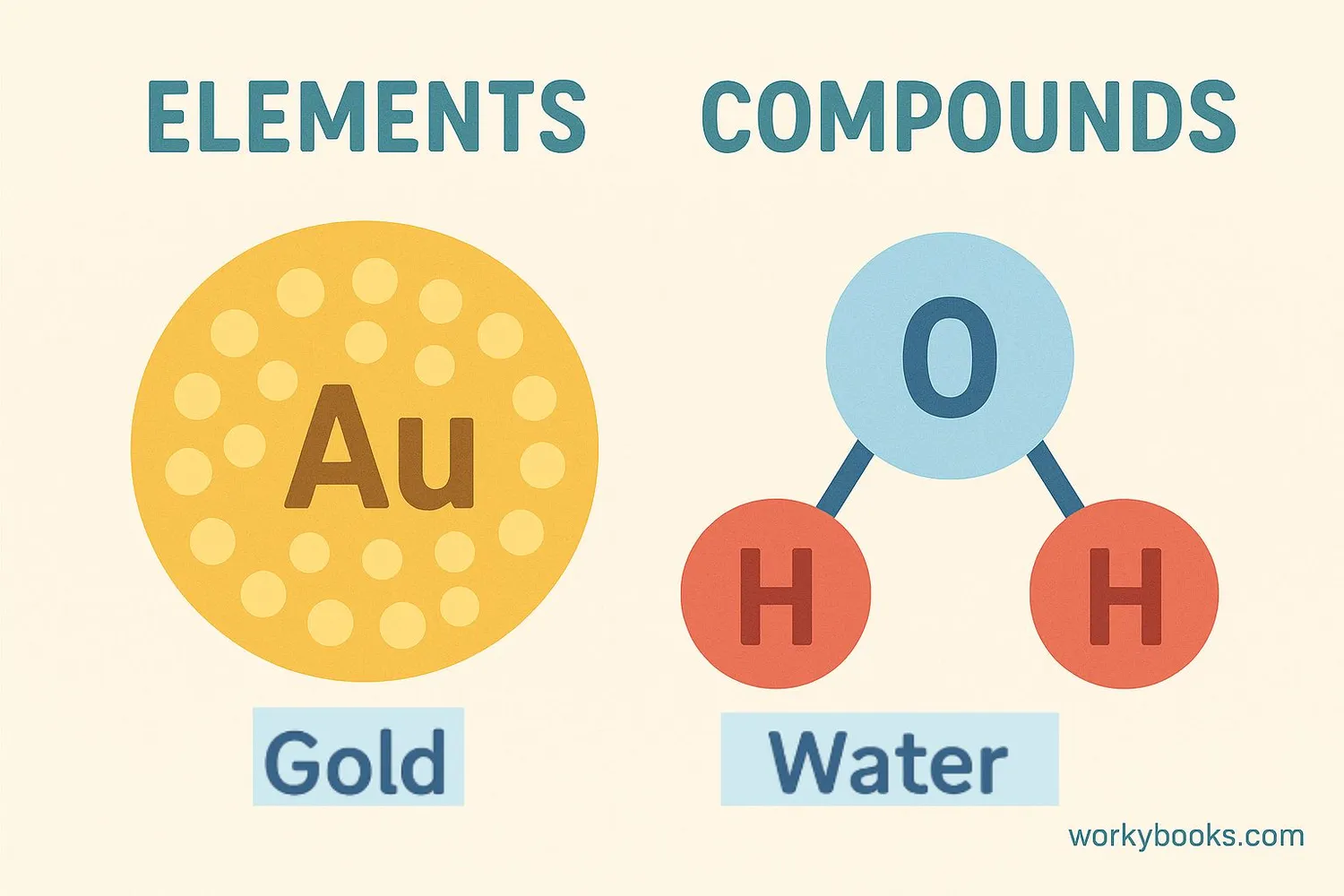
Pure substances can be further divided into elements and compounds:
Elements
The simplest form of matter made of only one type of atom. Cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples: oxygen, gold, carbon.
Compounds
Made of two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. Examples: water (H₂O), salt (NaCl), sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁).
The main difference between compounds and mixtures is that compounds are chemically combined while mixtures are physically combined. Compounds have properties different from their component elements, while mixtures keep the properties of their components.
Element Fact!
There are 118 known elements, but only about 90 occur naturally on Earth. The rest are created in laboratories.
Matter Classification Quiz
Test your knowledge about the classification of matter with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the classification of matter:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about matter!
Most Abundant Element
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, making up about 75% of all matter! On Earth, oxygen is the most abundant element in the crust.
Fourth State of Matter
Besides solid, liquid, and gas, there's a fourth state called plasma! Plasma is what stars are made of and is the most common state of matter in the universe.
Mostly Empty Space
Atoms are mostly empty space! If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be the size of a marble in the center, and the electrons would be like tiny specks in the outer seats.
Special Water Property
Water is special because it's less dense as a solid than as a liquid! That's why ice floats on water. Most substances are denser in their solid form.





