Gamma Radiation - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the powerful world of gamma rays and their role in our universe
What is Gamma Radiation?
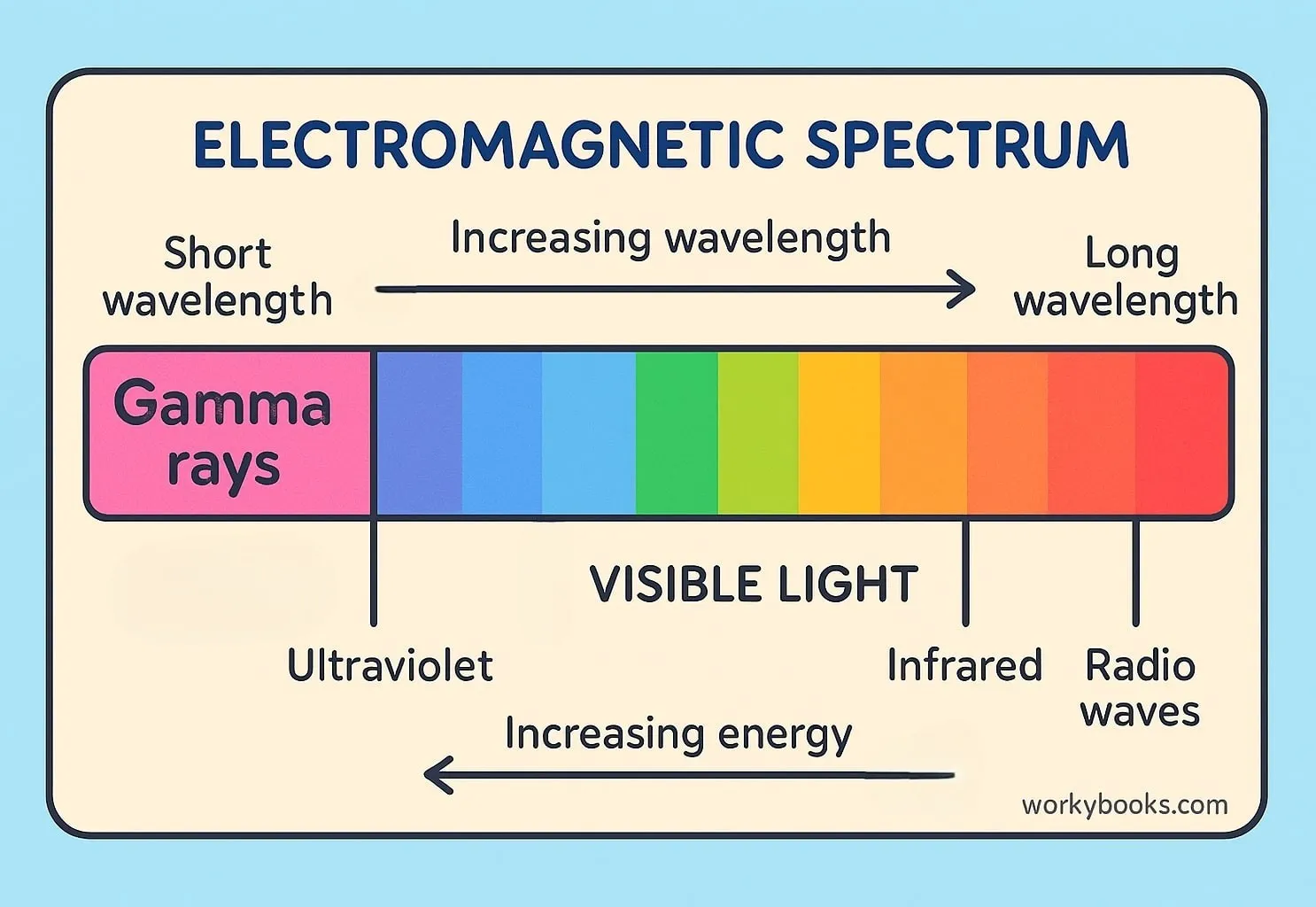
Gamma radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation with the highest energy and shortest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. It is a form of ionizing radiation that comes from the nucleus of atoms.
Think of gamma rays as the most powerful form of light energy. Unlike visible light that we can see, gamma rays are invisible and can pass through many materials, including our bodies. They are produced by some of the most energetic events in the universe, like exploding stars and nuclear reactions.
Radiation Fact!
Gamma rays have the smallest wavelengths (shorter than atoms) and the most energy of any wave in the electromagnetic spectrum.
How Gamma Radiation Works
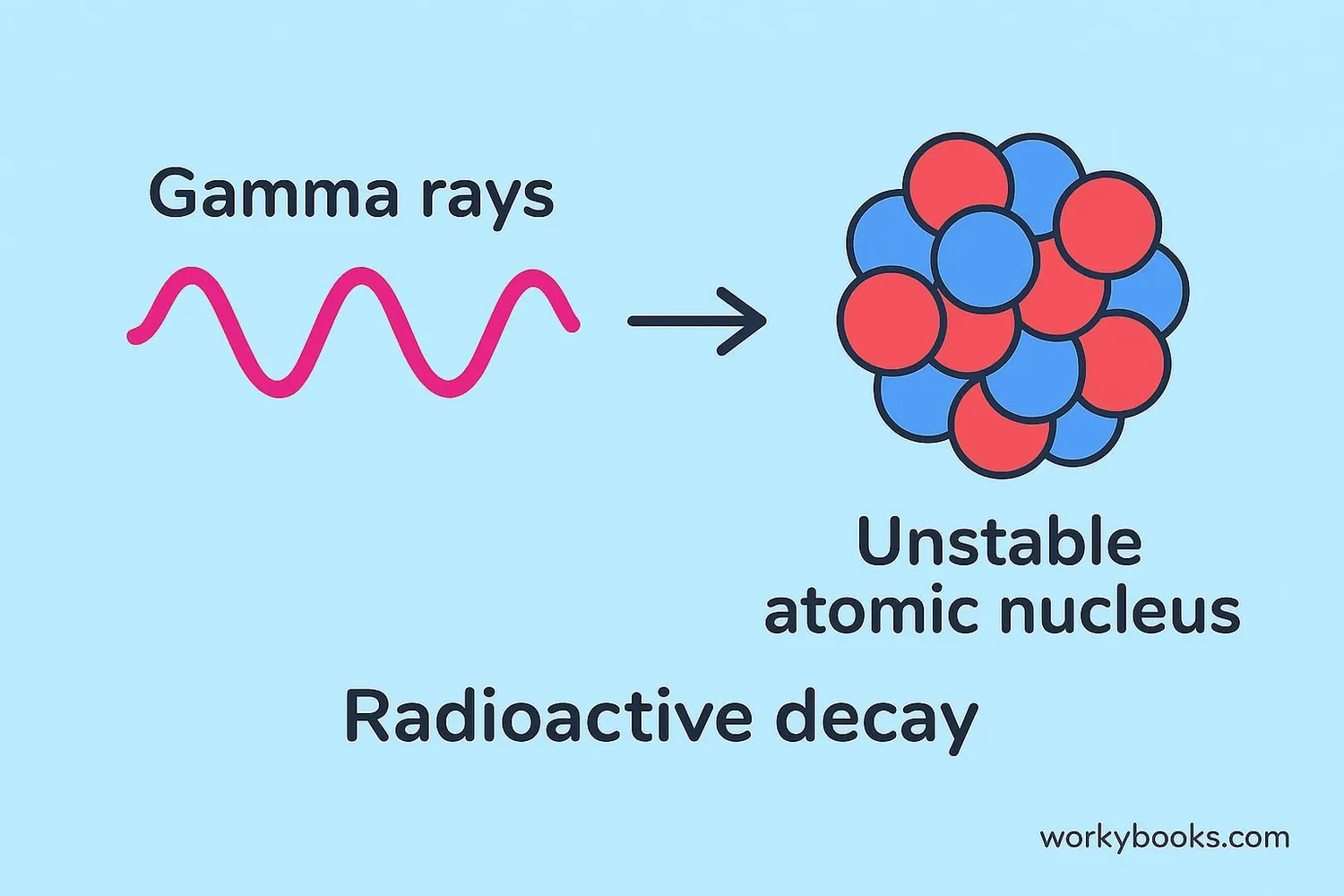
Gamma radiation is produced when the nucleus of an atom has too much energy. This can happen during:
Radioactive Decay
Unstable atoms release energy to become stable
Nuclear Reactions
Atoms split or combine in nuclear processes
Space Events
Supernovas, pulsars, and black holes produce gamma rays
Because gamma rays are high energy photons, they can penetrate through many materials. This is why thick lead or concrete is needed to block them. When gamma rays pass through living tissue, they can knock electrons out of atoms, creating ions. This is why they're called ionizing radiation.
Penetration Power!
Gamma rays can pass through several centimeters of lead! It takes a thick shield of dense material like lead or concrete to stop them.
Uses of Gamma Radiation
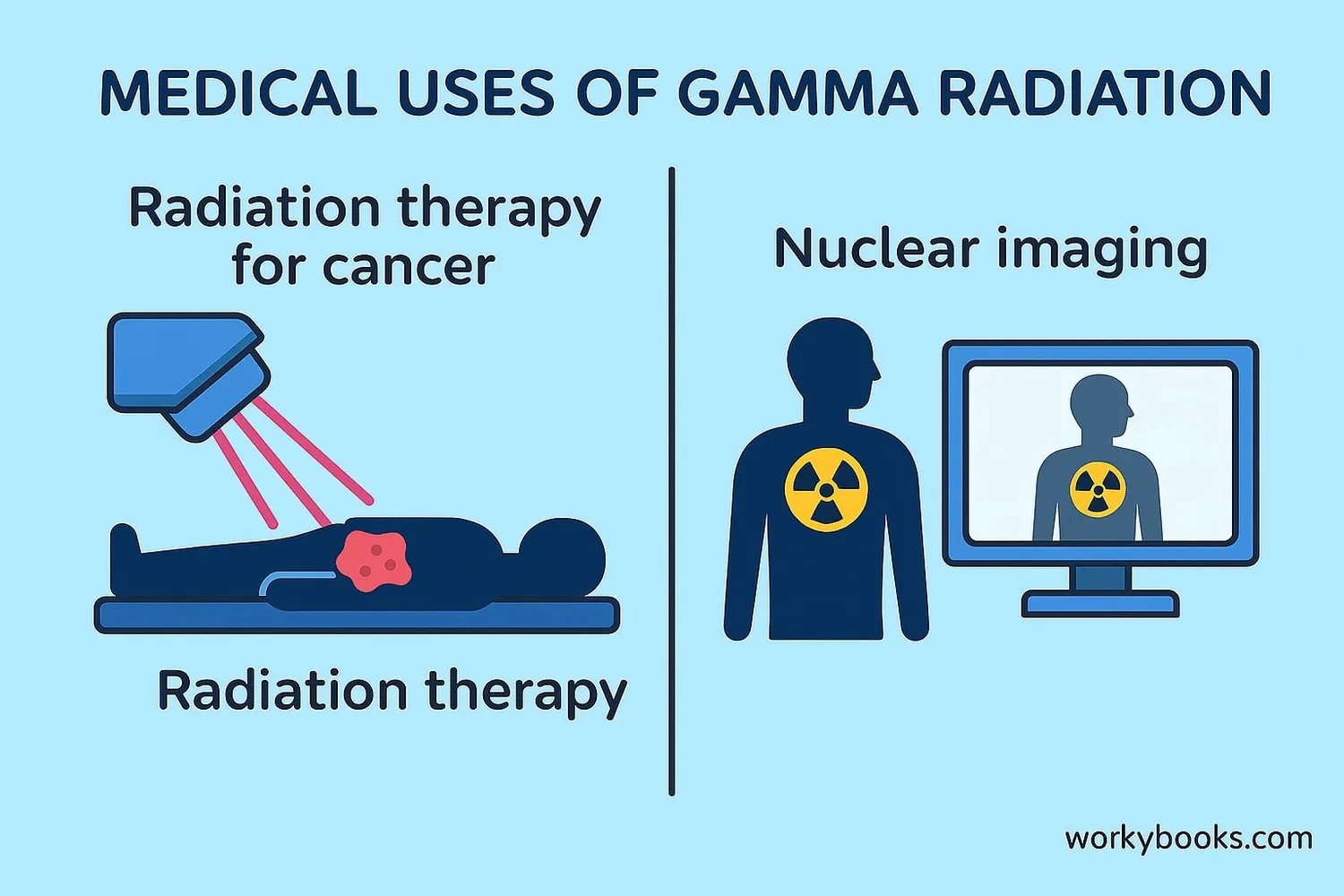
Despite being powerful and potentially dangerous, gamma radiation has many important uses that help people:
Medical Treatment
Radiation therapy uses focused gamma rays to destroy cancer cells
Medical Imaging
Nuclear medicine uses gamma rays to create images inside the body
Sterilization
Gamma rays kill bacteria and viruses on medical equipment
Gamma radiation is also used in:
• Food preservation (killing bacteria without making food radioactive)
• Industrial imaging (checking for flaws in metal parts)
• Scientific research (studying the structure of materials)
• Astronomy (observing the most energetic events in the universe)
Radiation Safety

Because gamma radiation can be harmful to living tissue, it's important to follow safety guidelines:
Shielding
Use dense materials like lead or concrete to block gamma rays
Distance
Stay as far away from radiation sources as possible
Time
Limit exposure time to radiation sources
Radiation protection is important for people who work with radioactive materials. They wear special badges called dosimeters that measure their exposure to radiation. In hospitals, thick walls protect staff and patients from radiation during treatments.
Natural sources of gamma radiation include rocks, soil, and even outer space, but these give us very small doses that our bodies can handle.
Safety First!
Never touch or play with unknown objects that might be radioactive. If you see a radiation warning symbol (three-bladed design), stay away and tell an adult.
Gamma Radiation Knowledge Check
Test your knowledge about gamma radiation with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about gamma radiation:
Interesting Gamma Radiation Facts
Discover some amazing facts about gamma radiation!
Most Energetic Events
Gamma-ray bursts are the most energetic events in the universe, releasing more energy in seconds than our sun will emit in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime!
Historical Discovery
French chemist Paul Villard discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation from radium. Ernest Rutherford named them "gamma rays" in 1903.
Medical Marvel
The Gamma Knife isn't actually a knife! It's a radiation therapy machine that uses 201 tiny gamma rays focused on a tumor to destroy it without cutting.
Space Telescopes
Special telescopes like NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope orbit Earth to study gamma rays from space that can't be detected through our atmosphere.





