Mass of the Moon - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how our Moon compares to Earth and why its mass matters
What is Mass?
Mass is the amount of matter (or "stuff") in an object. It's different from weight because weight depends on gravity. An object has the same mass everywhere, but its weight changes depending on where it is. For example, you would weigh less on the Moon than on Earth because the Moon has less gravity.
The Moon has a mass of about 7.35 × 1022 kilograms. That's 73,500,000,000,000,000,000,000 kilograms! That might sound like a lot, but compared to Earth, it's actually quite small.
Science Fact!
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and the fifth largest moon in our solar system.
How Do We Measure the Moon's Mass?
Scientists use the laws of gravity and motion discovered by Sir Isaac Newton to measure the Moon's mass. Here's how they do it:
Orbit Observation
Scientists carefully measure how the Moon orbits Earth
Gravity's Effect
They study how Earth and Moon pull on each other
Spacecraft Tracking
Spacecraft orbiting the Moon help measure its gravity
Mathematical Calculations
Using Newton's laws to calculate mass from gravity
The formula scientists use is based on Newton's law of universal gravitation:
F = G × (m₁ × m₂) / r²
Where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, m₁ and m₂ are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between them.
Earth-Moon Mass Comparison
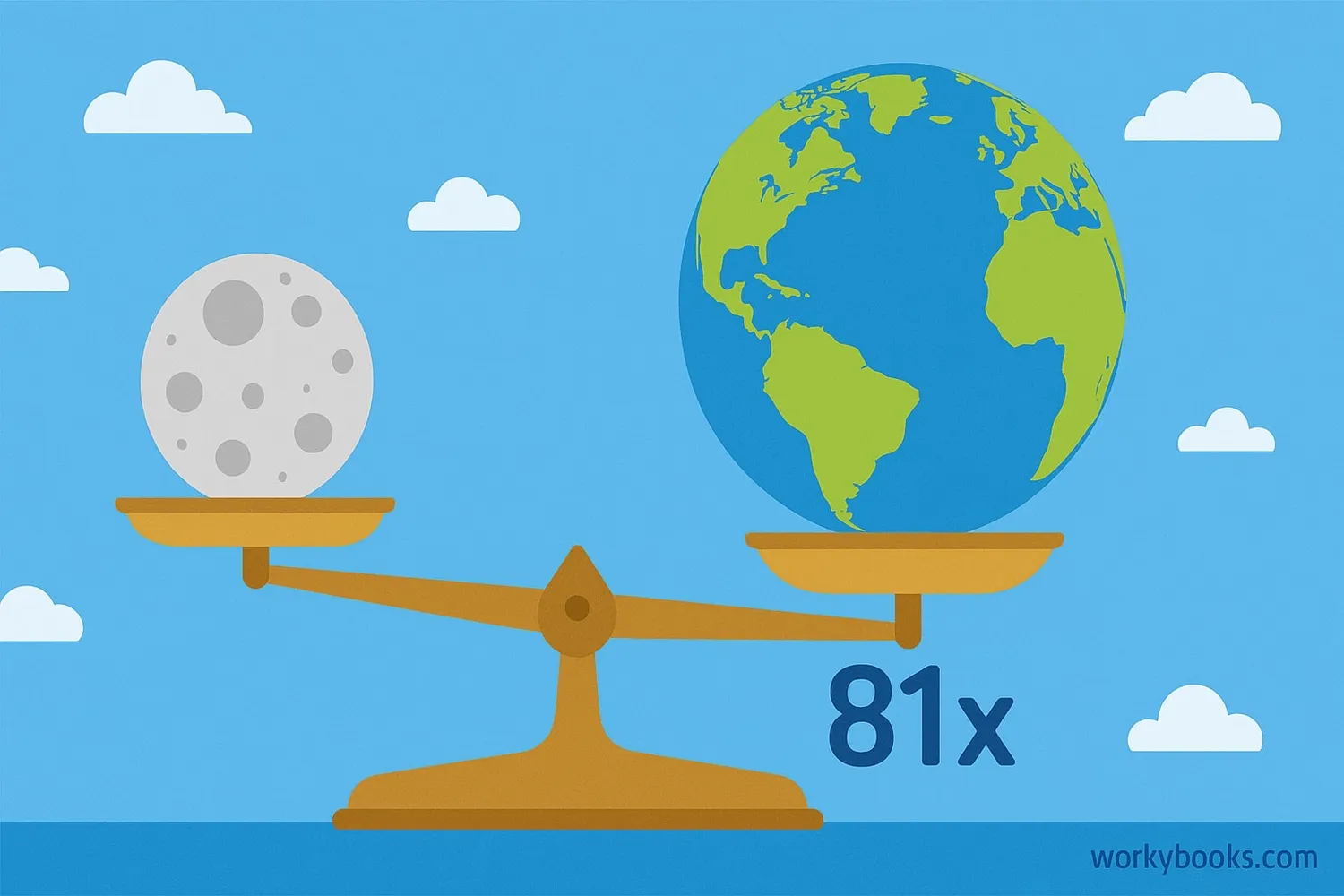
The Moon is much less massive than Earth. Let's look at how they compare:
Earth's Mass
Moon's Mass
Earth is about 81 times more massive than the Moon! That means you would need 81 Moons to equal the mass of one Earth.
Even though the Moon is much less massive, it still has enough gravity to affect Earth in important ways, especially with ocean tides.
Density Difference
The Moon is less dense than Earth. If Earth were the size of a basketball, the Moon would be about the size of a tennis ball.
How the Moon's Mass Affects Earth
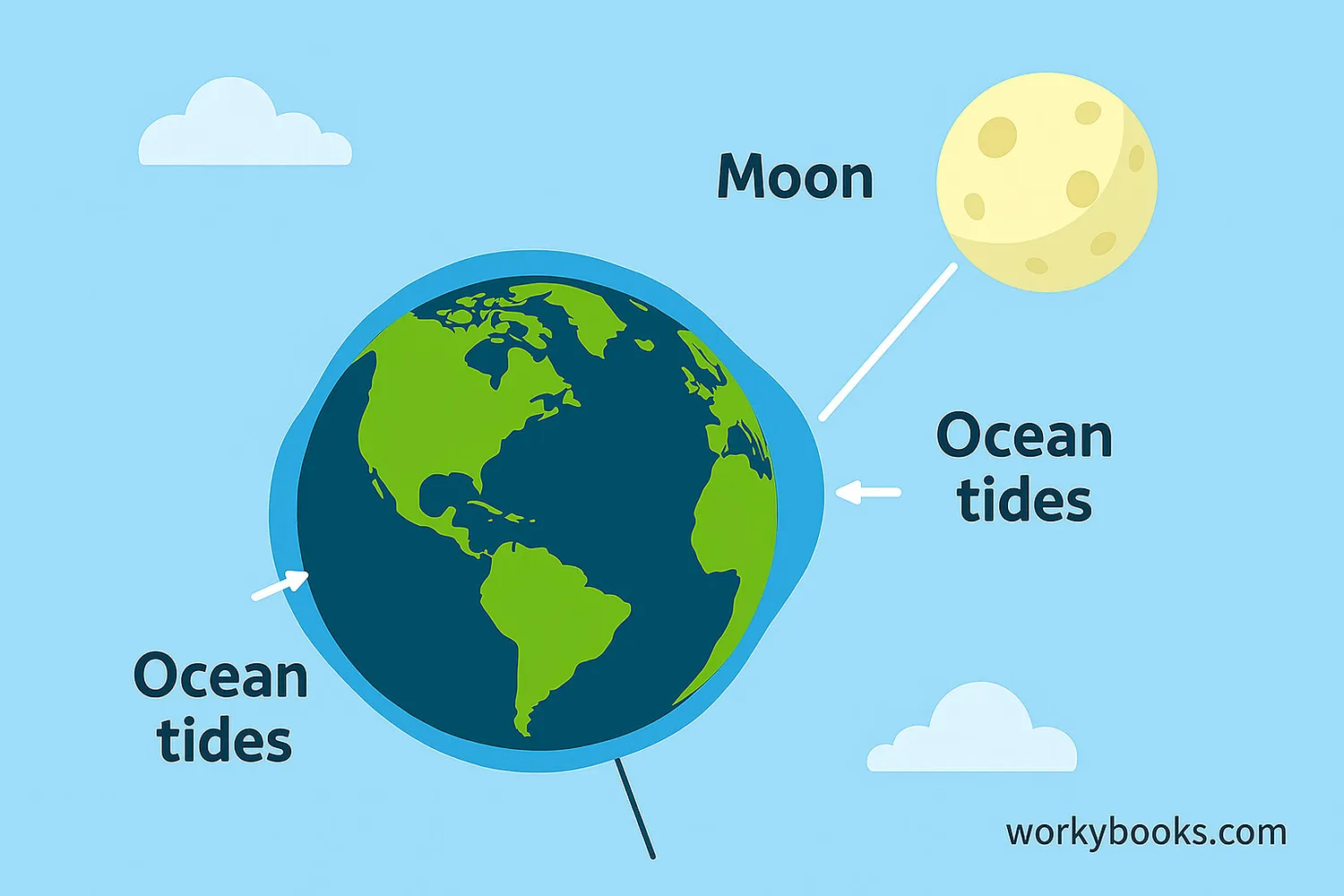
The Moon's mass creates gravity that affects Earth in several important ways:
Ocean Tides
The Moon's gravity pulls on Earth's oceans, creating high and low tides
Slowing Earth
Tidal forces gradually slow Earth's rotation, making our days longer
Stabilizing Climate
The Moon helps stabilize Earth's tilt, creating more consistent seasons
The Moon's gravity is strong enough to:
• Lift ocean water by about 1-2 meters (high tide)
• Cause Earth's rotation to slow by about 1.4 milliseconds per century
• Stabilize Earth's axial tilt between 22.1° and 24.5°
Without the Moon, Earth would have more extreme seasons and a faster rotation.
Moon Mass Quiz
Test your knowledge about the Moon's mass with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Moon's mass:
Space Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about the Moon and its mass!
Lunar Gravity
Astronauts on the Moon could jump six times higher than on Earth because of the Moon's weaker gravity!
Tidal Power
The Moon's gravity pulls Earth's oceans, creating tides that generate enough energy to power millions of homes through tidal power stations.
Moving Away
The Moon is slowly moving away from Earth at about 3.8 cm per year because of tidal interactions. This effect is directly related to the Moon's mass.
Moon Formation
Scientists believe the Moon formed when a Mars-sized object collided with early Earth. The debris from this collision eventually came together to form the Moon.





