Electric Circuits - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how electricity flows through paths to power our world!
What is an Electric Circuit?
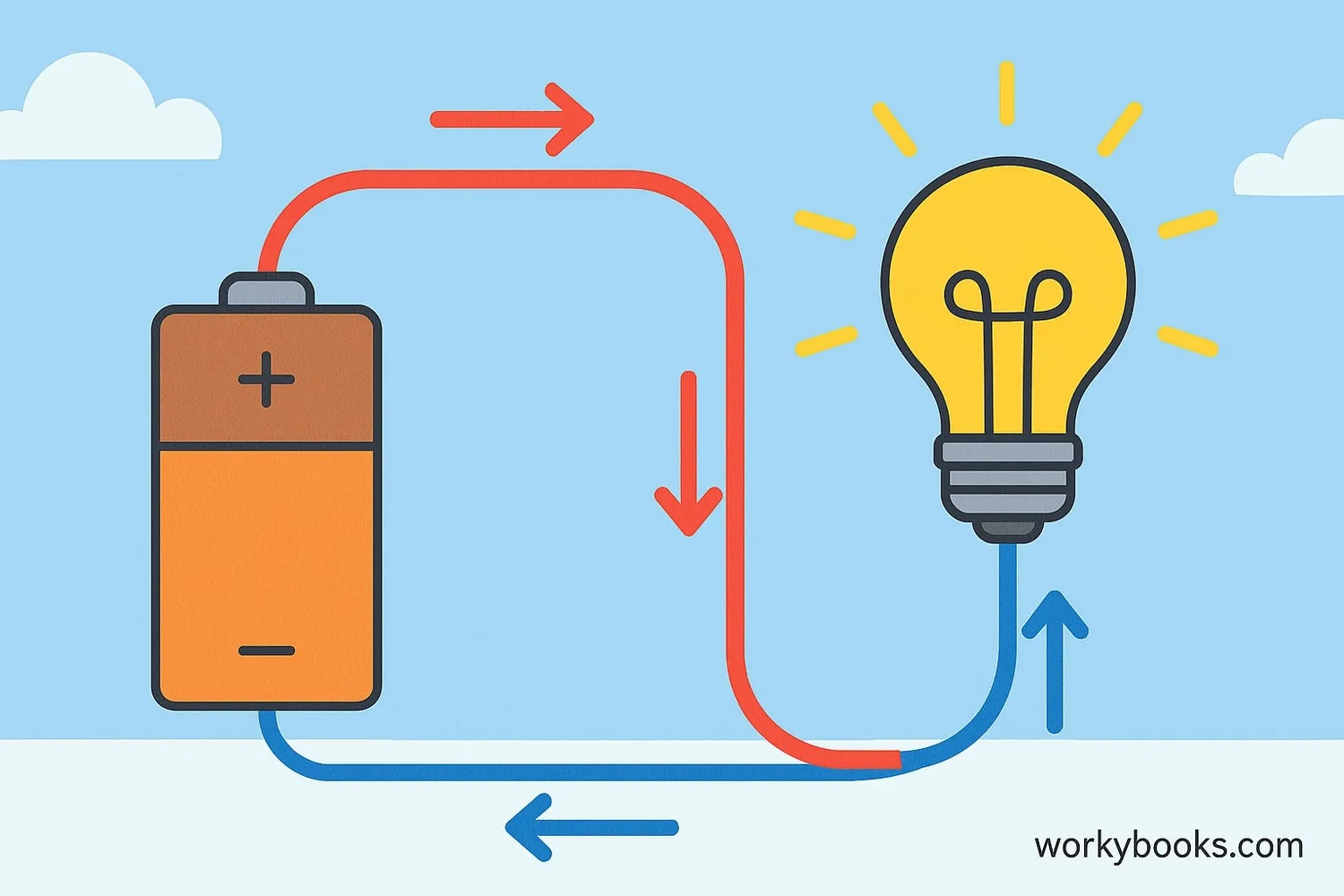
An electric circuit is a complete path that allows electricity to flow. It's like a looped road that electricity travels along to power devices like lights, phones, and computers.
Think of electricity as water flowing through pipes. The battery is like a pump that pushes the water. The wires are the pipes that carry the water. The light bulb is like a water wheel that uses the flowing water to do work. For the wheel to turn, the water must flow in a complete circle from the pump, through the pipes, to the wheel, and back to the pump. Similarly, for a light bulb to light up, electricity must flow in a complete circle from the battery, through the wires, to the bulb, and back to the battery.
Key Concept: Closed vs Open Circuits
A circuit must be closed (complete loop) for electricity to flow. If there's a break anywhere in the loop, it's an open circuit and electricity stops flowing.
Parts of an Electric Circuit
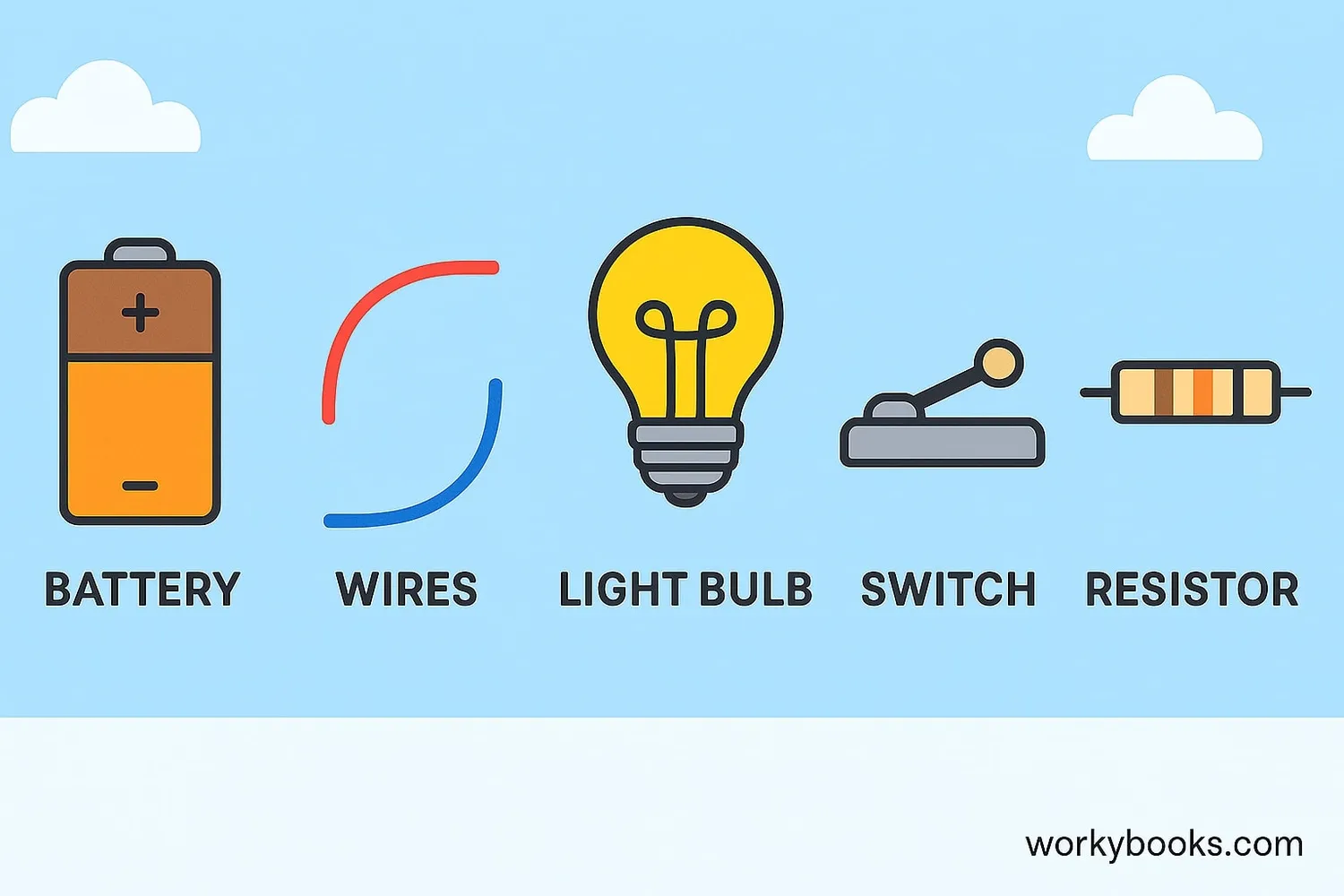
Every circuit has essential parts that work together to make electricity flow and do useful work. Here are the main components:
Power Source
Provides electrical energy (battery, solar cell, outlet)
Conductors
Wires that carry electricity (usually copper)
Load
Device that uses electricity (light bulb, motor, buzzer)
Switch
Controls the flow of electricity (on/off)
Some circuits also include additional components like resistors (limit electricity flow), capacitors (store electricity), and diodes (make electricity flow in one direction only).
Safety First!
Never experiment with electricity from wall outlets - it's very dangerous! Always use batteries when making circuits.
Types of Electric Circuits
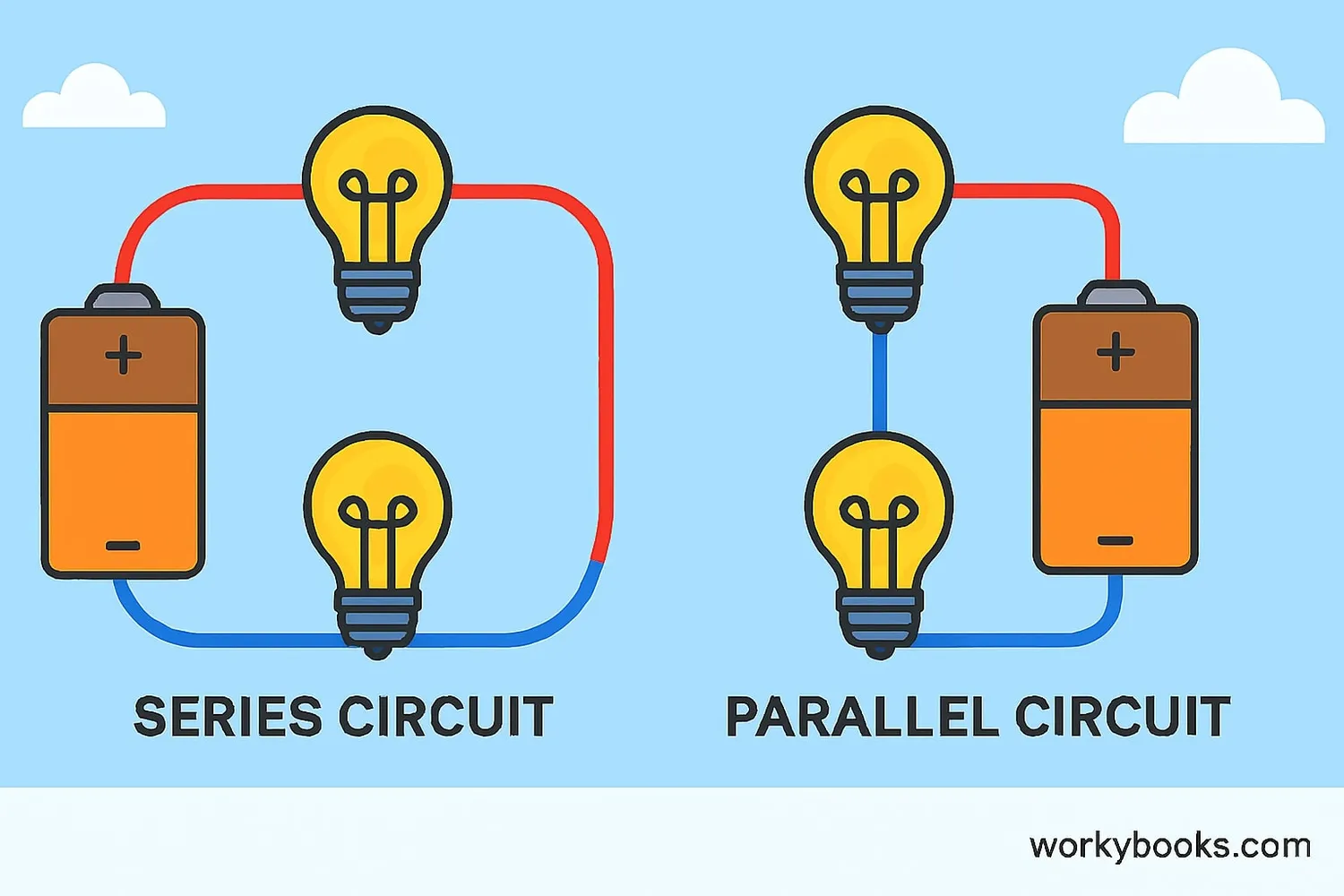
Circuits can be arranged in different ways to control how electricity flows. The two main types are:
Series Circuit
Components are connected in a single path. Electricity flows through one component to the next.
Parallel Circuit
Components have their own separate paths. Electricity can flow through multiple paths at once.
Series Circuit Example: Old Christmas tree lights where if one bulb burns out, all go out.
Parallel Circuit Example: Lights in your home where if one bulb burns out, others stay lit.
Circuit Design Matters!
Homes use parallel circuits so appliances work independently. Cars use series circuits for some lighting systems.
Circuit Diagrams
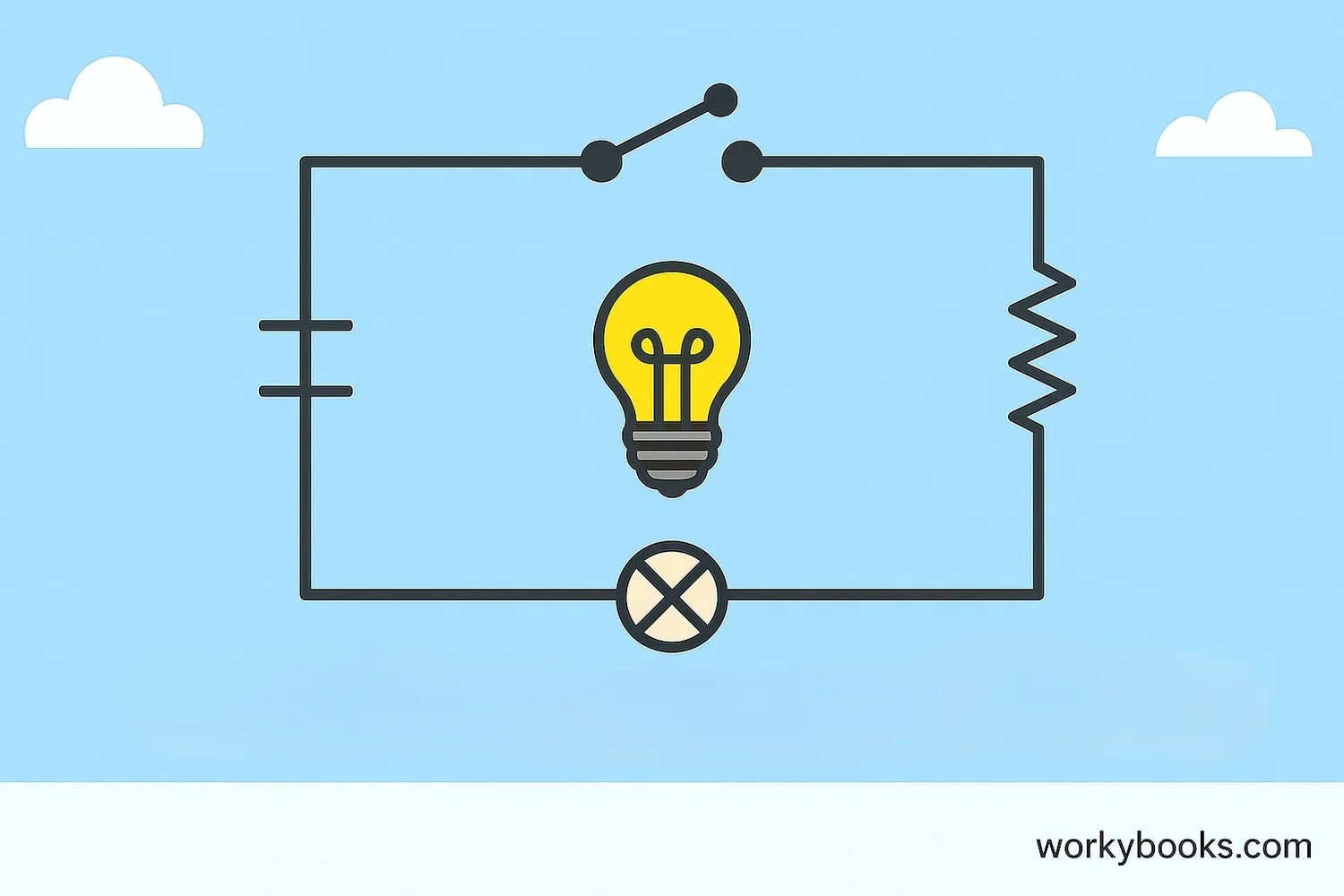
Engineers and scientists use special diagrams with symbols to represent circuits. This universal "language" helps people understand circuits anywhere in the world. Here are some common symbols:
| Component | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | | | (long line positive) | Provides electrical energy |
| Bulb | ⨀ with X inside | Converts electricity to light |
| Switch | —o— (open) —|— (closed) | Controls current flow |
| Resistor | —/\/\/— | Limits current flow |
| Wire | ——— | Conducts electricity |
When you look at a circuit diagram, remember that the lines represent wires connecting components. The symbols show exactly what each part does, making it easy to understand how the circuit works.
Electric Circuits Quiz
Test your circuit knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about electric circuits:
Circuit Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about electric circuits:
Speed of Electricity
Electricity travels through wires at nearly the speed of light - about 670 million miles per hour! That's why lights turn on instantly when you flip a switch.
Human Circuit
Your body can complete a circuit! That's why you might get a shock if you touch a live wire - electricity flows through you to reach the ground.
Historical Circuit
The first electric circuit was invented by Alessandro Volta in 1800. His "voltaic pile" was the first battery that could provide continuous electric current.
Tiny Circuits
A modern computer chip contains billions of microscopic circuits. Some are just 5 nanometers wide - that's 20,000 times thinner than a human hair!





