Unbalanced Forces - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how forces affect motion and cause changes in speed or direction
What Are Unbalanced Forces?
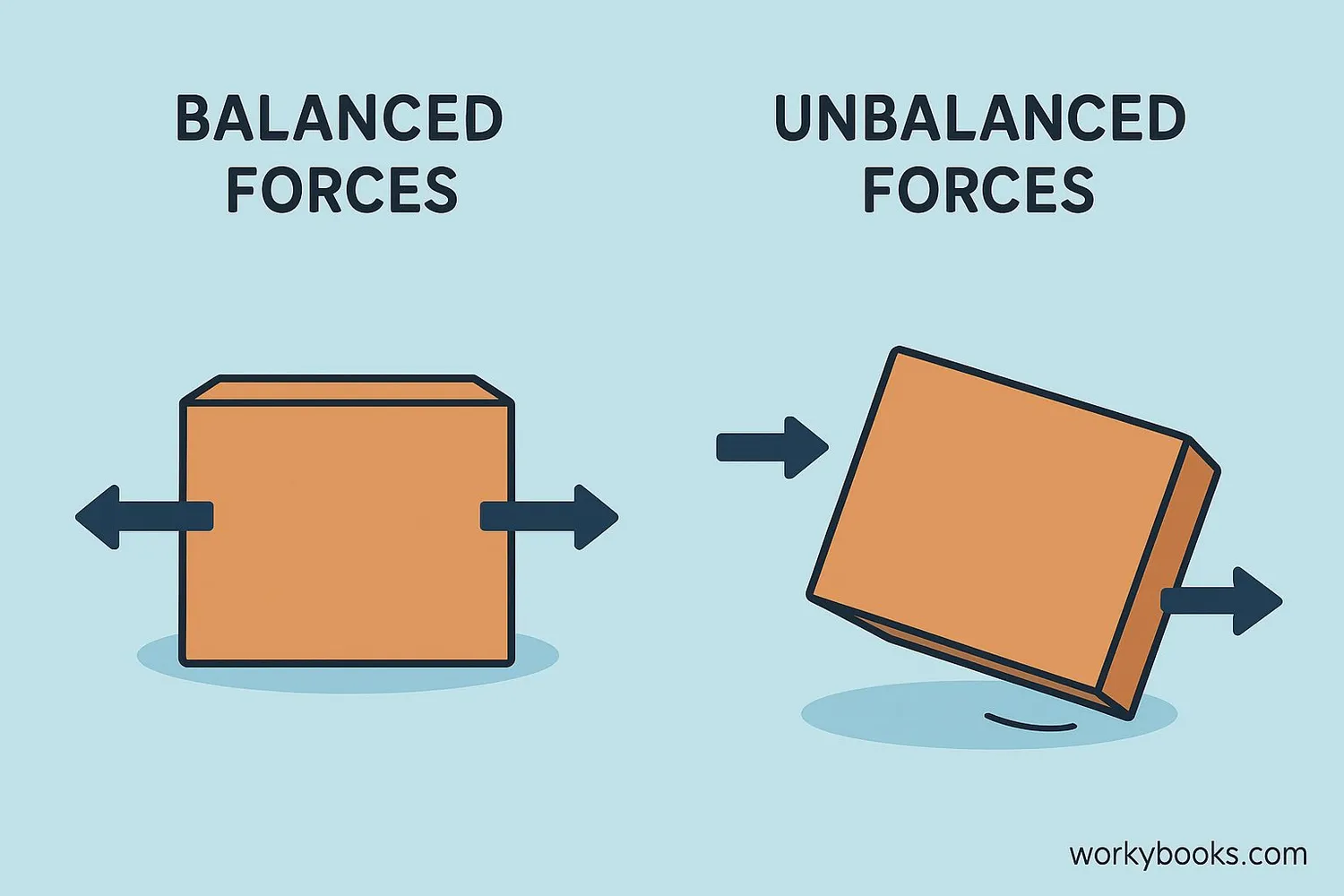
Unbalanced forces occur when the total force acting on an object is not zero. This means the forces don't cancel each other out, causing the object to change its motion - either by starting to move, stopping, speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
When forces are balanced, an object will remain at rest or continue moving at a constant speed in a straight line (Newton's First Law). But when forces become unbalanced, the object will accelerate in the direction of the greater force.
Key Concept
Unbalanced forces create a net force or resultant force that changes an object's motion according to Newton's Second Law: F = ma (Force equals mass times acceleration).
How Unbalanced Forces Affect Motion
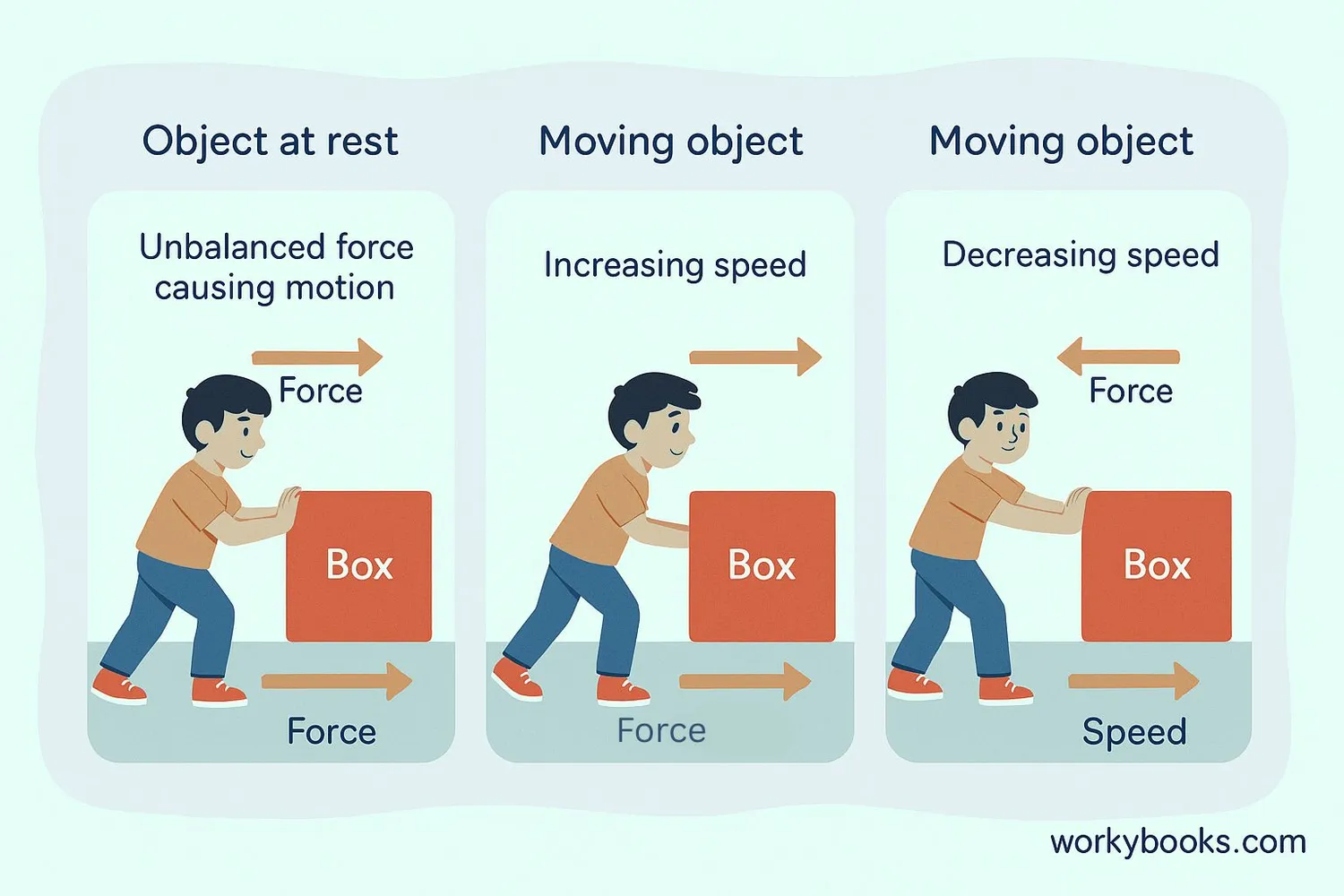
Unbalanced forces can affect objects in several ways:
Starting Motion
An unbalanced force can make a stationary object begin to move
Changing Speed
Forces in the direction of motion increase speed (acceleration)
Slowing Down
Opposing forces decrease speed (deceleration)
Changing Direction
Sideways forces alter the object's path
Stopping
Opposing forces can bring a moving object to rest
The magnitude (size) of the unbalanced force determines how much the motion changes. A small force causes gradual changes, while a large force creates rapid acceleration. The direction of the resultant force determines which way the object will accelerate.
Newton's Second Law
The acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting on it and its mass: a = F/m. More force means more acceleration, while more mass means less acceleration for the same force.
Real-World Examples
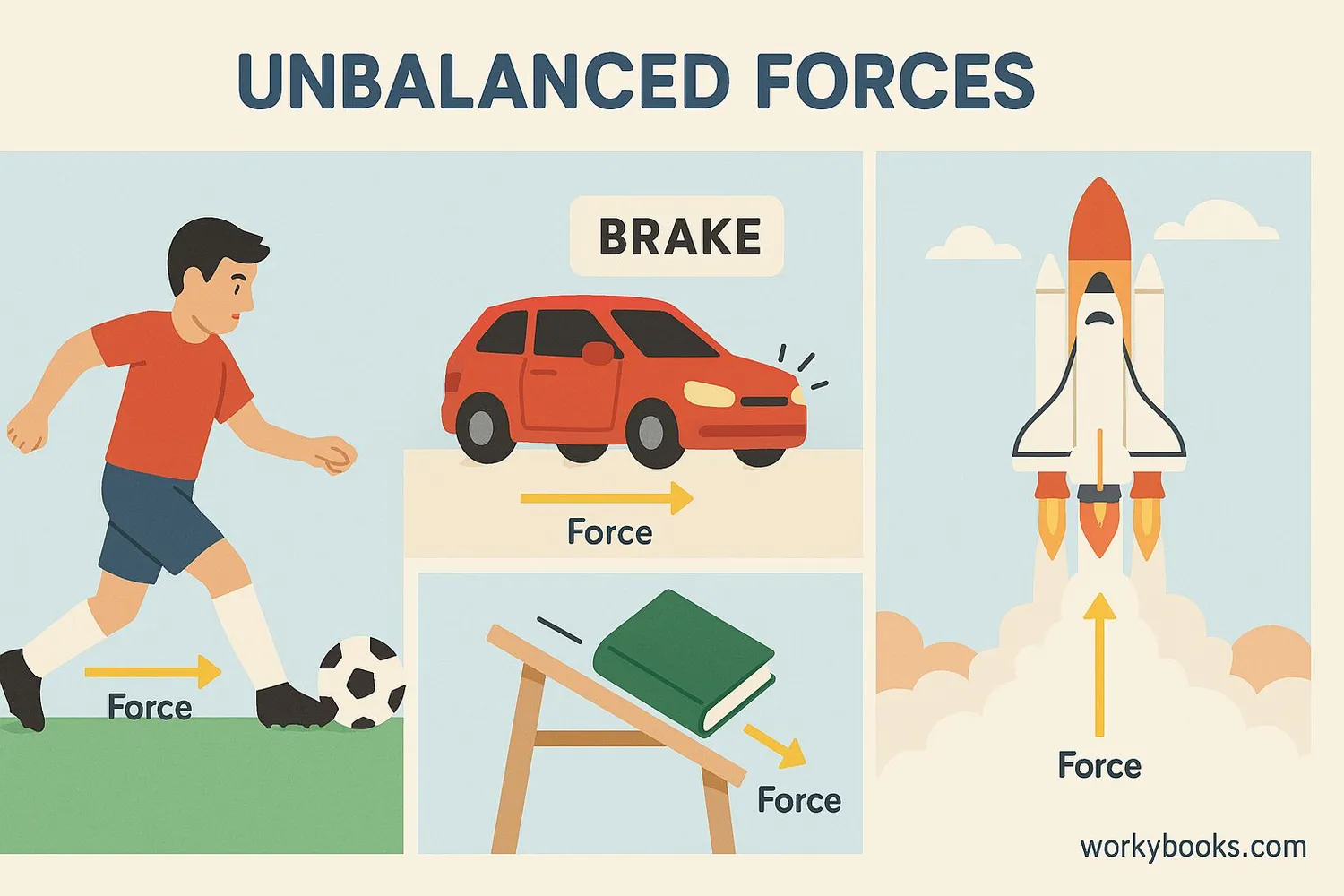
Unbalanced forces are all around us! Here are common examples you experience every day:
Sports
Kicking a soccer ball applies an unbalanced force that makes it move and change direction
Transportation
Car acceleration and braking are controlled by unbalanced forces
Space Travel
Rockets launch when thrust overcomes gravity (unbalanced forces)
Other examples include:
• Pushing a shopping cart
• A book sliding off a tilted table
• A parachutist accelerating until air resistance balances gravity
• Tug-of-war when one team pulls harder
• A door opening when you push it
In each case, the net force isn't zero, causing changes in motion that we can observe and measure.
Knowledge Check
Test your understanding of unbalanced forces with these questions:
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about unbalanced forces:
Physics Trivia
Amazing facts about forces and motion:
Rocket Science
A Saturn V rocket at launch produces 34.5 million newtons of thrust - that's enough unbalanced force to lift 2,700 cars straight up against Earth's gravity!
Animal Athletes
Frogs can jump over 20 times their body length because their leg muscles create huge unbalanced forces in milliseconds, accelerating them rapidly upward.
Sports Science
A professional baseball pitcher's arm creates about 100 N of unbalanced force on the ball during a fast pitch, accelerating it from 0 to 100 mph in less than 0.1 seconds!
Tiny Forces
At the atomic level, unbalanced electrostatic forces are a trillion trillion times stronger than gravity - that's why you can lift your hand against Earth's entire gravity!





