Egyptian Pharaohs
Egyptian pharaohs ruled one of the most fascinating ancient civilizations in human history. For over 3,000 years, these powerful divine rulers controlled the land along the Nile River. They built massive pyramids, created stunning artwork, and developed a complex society that still captivates students today.
Teaching about the pharaohs of Egypt offers students a window into a remarkable ancient world. This guide provides everything grade 6 teachers need to bring ancient Egypt for kids to life in the classroom. We explore famous Egyptian pharaohs, their achievements, and their lasting legacy.
Who Were the Egyptian Pharaohs?
The Egyptian pharaohs were more than just ancient kings. The Egyptian people believed their rulers were living gods on Earth. The word “pharaoh” means “great house” and originally referred to the royal palace. Over time, it became the title for Egyptian monarchs themselves.
These royal leaders held absolute power over ancient Egypt. They controlled the government, the military, and religious practices. The pharaohs owned all the land in Egypt and collected taxes from farmers and merchants. They also served as the high priest of every temple in the kingdom.
Egyptian rulers wore special symbols of their power. The double crown represented rule over Upper and Lower Egypt. They carried a crook and flail to symbolize their role as shepherds of the people. A false beard showed their connection to Osiris, the god of the afterlife.
The pharaohs believed they would live forever in the afterlife. This belief led them to build elaborate tombs filled with treasures. They preserved their bodies as mummies and pharaohs to ensure their survival in the next world.
Famous Egyptian Pharaohs
Ancient Egypt had over 170 pharaohs during its long history. Some became legendary figures whose names students still recognize today. Learning about these famous Egyptian pharaohs helps students understand the power and complexity of this Nile River civilization.
Khufu: The Pyramid Builder
Khufu and pyramids are forever linked in history. This pharaoh ordered the construction of the Great Pyramid at Giza. It stood as the tallest human-made structure for over 3,800 years. The pyramid contains an estimated 2.3 million stone blocks.
How pyramids were built remains a subject of study and debate. Workers quarried limestone blocks and transported them to the construction site. They used ramps, levers, and human labor to stack the massive stones. The precision of the Great Pyramid’s construction still amazes engineers today.
Hatshepsut: The Female Pharaoh
Hatshepsut female pharaoh broke barriers in ancient Egypt. She was one of the few women to rule as pharaoh with full royal powers. Hatshepsut initially served as regent for her young stepson Thutmose III. She eventually declared herself pharaoh and ruled for over twenty years.
Hatshepsut focused on trade and building projects rather than military conquest. She sent a famous expedition to the land of Punt to acquire incense, ebony, and exotic animals. Her mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahri remains one of ancient Egypt’s most beautiful monuments.
Akhenaten
Akhenaten stands out as one of the most controversial Egyptian pharaohs in history. He ruled Egypt for about seventeen years and completely transformed religious practices during his reign. His bold changes made him both fascinating and divisive among scholars studying ancient Egypt.
Before becoming pharaoh, Akhenaten was named Amenhotep IV. He changed his name to honor Aten, the sun disk god. This name change signaled the beginning of a religious revolution in the ancient world.
Akhenaten rejected the traditional Egyptian gods and goddesses that Egyptians had worshipped for centuries. He declared that Aten was the one true god. This made him one of history’s earliest leaders to promote monotheism, the worship of a single deity. He closed temples dedicated to other gods and redirected their wealth to Aten worship.

The pharaoh also built an entirely new capital city called Akhetaten, meaning “Horizon of Aten.” Today this site is known as Amarna. He moved his court and administration away from the traditional religious centers. The city featured open-air temples designed to let sunlight flood the worship spaces.
Akhenaten was married to the famous queen Nefertiti. Together they had six daughters. He was also the father of Tutankhamun, who would later become the famous boy pharaoh King Tut.
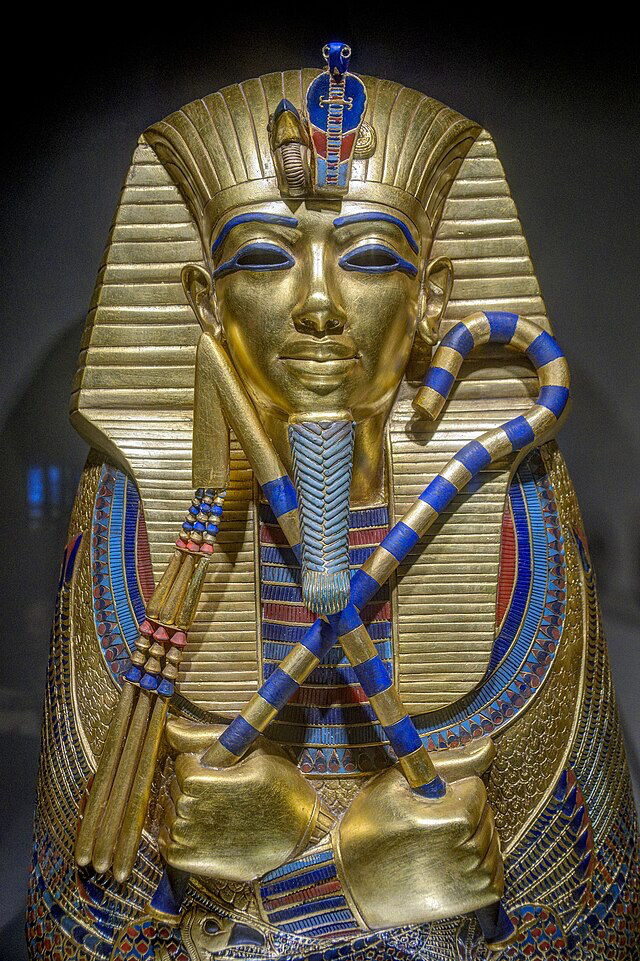
King Tut: The Boy Pharaoh
King Tut for kids is often the most exciting pharaoh to study. Tutankhamun became pharaoh at just nine years old. He ruled for about ten years before dying at age nineteen. Tutankhamun facts reveal that he was not a particularly powerful ruler during his lifetime.
So why is King Tut so famous today? In 1922, archaeologist Howard Carter discovered his tomb in the Valley of the Kings. Unlike other royal tombs, grave robbers had never found it. The tomb contained over 5,000 artifacts, including the famous golden death mask. This discovery sparked worldwide interest in ancient Egypt and Egyptian tombs and treasures.

Ramses the Great: The Builder King
Ramses II, known as Ramses the Great, ruled Egypt for an impressive 66 years. He was one of the most powerful and celebrated Egyptian rulers in history. Ramses led military campaigns and expanded Egypt’s territory through diplomacy and warfare.
This pharaoh was also a legendary builder. He constructed more temples and monuments than any other pharaoh. The temples at Abu Simbel feature massive statues of Ramses carved into the mountainside. He also completed the great hypostyle hall at Karnak Temple.
Cleopatra: The Last Pharaoh
Cleopatra for kids presents a fascinating story of intelligence and power. Cleopatra VII was the last active pharaoh of ancient Egypt. She was highly educated and spoke nine languages. She was the first ruler in her family to learn the Egyptian language.
Cleopatra formed alliances with powerful Roman leaders Julius Caesar and Mark Antony. She fought to keep Egypt independent from Rome. After her death in 30 BCE, Egypt became a Roman province. Her story marks the end of the pharaonic era.
Egyptian Pyramids and the Afterlife
The Egyptian pyramids served as royal tombs for the pharaohs. These pyramid builders created monuments designed to protect the pharaoh’s body and treasures for eternity. The pyramids represented rays of sunlight, helping the pharaoh’s soul ascend to heaven.
The most famous pyramids stand at Giza, near modern Cairo. The three main pyramids were built for Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure. The Great Sphinx facts for kids reveal that this mysterious statue guards the Giza pyramid complex. It has the body of a lion and the head of a human, likely representing Khafre.
Workers created chambers and passageways inside the pyramids. The burial chamber held the pharaoh’s sarcophagus and mummified body. Surrounding rooms contained food, furniture, jewelry, and other items for the afterlife.
The Egyptians believed in a detailed afterlife journey. After death, the pharaoh’s soul traveled through the underworld. The heart was weighed against the feather of Ma’at, the goddess of truth. If the heart was light and pure, the soul could enter paradise.
This belief system explains why Egyptians took such care with mummies and pharaohs. Preserving the body was essential for the soul’s survival. Tomb paintings and hieroglyphics provided instructions for the afterlife journey.
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt Under the Egyptian Pharaohs
Understanding daily life in ancient Egypt helps students see beyond the pyramids and treasures. The pharaohs ruled over a complex society with different social classes and occupations.
Most Egyptians were farmers who worked the land along the Nile. The river’s annual flooding deposited rich soil perfect for growing crops. Farmers paid taxes to the pharaoh in the form of grain and livestock. During flood season, many farmers worked on royal building projects.
Skilled craftsmen created the beautiful objects found in Egyptian tombs and treasures. They worked with gold, precious stones, wood, and stone. Scribes held important positions because they could read and write hieroglyphics for kids and adults alike. Learning hieroglyphics took years of study and practice.
Egyptian gods and goddesses played a central role in daily life. People worshipped many deities, each controlling different aspects of the world.
Ra was the sun god, Osiris ruled the underworld, and Isis was the goddess of magic and motherhood. The pharaoh served as the connection between the people and these powerful gods.
The Valley of the Kings: Royal Burial Ground
After the pyramid age ended, pharaohs chose a new burial location. The Valley of the Kings became the royal cemetery for over 500 years. This remote valley near Thebes contained tombs cut deep into the rock.
The pharaohs hoped the hidden tombs would protect their treasures from robbers. Unfortunately, most tombs were looted in ancient times. Only King Tut’s tomb survived largely intact, which is why its discovery was so significant.
Today, archaeologists have found over 60 tombs in the Valley of the Kings. The tombs feature beautiful paintings showing Egyptian gods and goddesses, the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife, and scenes from daily life in ancient Egypt. These images provide valuable information about ancient Egyptian beliefs and culture.
Ancient Egypt Teaching Resources for Your Classroom
Bringing the pharaohs of Egypt to life requires engaging teaching materials. Our collection of ancient Egypt teaching resources helps grade 6 teachers create memorable lessons about this ancient civilization for kids.
Our ancient Egypt reading passage collection covers all the major topics students need to learn. Each passage provides grade-appropriate information about famous Egyptian pharaohs, pyramids, mummies, and daily life. The Egyptian pharaohs worksheet PDF downloads make lesson planning simple and efficient.
Teachers appreciate our Egyptian pharaohs classroom activities that go beyond basic reading. Students can complete an ancient Egypt graphic organizer to compare different pharaohs. The pharaohs timeline activity helps students understand the long span of Egyptian history. Ancient Egypt comprehension questions check for understanding and encourage critical thinking.
Looking for ancient Egypt activities for students that spark creativity? Our collection includes Egyptian pharaohs coloring page options and ancient Egypt writing prompts. Students can write from the perspective of a pharaoh or describe a day in ancient Egypt.
We offer Egyptian pharaohs differentiated reading materials at multiple levels. This ensures every student can access the same fascinating content about these divine rulers. Our pharaohs reading comprehension passages include questions that develop analytical skills.
Our Egyptian pharaohs printable activities save teachers valuable preparation time. Download pharaohs of Egypt facts sheets, vocabulary cards, and assessment materials. The ancient Egypt lesson plan guide helps you organize a complete unit on this ancient civilizations topic.
Ready to transport your students to ancient Egypt? Explore our complete collection of ancient Egypt for 3rd grade through 6th grade materials in our digital library. Your students will discover the wonders of the pharaohs and develop a lasting appreciation for this remarkable civilization.
Looking for more ancient civilizations for kids resources? Check out our complete collection of world history reading passages and classroom activities designed for elementary and middle school students.



