Arabian Oryx: A Conservation Success - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how this desert antelope went from extinct in the wild to thriving again
What is the Arabian Oryx?
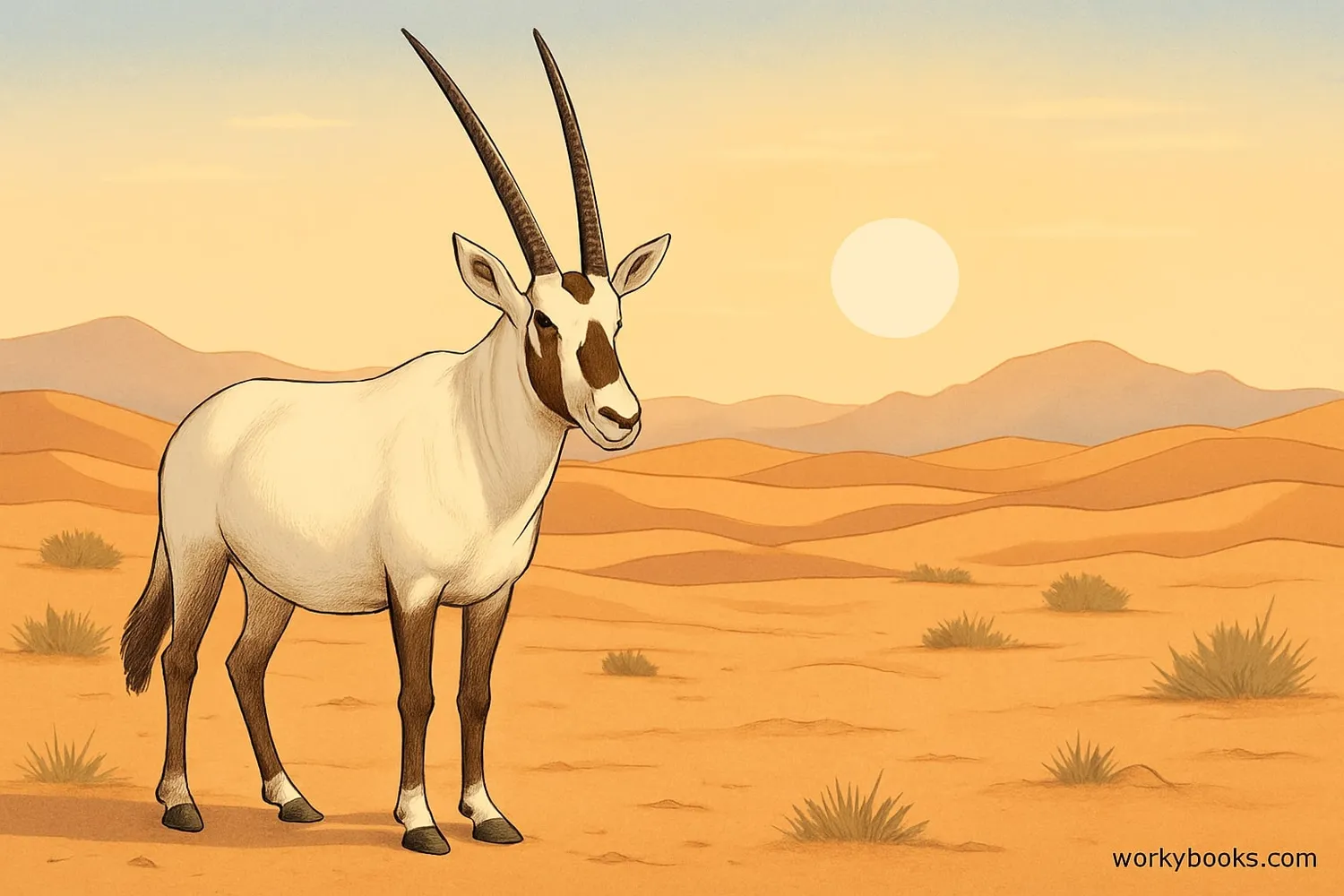

The Arabian Oryx is a medium-sized antelope that lives in the desert regions of the Arabian Peninsula. These beautiful animals are known for their bright white coats and long, straight horns that can grow up to 75 cm (30 inches) long!
The Arabian Oryx is special because it became extinct in the wild in 1972 due to hunting and habitat loss. But through amazing conservation efforts, it became the first animal to ever be upgraded from "Extinct in the Wild" to "Vulnerable" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Today, the Arabian Oryx is a symbol of successful wildlife conservation and teaches us how humans can help save endangered species.
Did You Know?
The Arabian Oryx is the national animal of several countries including Oman, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates!
Physical Characteristics
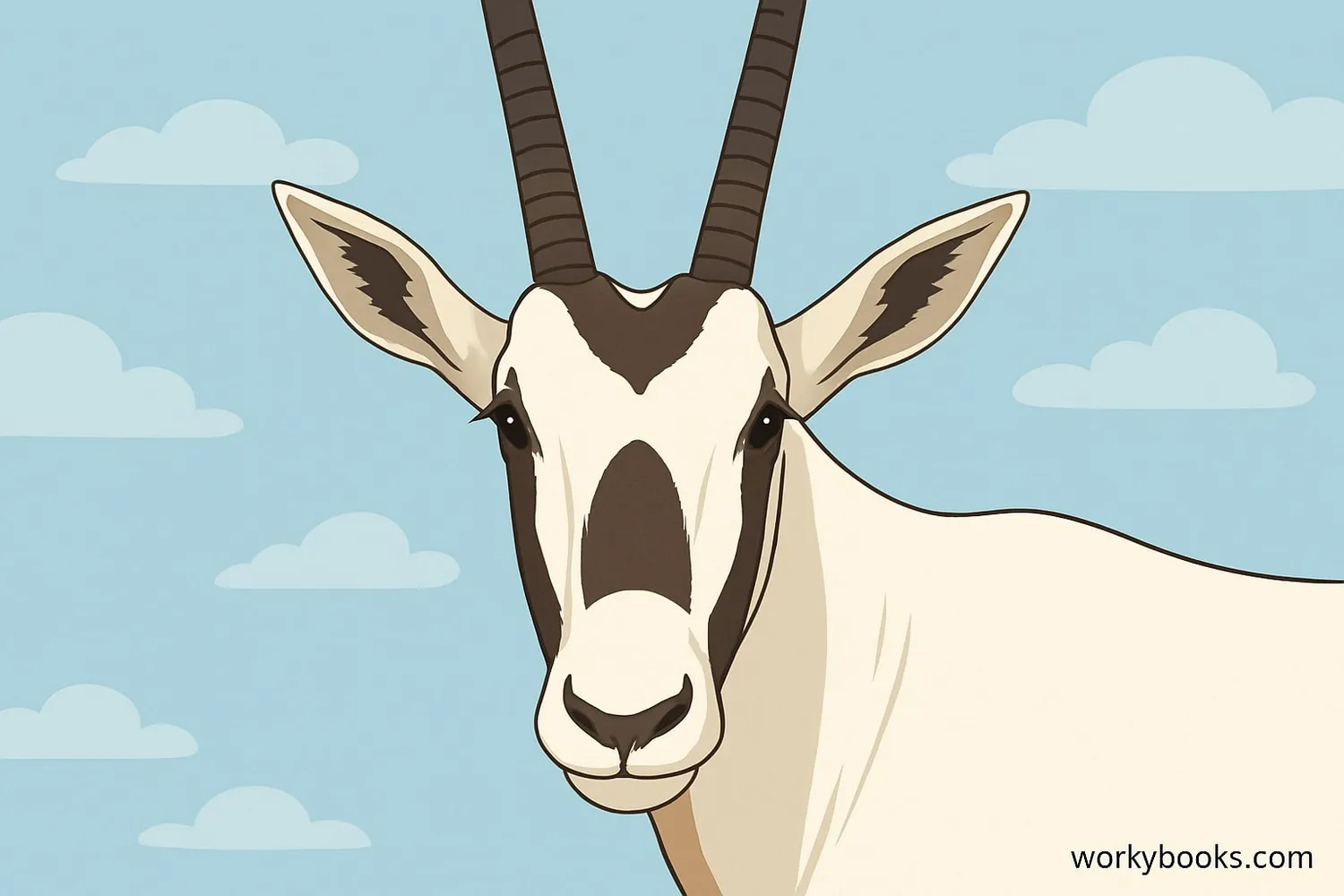

The Arabian Oryx has several special features that help it survive in the harsh desert environment:
White Coat
Reflects sunlight to stay cool in desert heat
Long Horns
Straight horns up to 75 cm long for defense
Hooved Feet
Wide hooves for walking on sand without sinking
Special Nose
Can cool warm air before it reaches the lungs
Dark Markings
Dark patches on face and legs help with camouflage
Arabian Oryx stand about 1 meter (3.3 feet) tall at the shoulder and weigh between 70-80 kg (150-180 pounds). Both males and females have horns, which they use to defend themselves from predators. Their white coat helps reflect the sun's intense heat, while the dark markings on their face and legs help break up their outline in the desert landscape.
Desert Survival
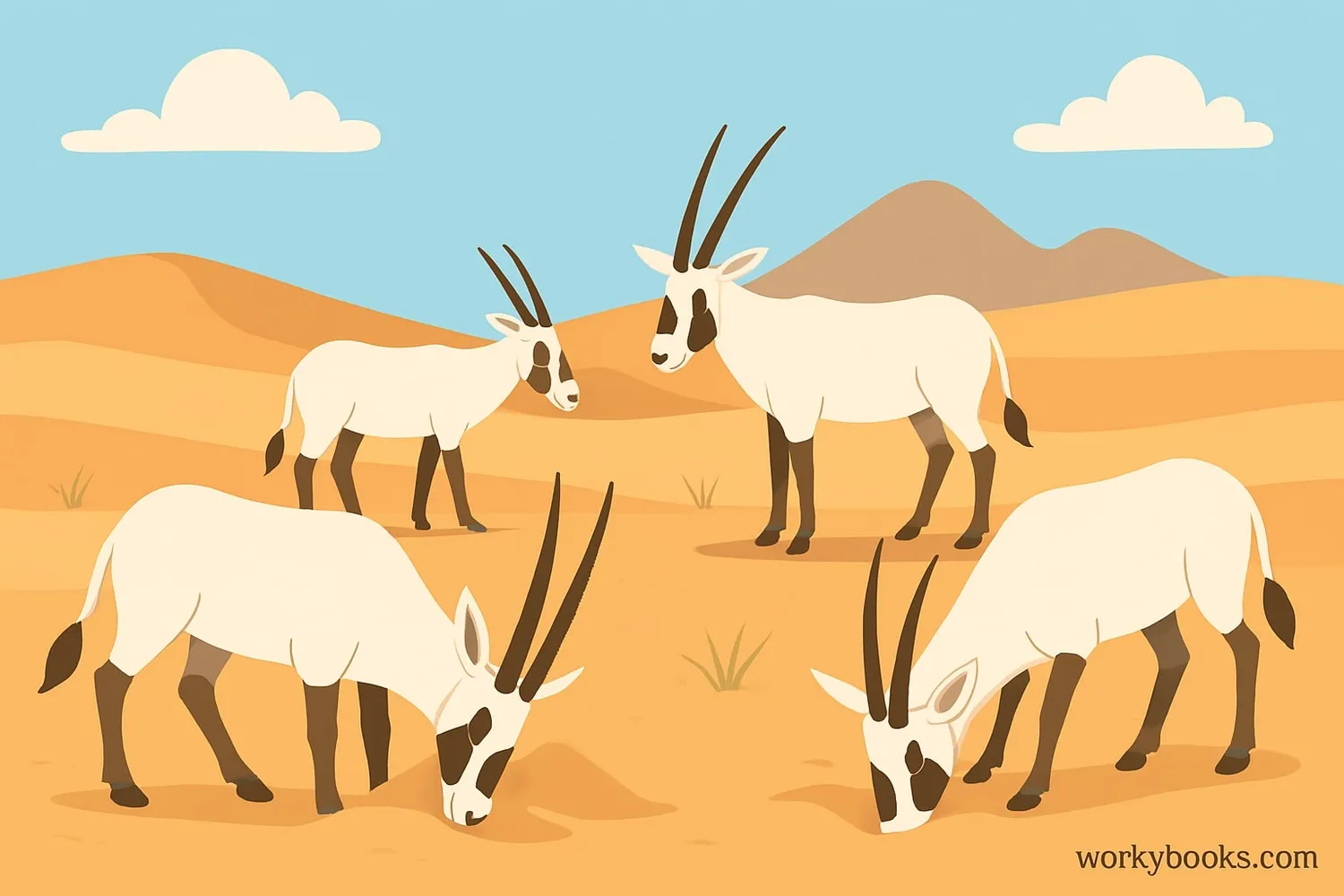

The Arabian Oryx is a true desert survivor! These remarkable animals have adapted to live in some of the harshest environments on Earth:
Water Conservation
Can survive weeks without drinking water by getting moisture from plants
Temperature Control
Can raise body temperature to 46°C (115°F) to avoid sweating
Desert Diet
Eats grasses, herbs, roots, tubers, and even melons when available
Arabian Oryx live in nomadic herds of 2-15 animals, constantly moving to find food. They're most active during early morning and late evening when temperatures are cooler. Their light-colored coat reflects sunlight, and they can raise their body temperature during the day to conserve water - avoiding sweating until nighttime when they can cool down more efficiently.
Remarkably, Arabian Oryx can detect rainfall from great distances and will travel toward it to find fresh vegetation. They can also dig depressions in the sand to reach water that has seeped below the surface after rare desert rains.
Conservation Success Story
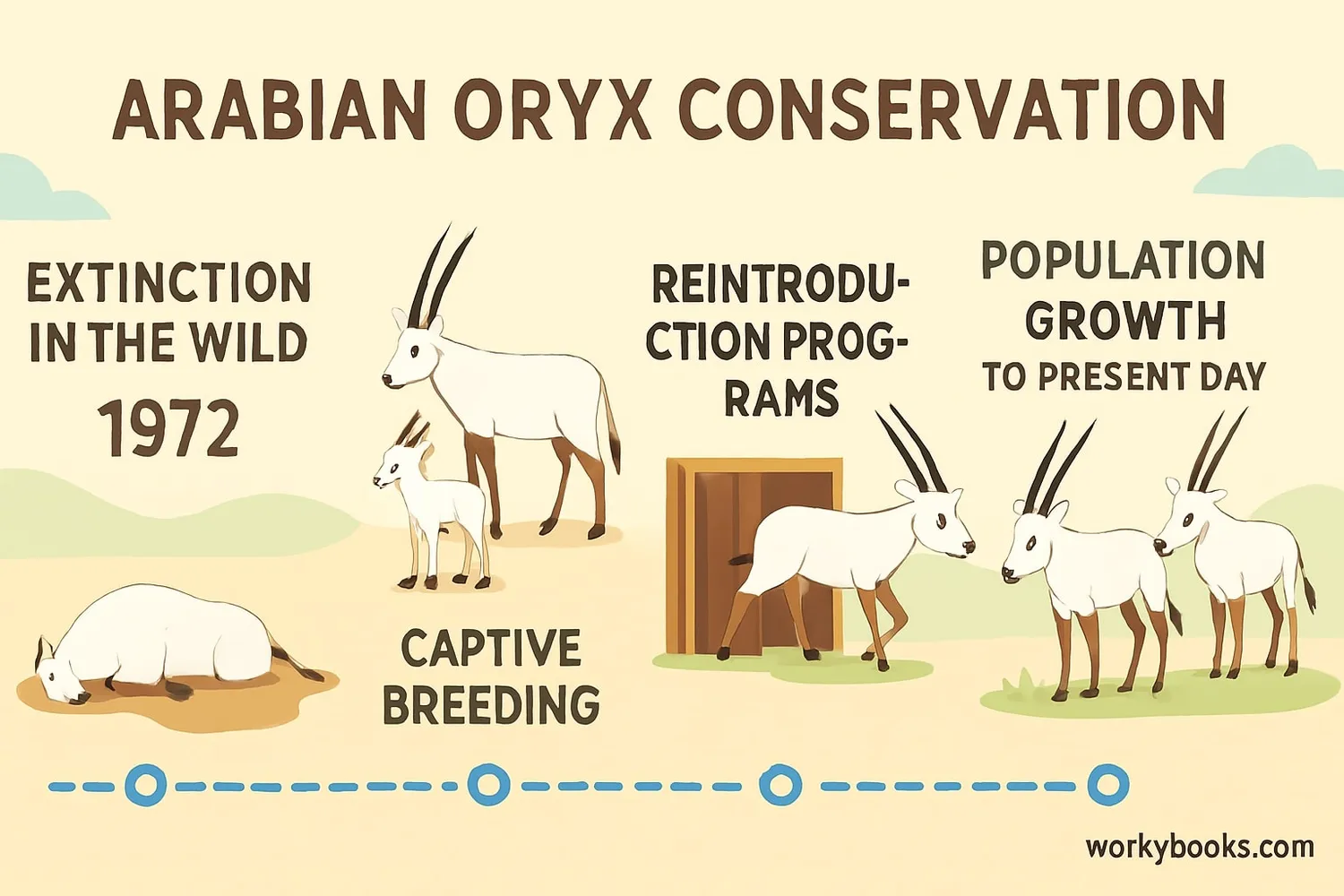
The Arabian Oryx has one of the most remarkable conservation stories in history:
1972: Extinct
Last wild oryx hunted in Oman, declared extinct in wild
Captive Breeding
"Operation Oryx" saved 9 animals to start breeding program
1982: Reintroduction
First oryx released back into wild in Oman
2011: Success!
Upgraded from "Endangered" to "Vulnerable" status
Today
Over 1,200 in wild across Arabian Peninsula
The recovery of the Arabian Oryx is considered one of the world's most successful wildlife conservation programs. It began with "Operation Oryx" in 1962 when conservationists captured the last few wild oryx to start a captive breeding program. From just 9 animals, conservationists bred enough oryx to begin reintroducing them to protected areas in 1982.
Today, there are protected herds in Saudi Arabia, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, and Oman. The population continues to grow thanks to ongoing conservation efforts and protected areas. The Arabian Oryx shows us that with dedication and science, we can bring species back from the brink of extinction!
Conservation Achievement
The Arabian Oryx is the first species to improve by three full categories on the IUCN Red List - from Extinct in the Wild to Vulnerable!
Arabian Oryx Quiz
Test what you've learned about the Arabian Oryx with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Arabian Oryx:
Amazing Arabian Oryx Facts
Discover some fascinating trivia about these desert survivors:
Heat Masters
Arabian Oryx can survive in temperatures over 45°C (113°F)! They raise their body temperature during the day to avoid sweating and lose heat at night.
Water Wizards
These antelope can detect rainfall from 50 miles away! They'll travel toward the rain to find fresh vegetation and water sources.
Horned Marvels
The Arabian Oryx's long, straight horns can grow up to 75 cm (30 inches) - longer than a school ruler! Both males and females have horns.
Cultural Icon
The Arabian Oryx is featured on the currency of Qatar and the emblem of Qatar Airways. It's also the national animal of Oman, UAE, and Jordan.




