Static Electricity - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the science behind sparks, shocks, and lightning!
What is Static Electricity?
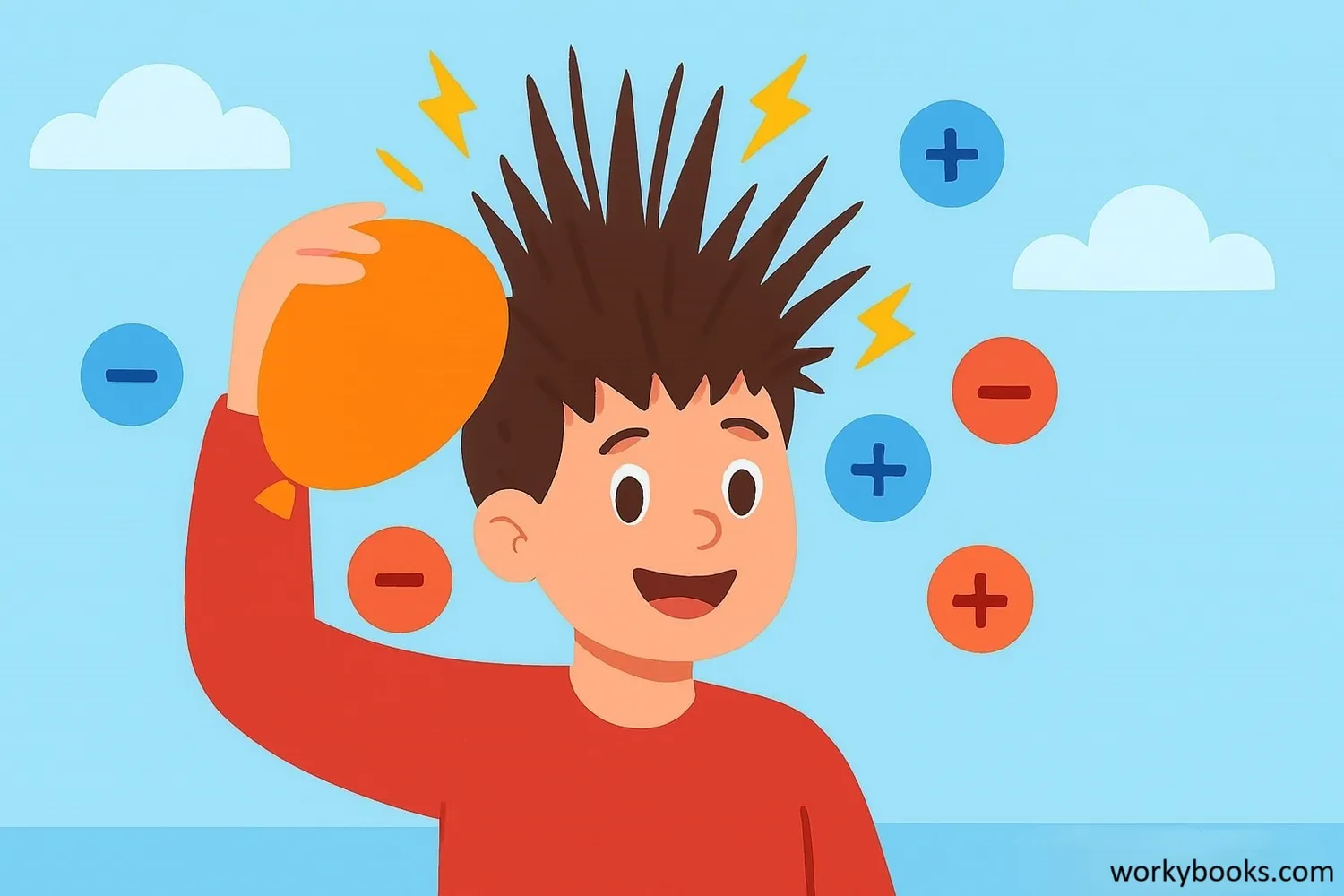

Static electricity is a buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object. Unlike current electricity that flows through wires, static electricity stays in one place until it finds a way to discharge.
Think about when you rub a balloon on your hair and it sticks to the wall! That's static electricity in action. All matter is made of atoms containing positive protons, negative electrons, and neutral neutrons. When two objects rub together, electrons can transfer from one surface to another, creating an imbalance of charges.
Science Fact!
The word "static" means "not moving," which helps us remember that this type of electricity stays in one place until discharged!
How Static Electricity Works
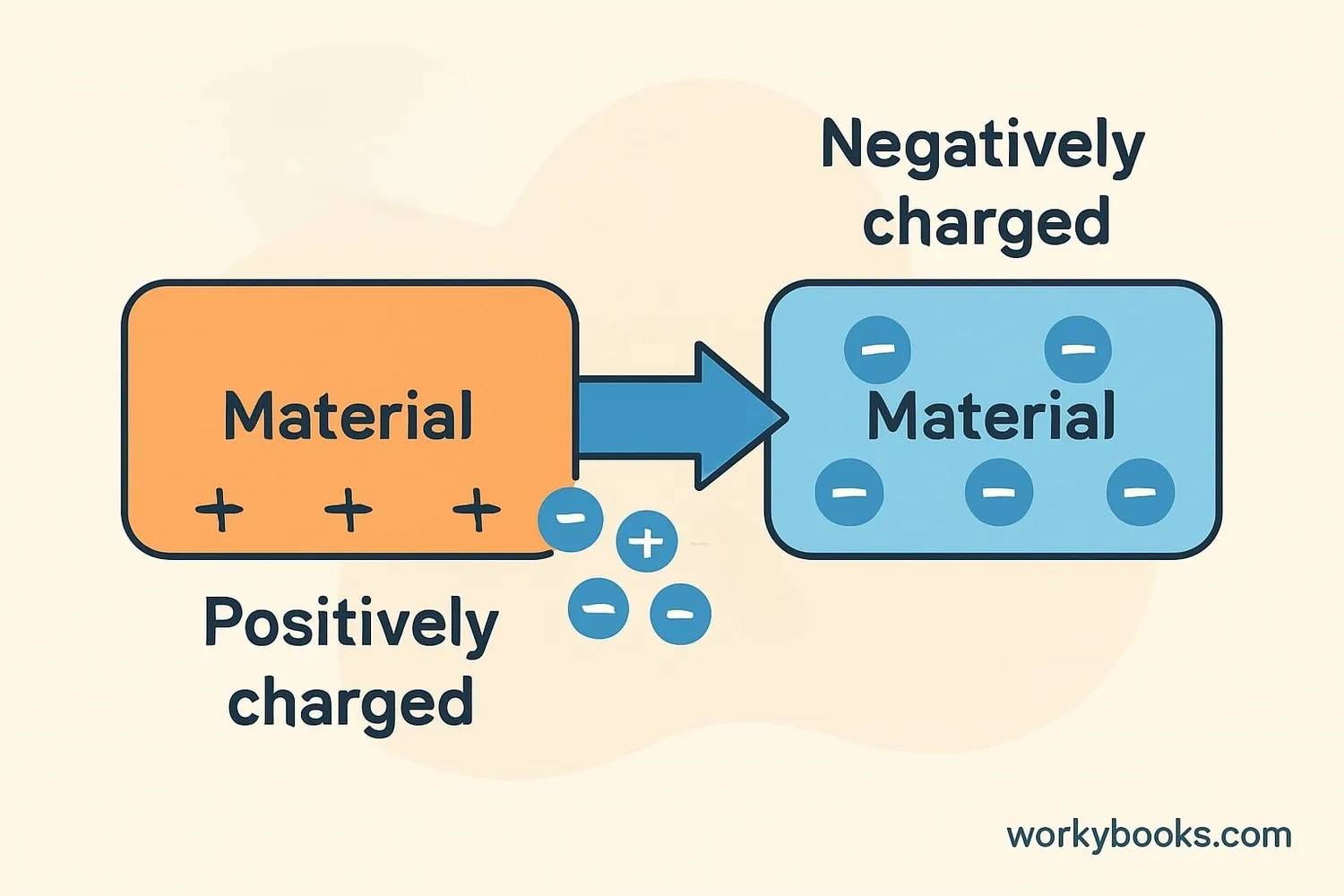
Static electricity occurs through a process called the triboelectric effect (or contact electrification). Here's how it works:
Contact
Two different materials rub against each other
Electron Transfer
Electrons move from one material to the other
Charge Separation
One material gains electrons (negative charge), the other loses electrons (positive charge)
Charge Buildup
Charges build up on the surfaces of the materials
Discharge
When the charged object touches a conductor, electrons flow rapidly causing a spark
Materials can be arranged in a triboelectric series showing which ones tend to gain or lose electrons. For example:
Gains electrons (becomes negative): Rubber balloon, wool, human hair
Loses electrons (becomes positive): Glass, nylon, human skin
Conductors & Insulators
Electrical conductors (like metals) allow charges to flow easily, while insulators (like plastic) prevent charge movement, allowing static buildup.
Examples & Effects of Static Electricity
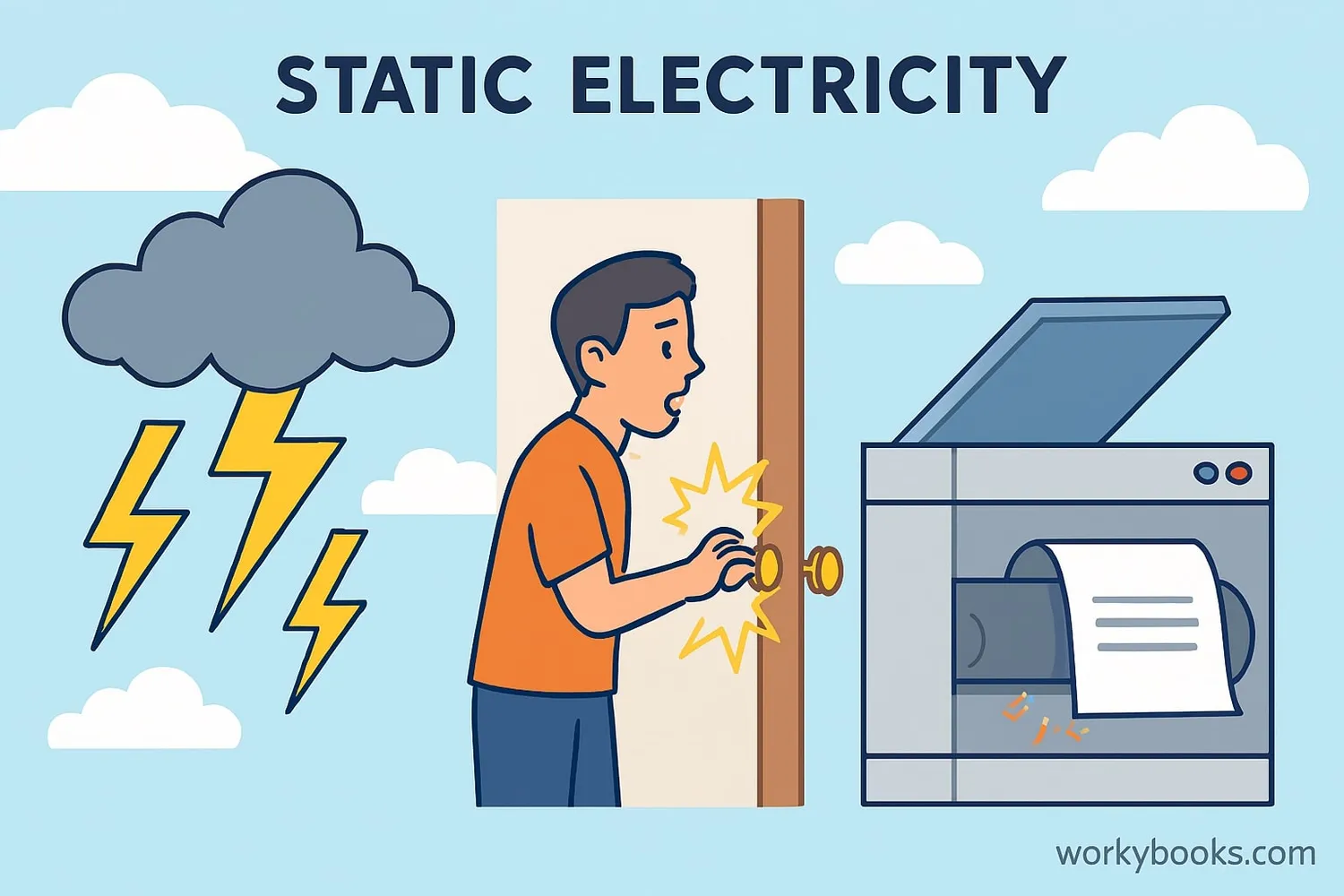
Static electricity is all around us! Here are some common examples:
Lightning
Huge spark caused by static electricity buildup between clouds or between clouds and the ground
Static Shock
The zap you feel when touching a metal object after walking on carpet
Photocopiers
Use static electricity to attract toner particles to paper
We can also create static electricity with special machines:
Van de Graaff Generator: A machine that uses a moving belt to create very high voltages of static electricity. It makes hair stand on end!
Wimshurst Machine: An electrostatic generator that uses rotating disks to separate positive and negative charges.
Static Safety!
Static electricity can be dangerous near flammable gases or liquids. That's why fuel trucks have chains that drag on the ground to safely discharge static buildup.
Static Electricity Quiz
Test your static electricity knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about static electricity:
Fun Static Electricity Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about static electricity!
Powerful Sparks
A single lightning bolt can contain up to one billion volts of electricity - enough to power a 100-watt lightbulb for three months!
Spider Flight
Some spiders use static electricity to "balloon" through the air! They release silk threads that are lifted by the Earth's electric field.
Moon Dust
Astronauts found that moon dust sticks to everything because of static electricity. The dust particles become charged by solar radiation.
Ancient Knowledge
People knew about static electricity as early as 600 BCE! The ancient Greeks discovered that rubbing amber with fur would attract lightweight objects.





