Electromagnets - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how electricity creates temporary magnets that power our world!
What is an Electromagnet?
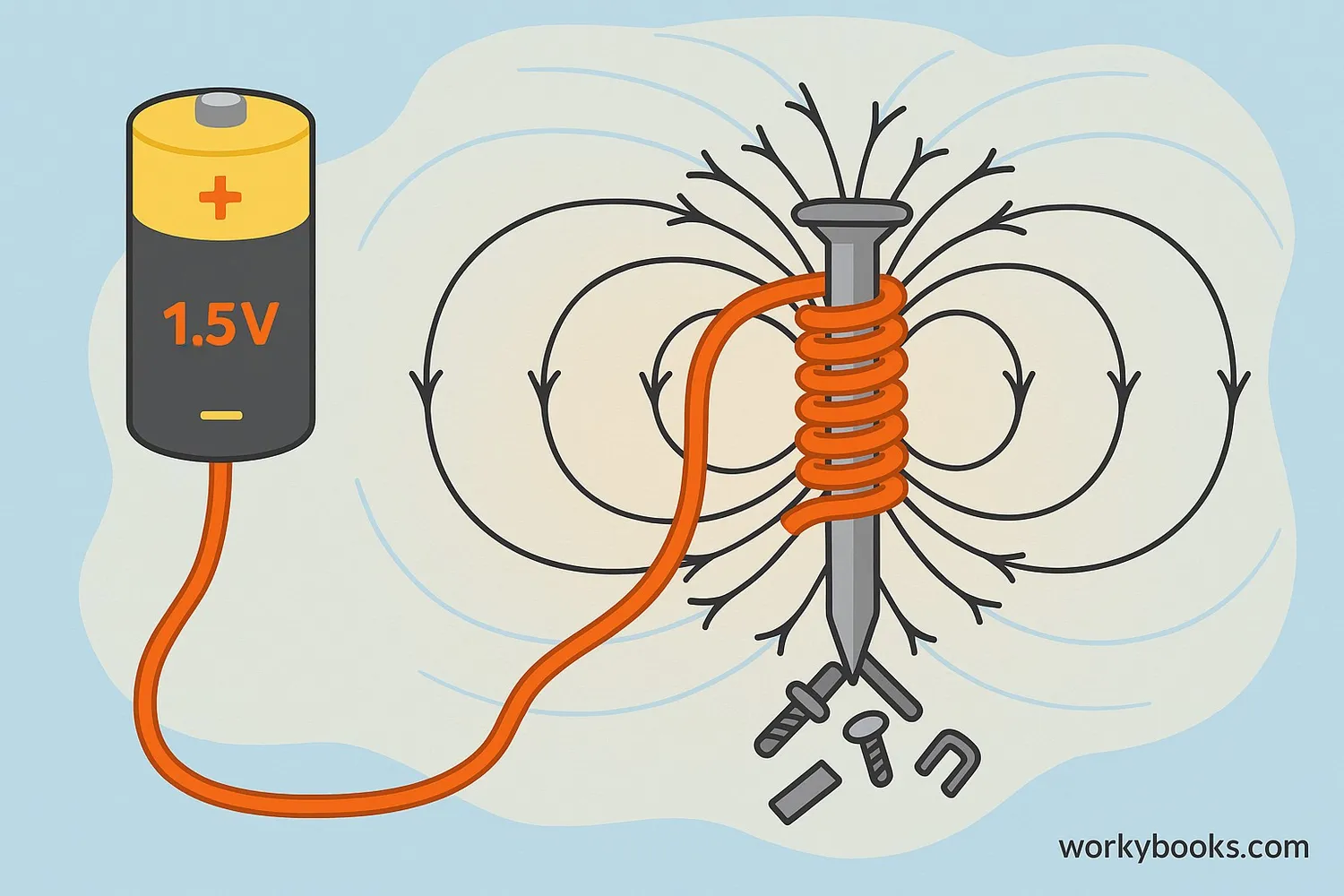
An electromagnet is a special type of magnet that only works when electricity flows through it! Unlike regular magnets that are always magnetic, electromagnets can be turned on and off by controlling the electric current.
Think of it like magic: when you send electricity through a wire, it creates an invisible magnetic field around the wire. But if you wrap that wire into a coil around an iron core (like a nail), the magnetic field becomes much stronger! This temporary magnet is called an electromagnet.
Science Fact!
The strength of an electromagnet depends on three things: the amount of electric current, the number of wire coils, and the material of the core!
How Electromagnets Work
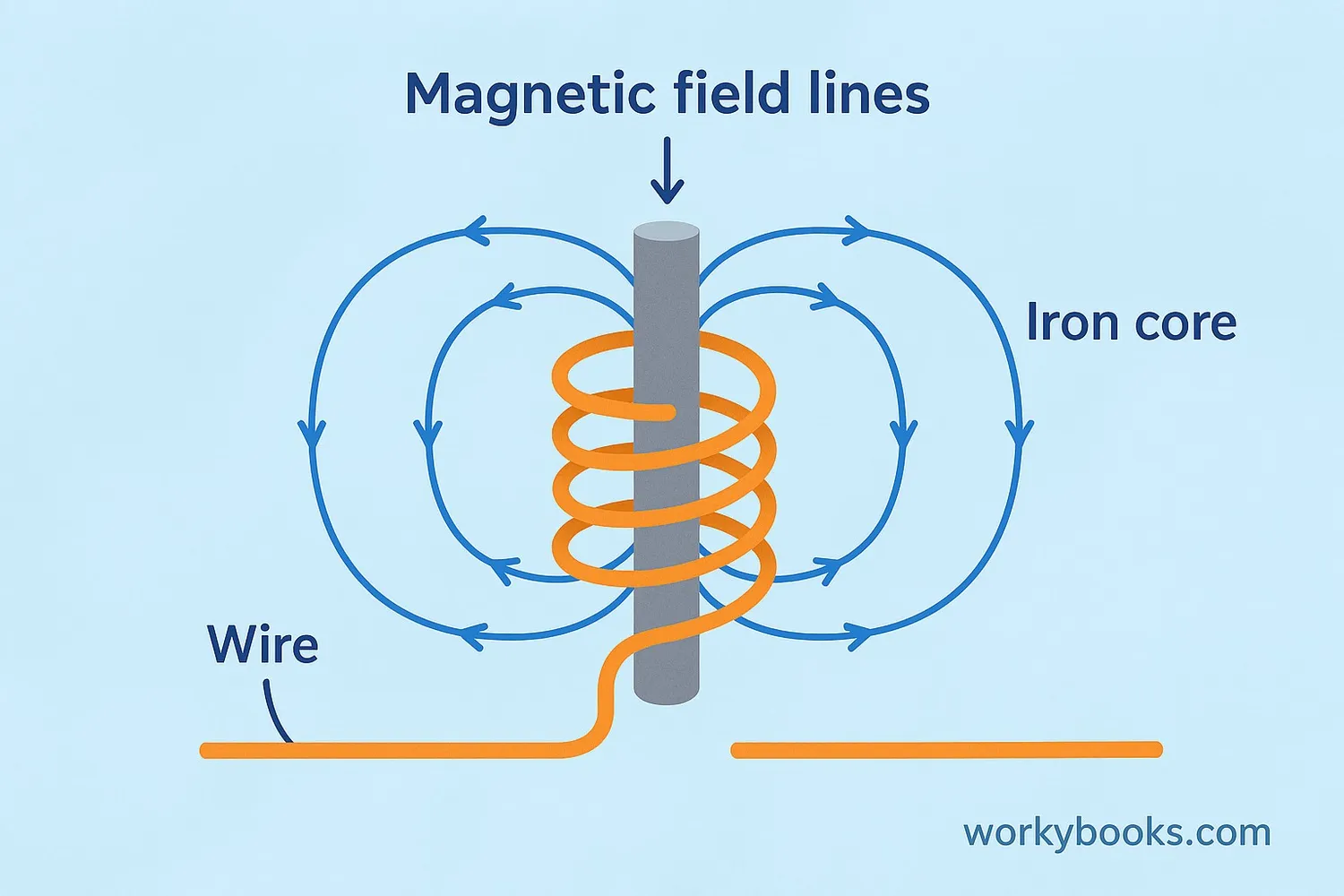
Electromagnets work because of a scientific principle called electromagnetism - the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Here's how they work step by step:
Electric Current
Electricity flows through a wire
Magnetic Field
The current creates a magnetic field around the wire
Solenoid Coil
Wrapping the wire into a coil strengthens the magnetic field
Iron Core
Adding an iron core inside the coil makes the magnet even stronger
Magnetic Force
The electromagnet attracts metal objects when electricity flows
This amazing discovery was made by scientist Michael Faraday in 1831. His law of induction explains how electricity can create magnetism and how magnetism can create electricity. This principle powers most of our modern technology!
Faraday's Law
Michael Faraday discovered that changing a magnetic field creates an electric current - the principle behind electric generators!
Why Electromagnets Matter
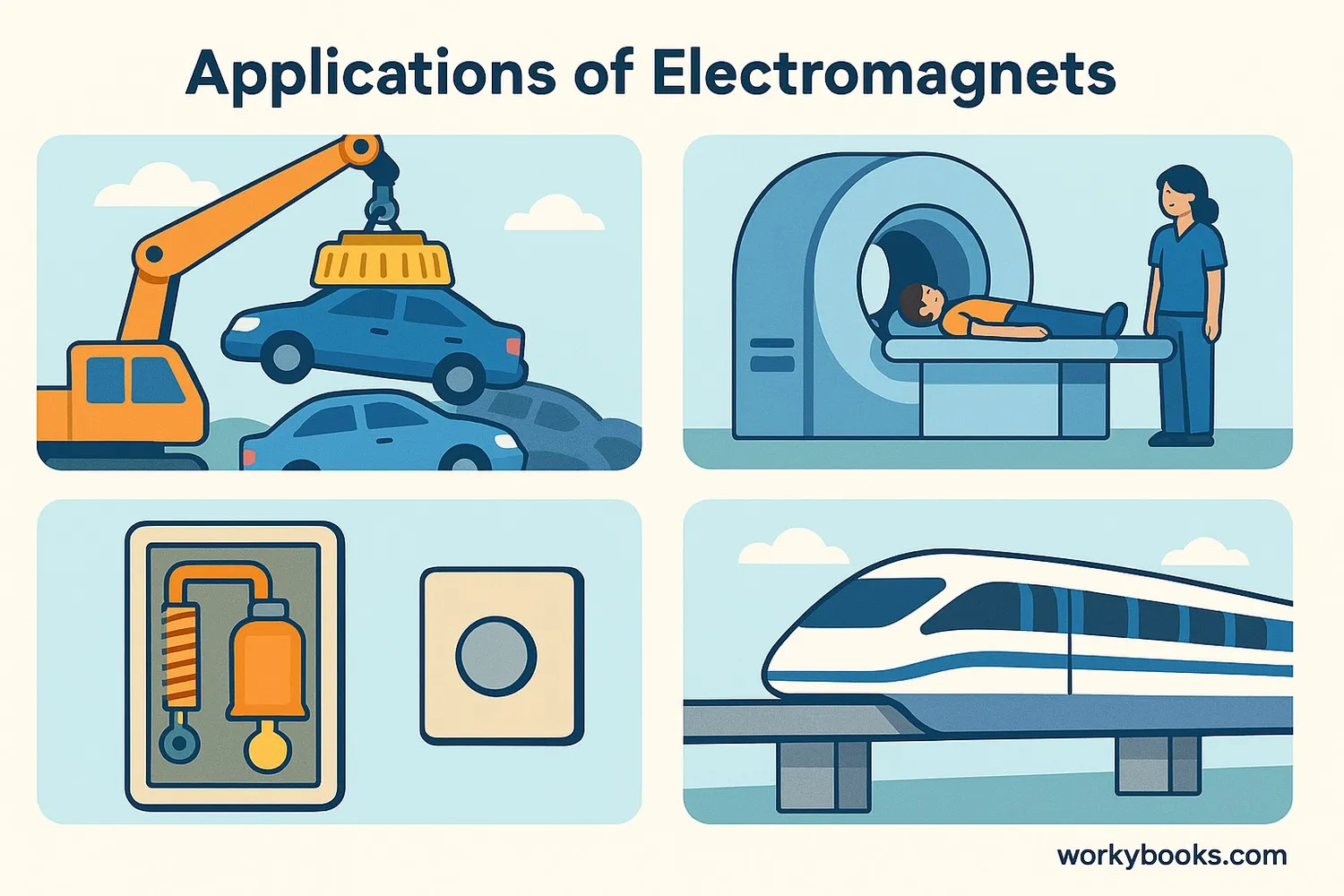
Electromagnets are everywhere in our modern world! Because we can turn them on and off, they're much more useful than permanent magnets. Here are some important ways we use electromagnets:
Scrapyard Cranes
Giant electromagnets lift and move heavy metal objects
Maglev Trains
Magnetic levitation allows trains to float above tracks
Medical MRI
Powerful electromagnets create images inside the body
Other important uses include:
• Electric motors in appliances and vehicles
• Speakers and headphones
• Doorbells and relays
• Credit card magnetic strips
• Particle accelerators for scientific research
Without electromagnets, we wouldn't have many modern technologies we rely on every day!
Electromagnet Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about electromagnets with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about electromagnets:
Electromagnet Science Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about electromagnets!
Historical Discovery
The first electromagnet was created in 1825 by William Sturgeon. It could lift 9 pounds with just 7 ounces of iron wrapped with wire - 20 times its own weight!
World's Strongest
The world's strongest electromagnet is at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory in Florida. It produces a magnetic field 1.2 million times stronger than Earth's!
Medical Marvel
MRI machines use powerful electromagnets 30,000 to 60,000 times stronger than Earth's magnetic field to create detailed images of our bodies!
Floating Trains
Maglev trains use electromagnets to levitate above the tracks, eliminating friction. The fastest maglev train reaches 375 mph - faster than most airplanes!





