Erosion - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how wind, water, and ice shape our planet's landscapes
What is Erosion?

Erosion is the process where rocks and soil are worn away and moved from one place to another by natural forces like water, wind, or ice. It's different from weathering, which is the breaking down of rocks without moving them.
Think of erosion like nature's moving company! It slowly transports pieces of the Earth's surface to new locations, creating many of the landscapes we see around us - from canyons and valleys to beaches and deltas.
Erosion Fact!
The Grand Canyon was formed over millions of years by erosion from the Colorado River!
Types of Erosion
Erosion happens in several different ways depending on what force of nature is doing the work:
Water Erosion
Moving water in rivers, streams, and rainfall carries away soil and rock particles
Wind Erosion
Wind picks up and carries fine particles, especially in dry areas
Glacial Erosion
Massive sheets of ice scrape and carry rocks as they slowly move
Coastal Erosion
Ocean waves wear away shorelines and cliffs
Gravity Erosion
Rocks and soil move downhill in landslides and rockfalls
Wind Erosion Fact!
Some of Earth's most spectacular geological formations, like Utah's Arches National Park, were created by wind erosion over millions of years!
Causes and Effects of Erosion
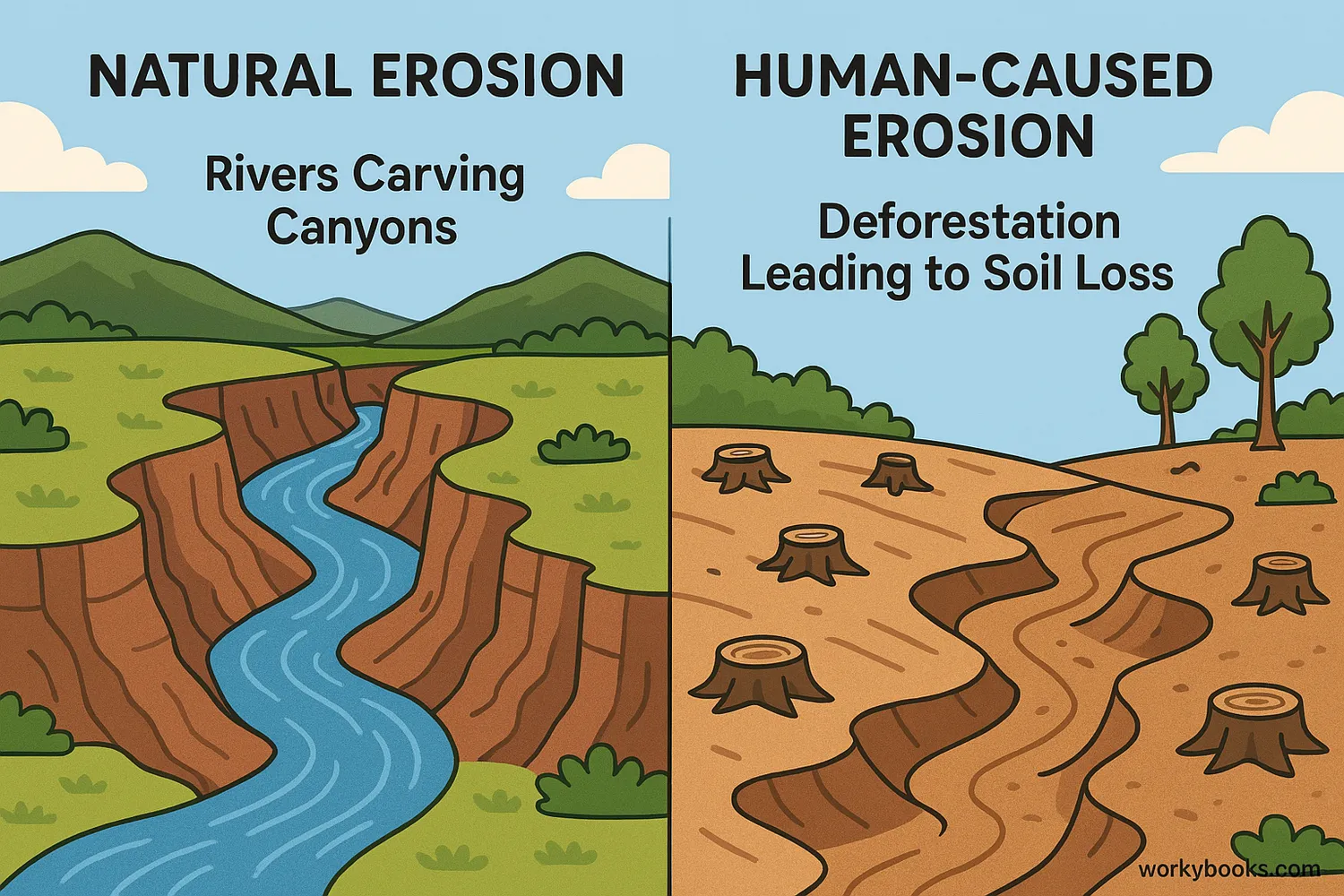
Erosion happens naturally, but human activities can speed it up. Understanding the causes helps us prevent problems.
Natural Causes
Rainfall, flowing water, wind, ice, and gravity are all natural erosion forces
Human Causes
Deforestation, construction, farming, and mining can accelerate erosion
Effects
Loss of fertile soil, water pollution, habitat destruction, and landscape changes
While erosion is a natural process that creates beautiful landscapes, when it happens too quickly it can cause problems:
• Loss of fertile topsoil needed for farming
• Pollution of rivers and lakes with sediment
• Damage to roads and buildings
• Destruction of animal habitats
Erosion Control
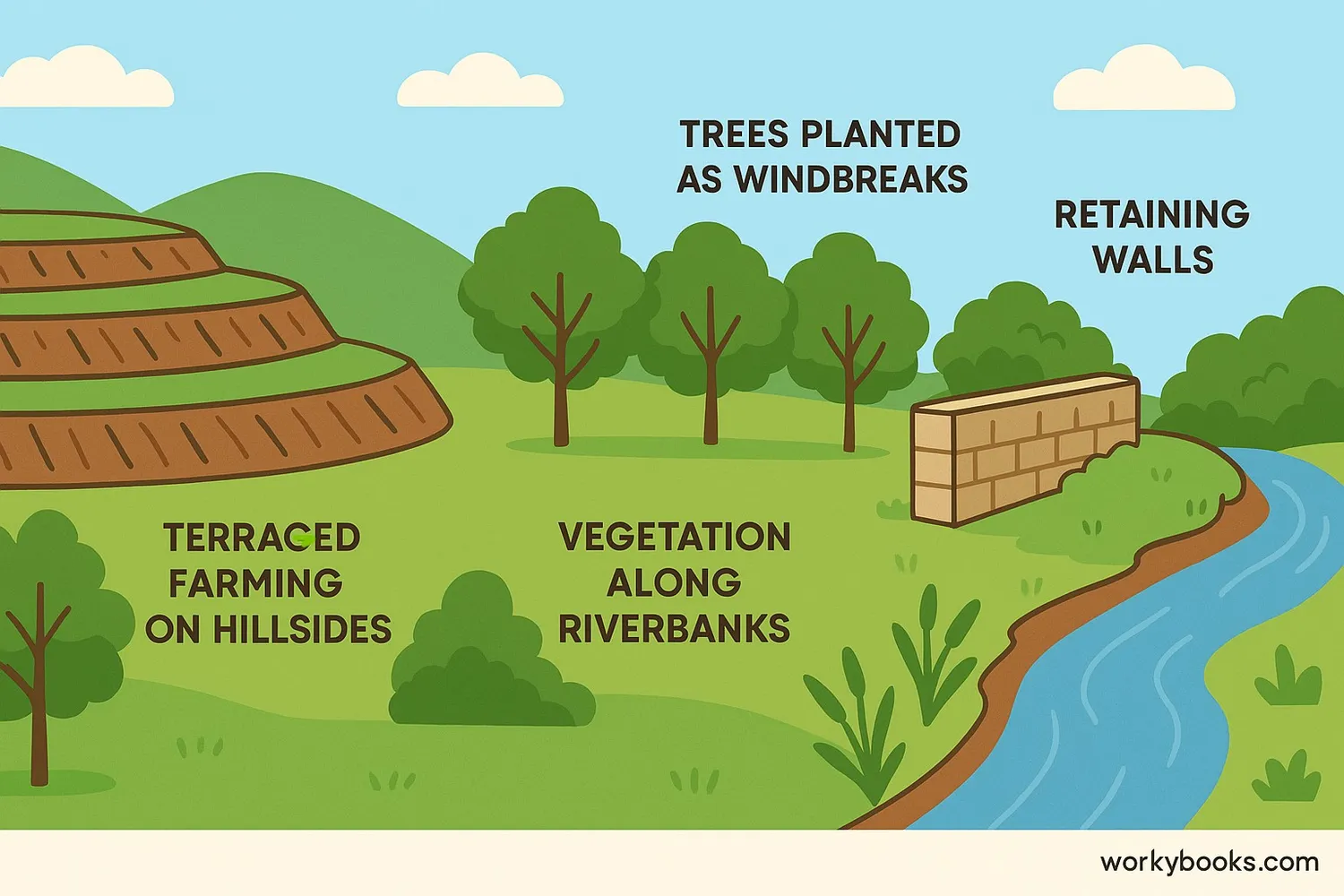
People have developed many ways to slow down erosion and protect the soil. These methods help keep our land healthy and productive.
Planting Vegetation
Plant roots hold soil in place, while leaves protect from rain impact
Terracing
Creating steps on hillsides to slow water runoff
Contour Plowing
Plowing across slopes rather than up and down
Other effective erosion control methods include:
• Building retaining walls in areas with steep slopes
• Using erosion control blankets on bare soil
• Creating windbreaks with trees and shrubs
• Installing proper drainage systems
• practicing no-till farming to keep soil structure intact
Erosion Quiz
Test your erosion knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about erosion:
Fun Erosion Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about erosion!
Grand Canyon Scale
The Grand Canyon is 277 miles long, up to 18 miles wide, and over a mile deep—all carved by erosion from the Colorado River!
Dust Travels Far
Wind erosion can carry dust particles across entire oceans! Dust from the Sahara Desert often travels across the Atlantic to the Amazon rainforest.
Disappearing Coastlines
Some coastlines are eroding at rates of over 6 feet per year! Cape Cod in Massachusetts loses about 3 feet of coastline each year to erosion.
Precious Topsoil
It can take 500-1,000 years to form just 1 inch of topsoil, but erosion can remove it in just a few years if not properly managed.





