Paleomagnetism - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how rocks record Earth's magnetic history
What is Paleomagnetism?
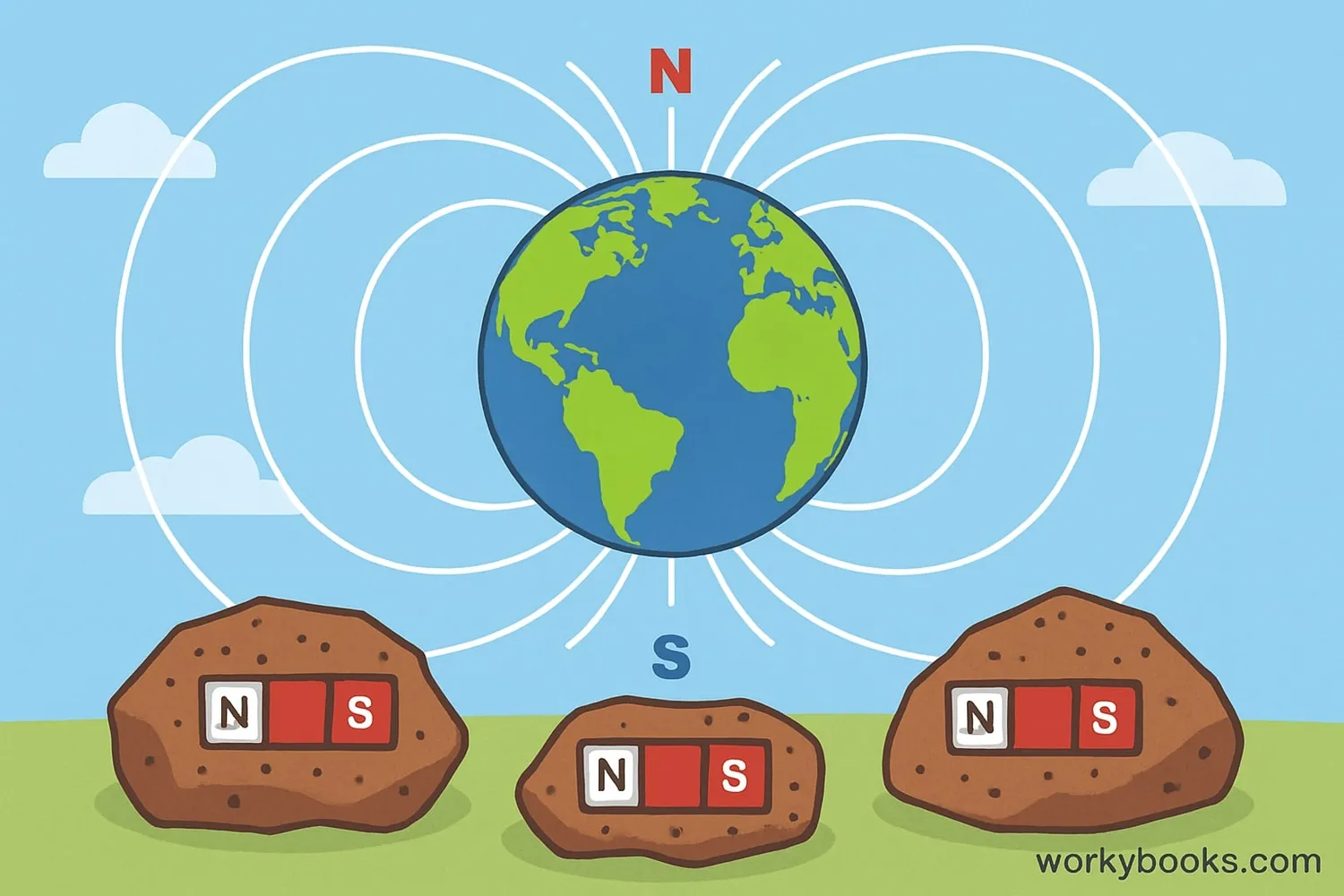
Paleomagnetism is the study of Earth's ancient magnetic field recorded in rocks. Just like a diary keeps memories, rocks can preserve a record of Earth's magnetic field from when they formed!
When rocks form, tiny magnetic minerals inside them align with Earth's magnetic field, like compass needles pointing north. These minerals lock in that magnetic information as the rock hardens. Scientists can measure this magnetism millions of years later to learn about Earth's magnetic history.
Science Fact!
Some rocks are millions of years old, but they still remember which way was north when they formed!
How Paleomagnetism Works

Rocks become magnetic recordkeepers through a special process:
Rock Formation
Rocks form from molten lava or settle as sediments
Mineral Alignment
Tiny magnetic minerals align with Earth's magnetic field
Locking In
As the rock cools or hardens, the magnetic direction is preserved
Discovery
Scientists measure the rock's magnetism with special instruments
Interpretation
The magnetic direction reveals Earth's magnetic field at that time
The most important rocks for paleomagnetism are volcanic rocks (like basalt) and sedimentary rocks containing magnetic minerals. When scientists collect samples from different places and different ages, they can create a timeline of how Earth's magnetic field has changed throughout history.
Magnetic Reversals!
Earth's magnetic poles have completely reversed hundreds of times! When this happens, compasses would point south instead of north.
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
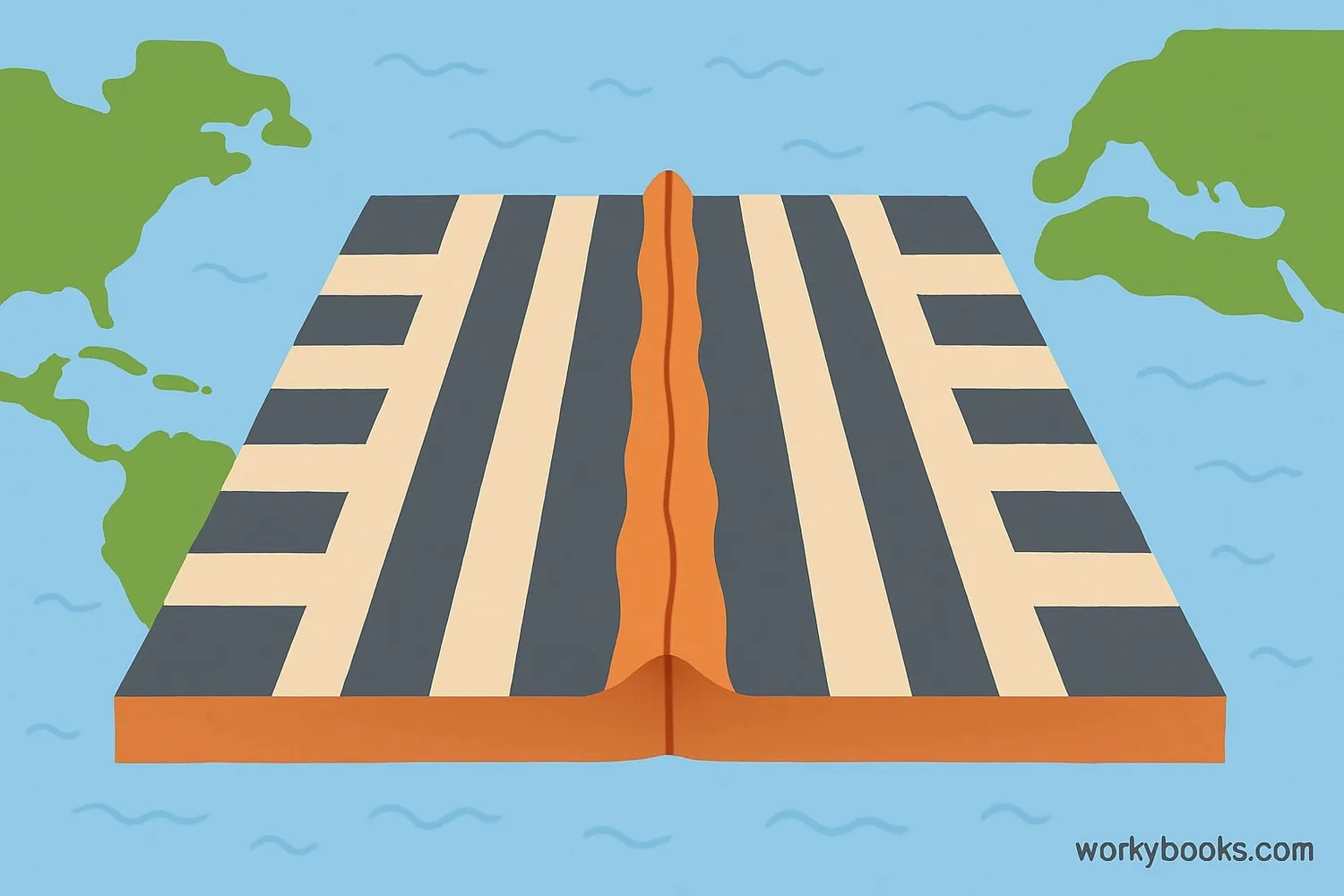
Paleomagnetism provides some of the strongest evidence for plate tectonics. Here's how:
Seafloor Stripes
Ocean floors show alternating bands of normal and reversed magnetism
Symmetrical Patterns
These bands are mirror images on either side of mid-ocean ridges
Continental Movement
Different continents show different magnetic histories
The discovery of magnetic stripes on the ocean floor was revolutionary! It showed that new ocean crust forms at mid-ocean ridges and spreads outward. Each stripe represents a period when Earth's magnetic field was normal or reversed. The symmetrical pattern on both sides of the ridge proves the seafloor is spreading.
Paleomagnetism also helps us understand continental drift. By studying the magnetic direction in rocks of the same age from different continents, scientists can determine how those continents have moved over time.
Dating Rocks!
Scientists use magnetic reversals like barcodes to date rocks. Each reversal has a specific time in Earth's history.
Paleomagnetism Quiz
Test your knowledge with this paleomagnetism quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about paleomagnetism:
Fun Paleomagnetism Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about Earth's magnetic history:
Ancient Records
The oldest magnetic record found in rocks is about 3.5 billion years old! That's older than most fossils and nearly as old as Earth itself.
Speedy Changes
During magnetic reversals, Earth's magnetic poles can move as fast as 6 degrees per day! That's about 600 miles of movement per day at the equator.
Animal Navigation
Pigeons have tiny magnetic minerals in their beaks that help them navigate using Earth's magnetic field, just like ancient rocks record the field!
Space Protection
Earth's magnetic field protects us from solar radiation. During reversals when the field is weaker, we might see more auroras and need better sun protection.




