Gravimetry - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how scientists measure mass and analyze materials through weighing!
What is Gravimetry?

Gravimetry is a method of measurement that involves weighing materials to determine their mass or composition. The word "gravimetry" comes from the Latin word "gravis" meaning "heavy" and the Greek word "metron" meaning "measure."
Think of gravimetry as a super-precise way of weighing things! Scientists use special balances that can measure incredibly small amounts of materials. This helps them understand what something is made of or how much of a certain substance is present in a sample.
Gravimetric analysis is a type of gravimetry where scientists measure the mass of a substance before and after a chemical reaction to figure out how much of a particular component was in the original sample.
Measurement Fact!
Some scientific balances can measure weights as small as one-millionth of a gram! That's much lighter than a single grain of salt.
How Gravimetric Analysis Works
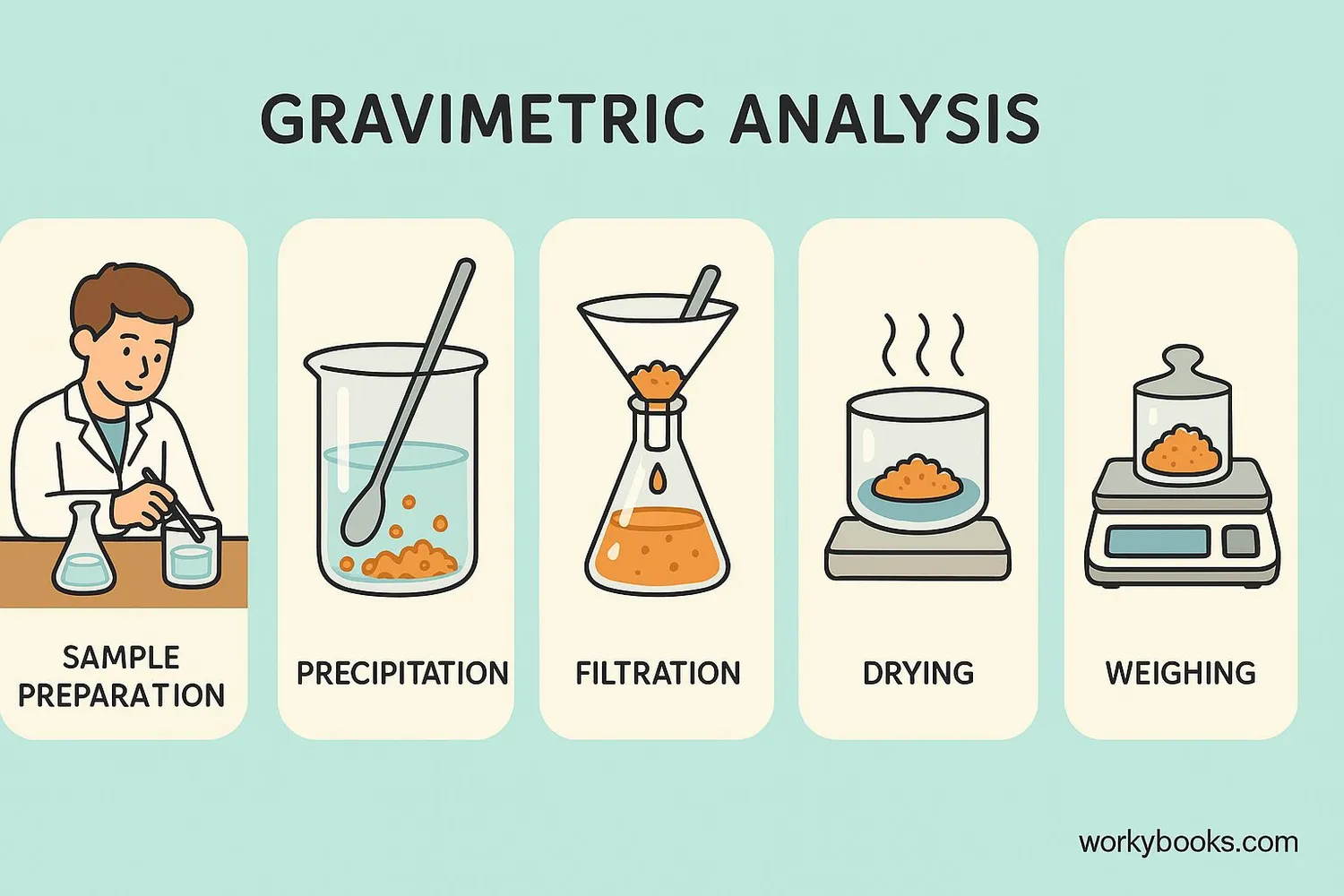
Gravimetric analysis follows specific steps to accurately measure the amount of a substance in a sample. Here's how scientists perform this careful measurement process:
Sample Preparation
The material to be analyzed is carefully prepared and weighed
Dissolving
The sample is dissolved in an appropriate solvent
Precipitation
A chemical is added to cause the target substance to form a solid
Filtration
The solid precipitate is separated from the liquid
Drying
The precipitate is carefully dried to remove all moisture
Weighing
The dried precipitate is weighed on a precision balance
By comparing the weight of the final precipitate to the original sample weight, scientists can calculate exactly how much of the substance they were looking for was in the sample.
This process requires patience and precision, but it gives very accurate results that help chemists understand the composition of materials.
Precision Matters!
Gravimetric analysis is so precise that it's often used to check the accuracy of other analytical methods. It's considered one of the most reliable measurement techniques in chemistry.
Why Gravimetry is Important
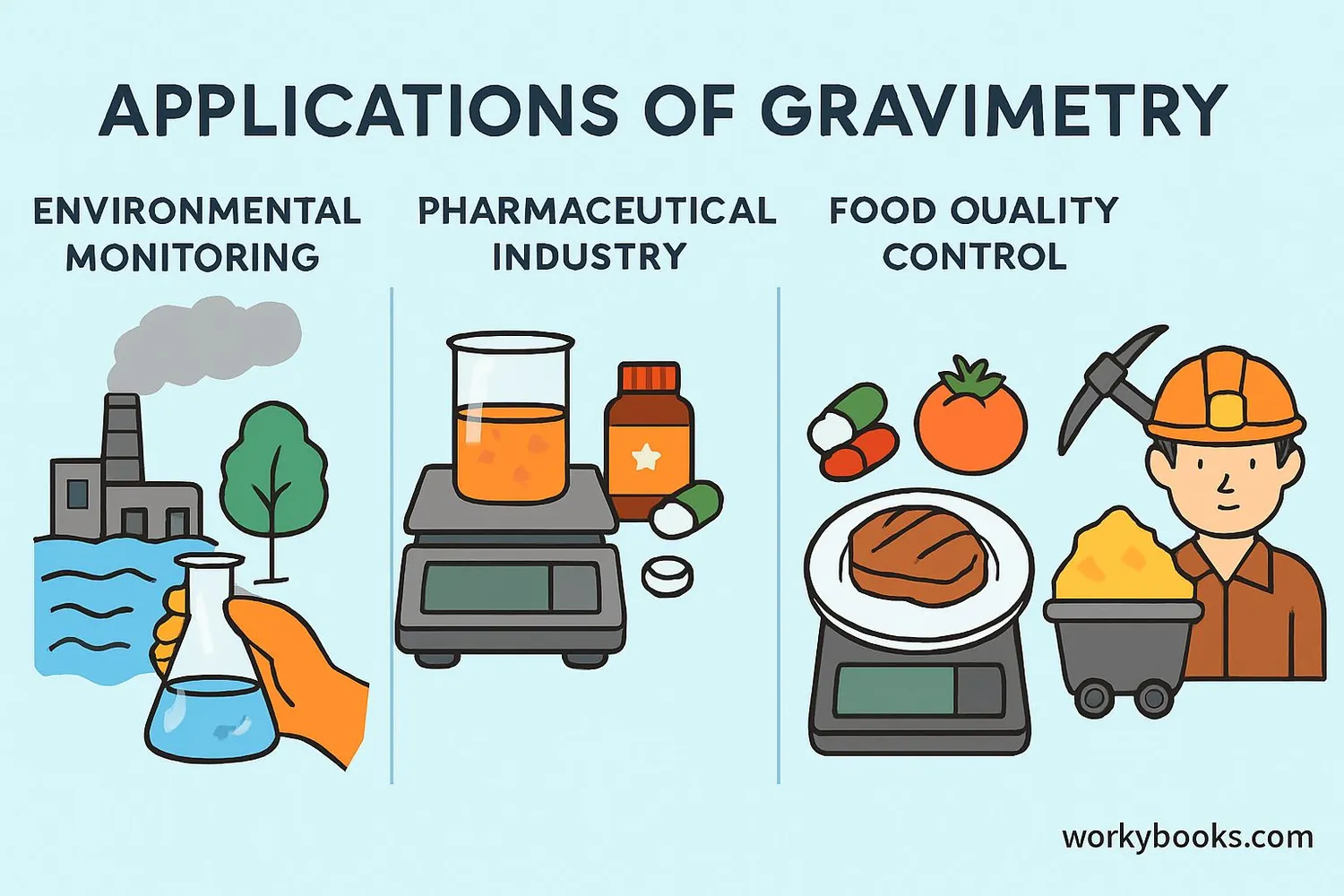
Gravimetry plays a crucial role in many scientific and industrial fields. Here's why this measurement technique is so valuable:
Quality Control
Ensures medicines, foods, and products meet safety standards
Environmental Monitoring
Measures pollutants and contaminants in air, water, and soil
Industrial Processes
Controls manufacturing quality in various industries
Gravimetry helps us in many aspects of daily life:
• Ensuring medications contain the right amount of active ingredients
• Checking that food products meet nutritional labeling requirements
• Monitoring air quality by measuring particulate matter
• Analyzing ore samples in mining to determine metal content
• Verifying the composition of construction materials
Without gravimetric analysis, we would have a much harder time ensuring the quality and safety of products we use every day!
Gravimetry vs. Volumetric Analysis
While gravimetry measures mass, volumetric analysis measures volume. Gravimetry is often more accurate but can be more time-consuming than volumetric methods.
Gravimetry Quiz
Test your knowledge about gravimetry with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about gravimetry:
Interesting Gravimetry Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about gravimetry and measurement!
Incredible Precision
The most sensitive laboratory balances can measure changes in mass as small as 0.1 micrograms—that's about the weight of a single human cell!
Ancient Origins
The concept of weighing materials dates back to ancient Egypt around 2500 BCE, where balance scales were used for trade and gold measurement.
Space Applications
NASA uses gravimetric techniques to analyze soil and rock samples from other planets. The Mars rovers have instruments that can perform basic gravimetric analysis.
Food Industry Use
Gravimetry helps ensure the accuracy of nutrition labels on food products by measuring fat, protein, and moisture content through precise weighing techniques.





