Transform Boundaries - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how Earth's plates slide past each other to create earthquakes and shape our planet
What is a Transform Boundary?
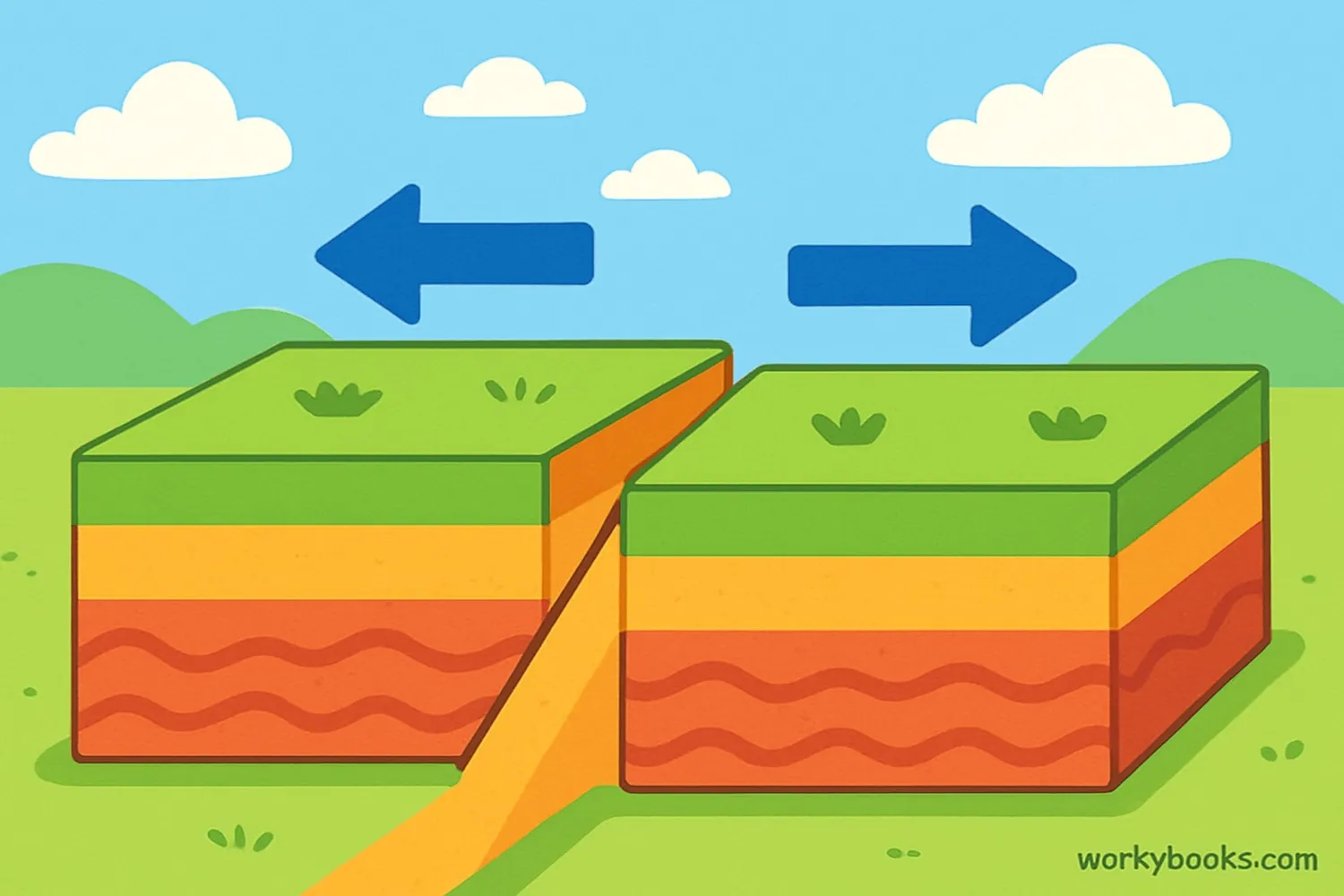
A transform boundary is where two of Earth's tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally. Imagine two huge puzzle pieces rubbing sideways against each other! This movement creates special cracks in Earth's crust called strike-slip faults.
Transform boundaries are different from other plate boundaries:
• Divergent boundaries - where plates move apart
• Convergent boundaries - where plates collide
• Transform boundaries - where plates slide past each other
The most famous transform boundary is the San Andreas Fault in California, where the Pacific Plate and North American Plate slide past each other at about 2 inches per year - that's about as fast as your fingernails grow!
Earth Science Fact!
Transform boundaries don't create or destroy crust - they just move it sideways!
How Transform Boundaries Work
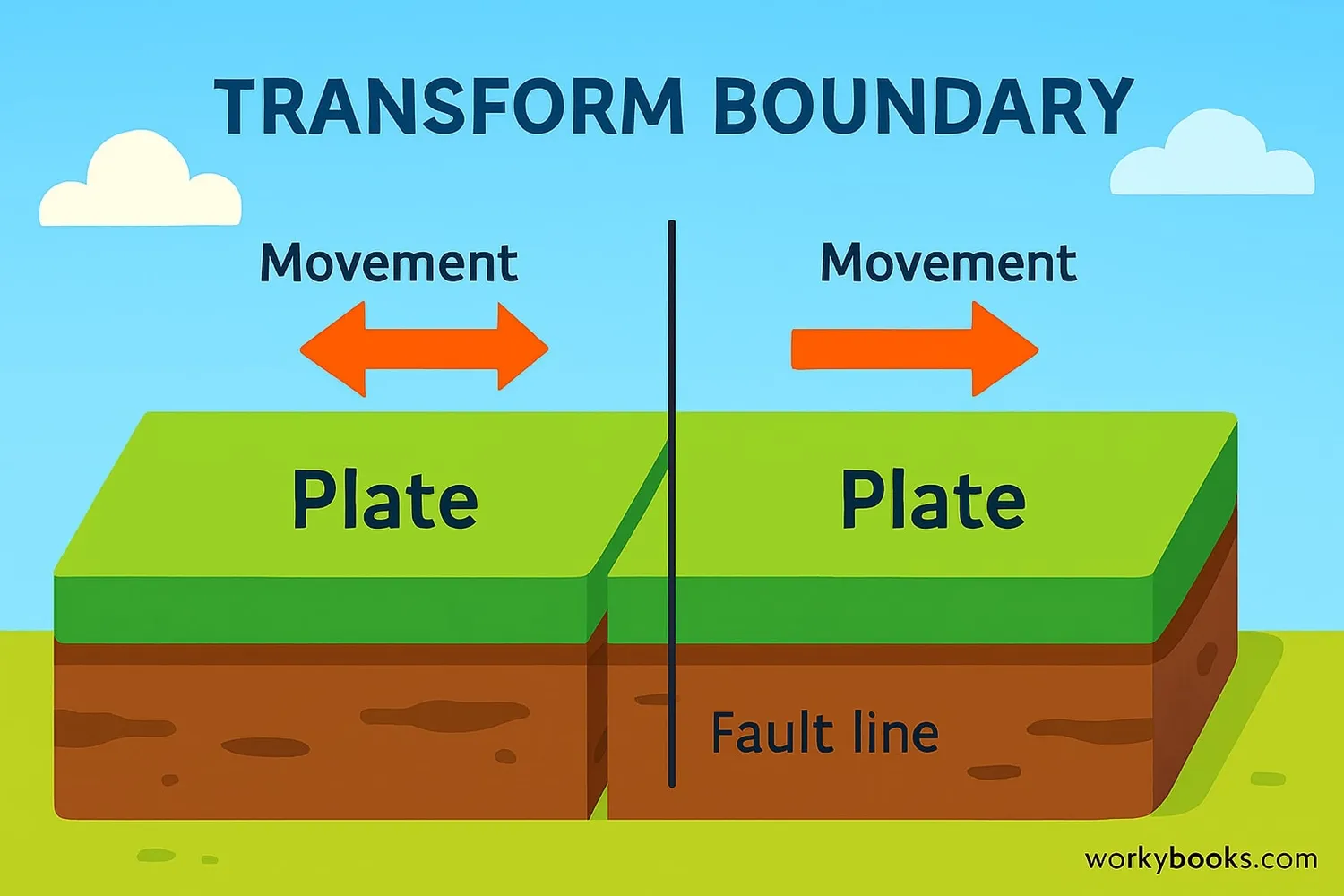
Transform boundaries work through a process called shear motion - where two plates grind past each other like two pieces of sandpaper rubbing together. This happens because:
Plate Movement
Tectonic plates slowly move in different directions
Friction Builds
Rocks along the boundary lock together
Energy Storage
Pressure builds as plates try to move
Sudden Release
Rocks break and plates suddenly slip
Earthquake!
Stored energy releases as seismic waves
Transform boundaries connect other plate boundaries. For example, the San Andreas Fault connects:
• A divergent boundary in the Gulf of California
• A convergent boundary near northern California
This connection helps plates move smoothly around Earth's surface. Most transform boundaries are found on the ocean floor, where they connect segments of mid-ocean ridges.
Fault Fact!
The friction at transform boundaries can cause rocks to melt, creating unique rock formations called "pseudotachylytes"!
Why Transform Boundaries Matter

Transform boundaries are important because they:
Create Earthquakes
Sudden movement along faults releases seismic energy
Shape Landscapes
Offset rivers, valleys, and mountain ranges
Form Ocean Features
Create fracture zones on the seafloor
Transform boundaries affect our lives by:
• Creating earthquake hazards near populated areas
• Shaping the geography where we live
• Helping scientists understand plate tectonics
• Influencing where we build cities and structures
Understanding transform boundaries helps scientists predict earthquake risks and helps communities prepare for seismic events.
Plate Tectonics Quiz
Test your knowledge about transform boundaries and plate tectonics with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about transform boundaries:
Earth Science Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about transform boundaries and plate tectonics:
Highway Offset
The Carrizo Plain section of the San Andreas Fault has offset streams and roads by over 400 feet since the fault formed!
Ocean Fractures
The longest transform fault is the Romanche Fracture Zone in the Atlantic Ocean, stretching over 1,200 miles - longer than the distance from New York to Florida!
Big Shaker
The 1906 San Francisco earthquake (magnitude 7.9) caused the ground to shift up to 20 feet along the San Andreas Fault in just one minute!
Scientific Discovery
The theory of plate tectonics was only widely accepted in the 1960s! Before then, scientists didn't understand how transform boundaries worked.





