Azimuth - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how to measure directions using angles and compasses
What is Azimuth?
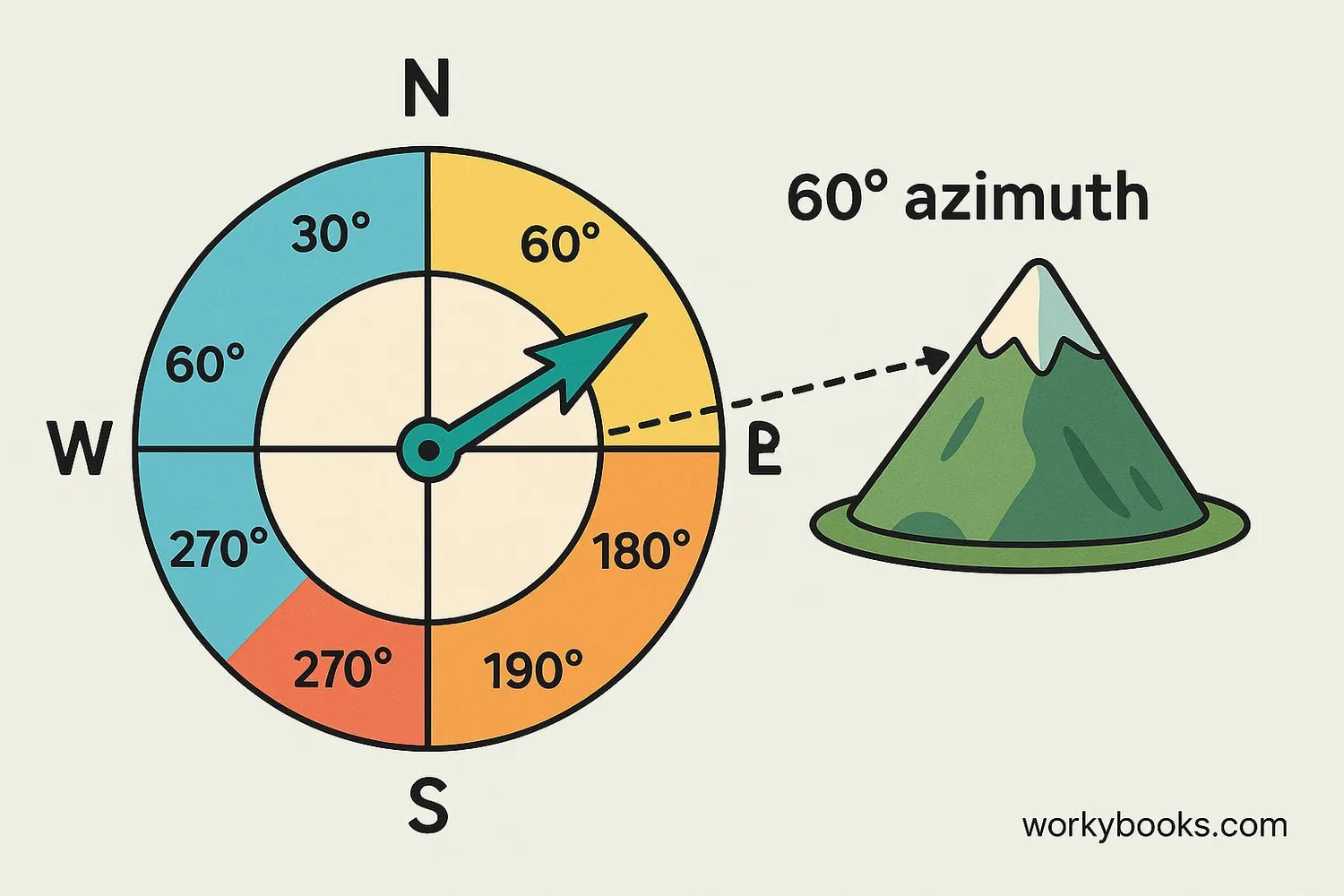
Azimuth is a special way to measure directions using angles. It tells us the horizontal direction from one point to another. The measurement starts from true north (the direction toward the North Pole) and goes clockwise around in a circle.
Imagine standing in the middle of a giant compass. If you face exactly north, that's 0° azimuth. If you turn to face east, that's 90° azimuth. South is 180°, and west is 270°. Azimuth helps us be very precise about directions!
Direction Fact!
Azimuth angles always range from 0° to 360°, making a complete circle. This helps navigators describe any direction accurately.
Start at North
All azimuth measurements begin at 0° pointing north
Measure Clockwise
Angles increase as you move clockwise around the circle
Full Circle
360° brings you back to north, completing the circle
Types of Azimuth
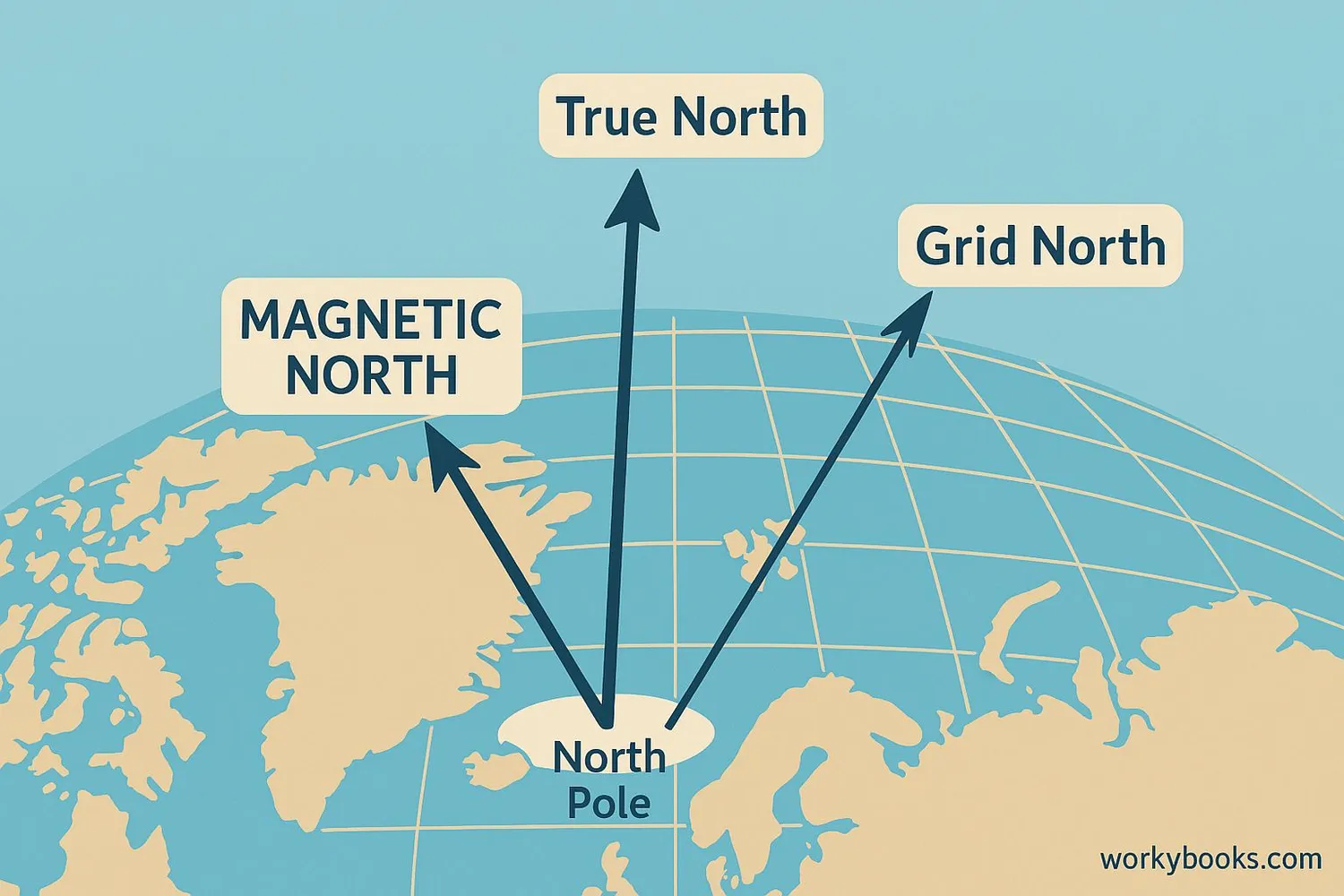
There are different types of azimuth depending on what we use as our reference point. Each type is important for different activities:
True Azimuth
Measured from true north (the North Pole). Used in astronomy and navigation when precision matters most.
Magnetic Azimuth
Measured from magnetic north (where compasses point). Used for hiking and everyday navigation with a compass.
Grid Azimuth
Measured from grid north on maps. Used by surveyors and in military applications where map grids are important.
Magnetic Variation!
Magnetic north moves about 40 kilometers each year! That's why true and magnetic azimuth can be different by up to 15° depending on your location.
How Azimuth is Used
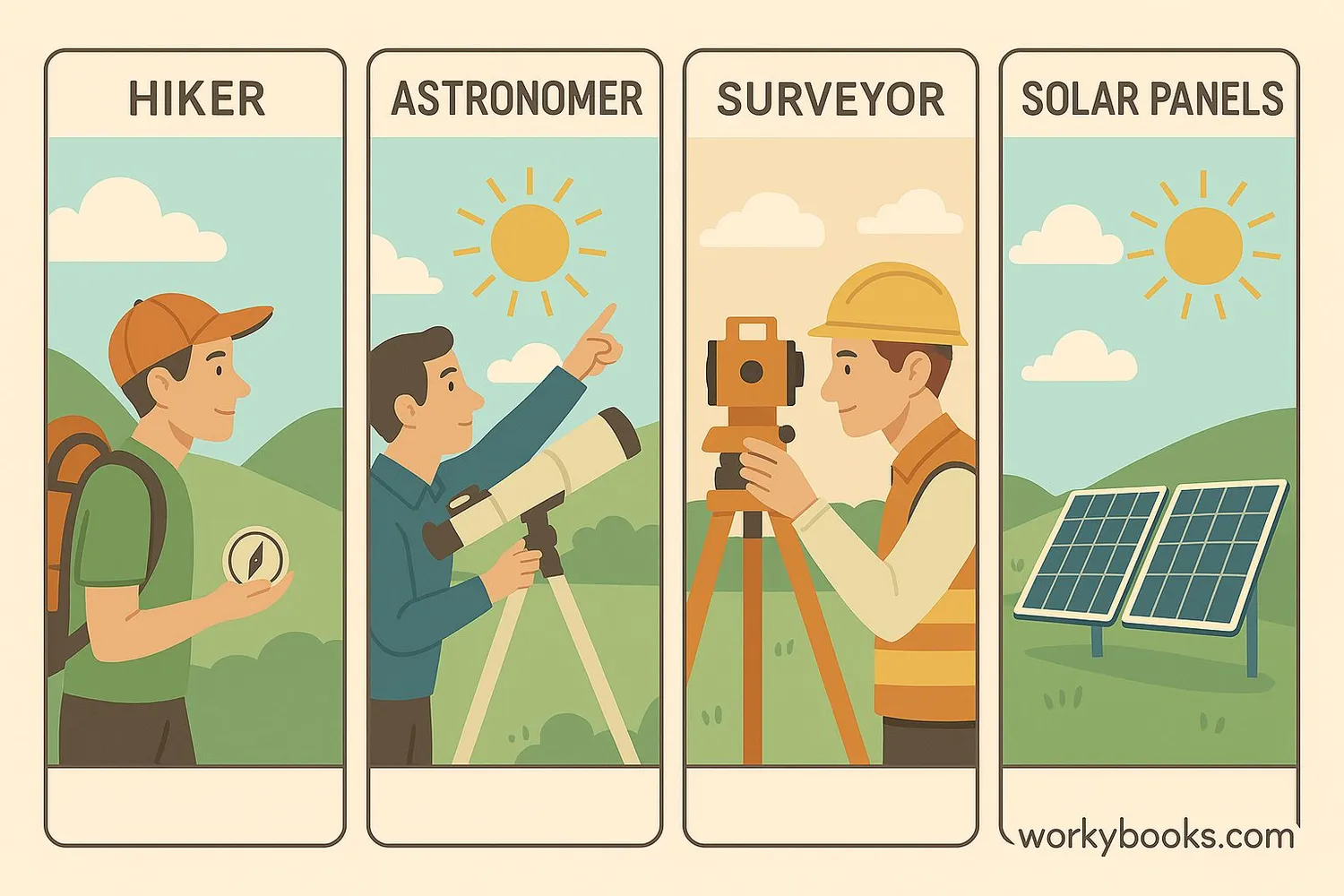
Azimuth is a powerful tool used in many different fields. Here's how different professionals use azimuth measurements:
Navigation
Hikers and sailors use azimuth with compasses to find their way and reach destinations accurately.
Astronomy
Astronomers use azimuth to locate stars and planets in the night sky using telescope coordinates.
Surveying
Surveyors measure azimuth to map land boundaries and construction sites with precision.
Solar Energy
Solar panels use solar azimuth angles to track the sun and capture maximum energy.
GPS Technology
GPS devices calculate azimuth to provide turn-by-turn directions and show heading information.
The solar azimuth angle is especially important for renewable energy. It changes throughout the day as the sun moves across the sky. At solar noon (when the sun is highest), the solar azimuth angle is exactly 180° in the northern hemisphere.
Azimuth Quiz
Test your understanding of azimuth with this 5-question quiz! Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about azimuth:
Azimuth Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about azimuth and directions!
Ancient Navigation
Polynesian navigators used star azimuths to sail across the Pacific Ocean thousands of years ago, long before modern compasses were invented!
Bird Navigation
Some birds can sense Earth's magnetic field and use it like a compass! They navigate using a natural sense of magnetic azimuth during migration.
Solar Tracking
Advanced solar power plants use precise solar azimuth calculations to rotate panels throughout the day, increasing energy production by up to 40%!
Historical Measurement
Ancient Egyptians used a tool called a "merkhet" to measure star azimuths and align their pyramids with incredible precision - some are aligned within 0.05 degrees!





