Blobfish - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the amazing adaptations of this deep-sea creature
What is a Blobfish?

The blobfish (Psychrolutes marcidus) is a fascinating deep-sea fish that lives in the cold, dark waters off the coasts of Australia, Tasmania, and New Zealand. It's often called the "world's ugliest fish," but this isn't really fair!
What makes the blobfish special is its unique body structure. Unlike most fish, it doesn't have a swim bladder (an air-filled sac that helps with floating). Instead, its body is made of a gelatinous material that is slightly less dense than water. This allows it to float just above the sea floor without using much energy.
Science Fact!
The blobfish only looks "blobby" when brought to the surface. In its deep-sea home, it looks like a normal fish!
Habitat & Adaptations

Blobfish live in extremely deep waters between 600-1200 meters (2,000-4,000 feet) below the surface. At these depths:
Pressure
60-120 times greater than at sea level
Temperature
Just above freezing (2-4°C or 35-39°F)
Light
Complete darkness except for bioluminescence
Blobfish have amazing adaptations for this environment:
Gelatinous body: Their jelly-like flesh allows them to withstand the crushing pressure without being damaged. If brought to the surface, their bodies expand and change shape because the pressure decreases.
Energy conservation: They float just above the seafloor, barely moving, to conserve energy in an environment with scarce food.
Lack of muscle: They don't have strong muscles because they don't need to swim against currents in their deep habitat.
Unique Appearance
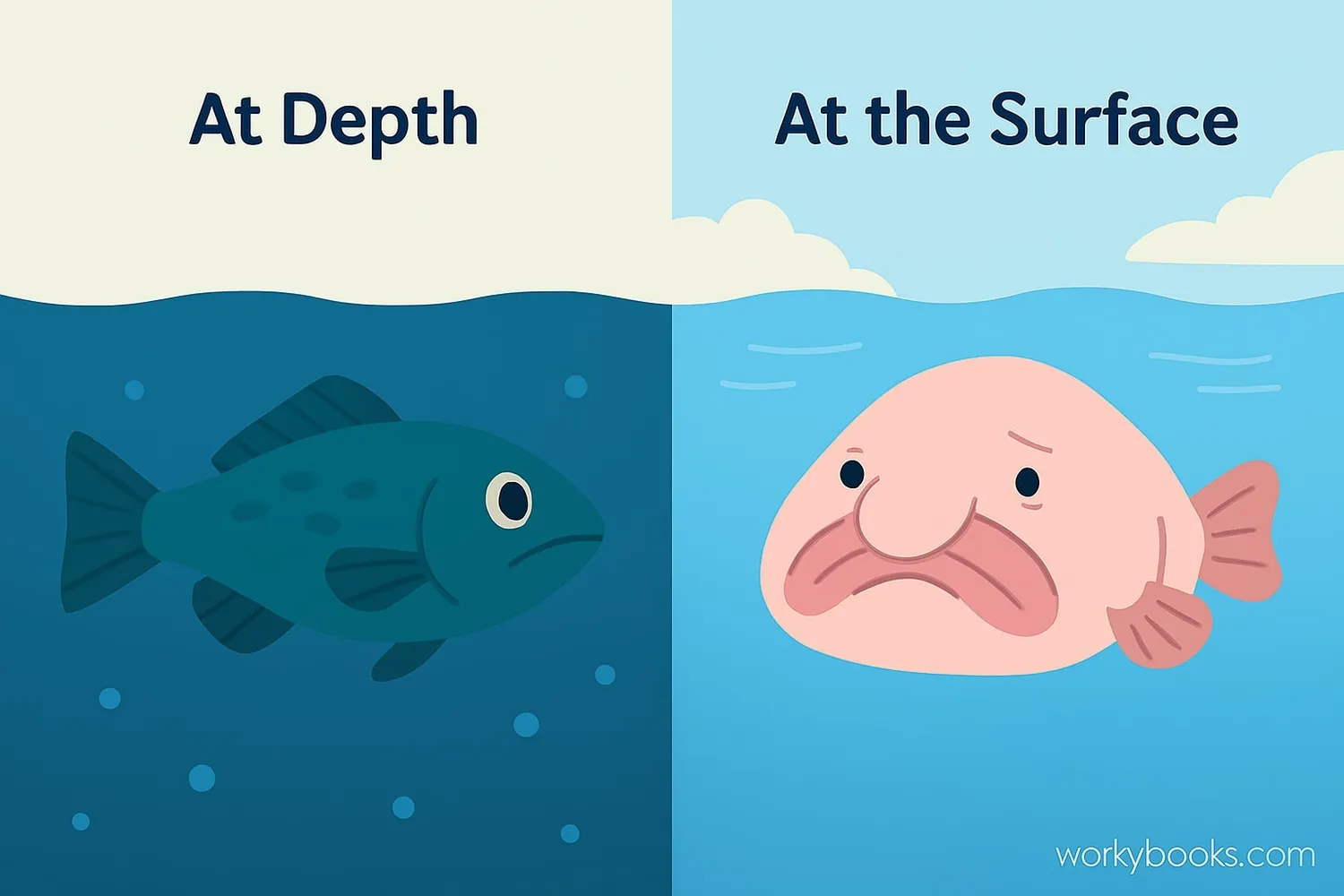
The blobfish's appearance is often misunderstood. Here's what we know about how they look:
Size
Typically 30-40 cm (12-16 inches) long
Color
Pinkish-gray in their natural habitat
Density
Body slightly less dense than water
Why do they look so different at the surface?
When brought to the surface, the blobfish undergoes dramatic changes due to decompression. The extreme pressure difference causes their gelatinous bodies to expand and lose shape. This is why they appear as a "blob" in photographs - it's not how they naturally look!
In their natural habitat, blobfish look more like typical fish with a bulbous head, small eyes, and a large mouth. Their skin is loose and flabby to help them withstand the pressure.
Diet & Lifestyle

Blobfish are opportunistic feeders with a simple lifestyle perfectly adapted to their deep-sea environment:
Energy Conservation Experts
Blobfish use less energy than almost any other fish! They barely move, floating just above the sea floor waiting for food to come to them.
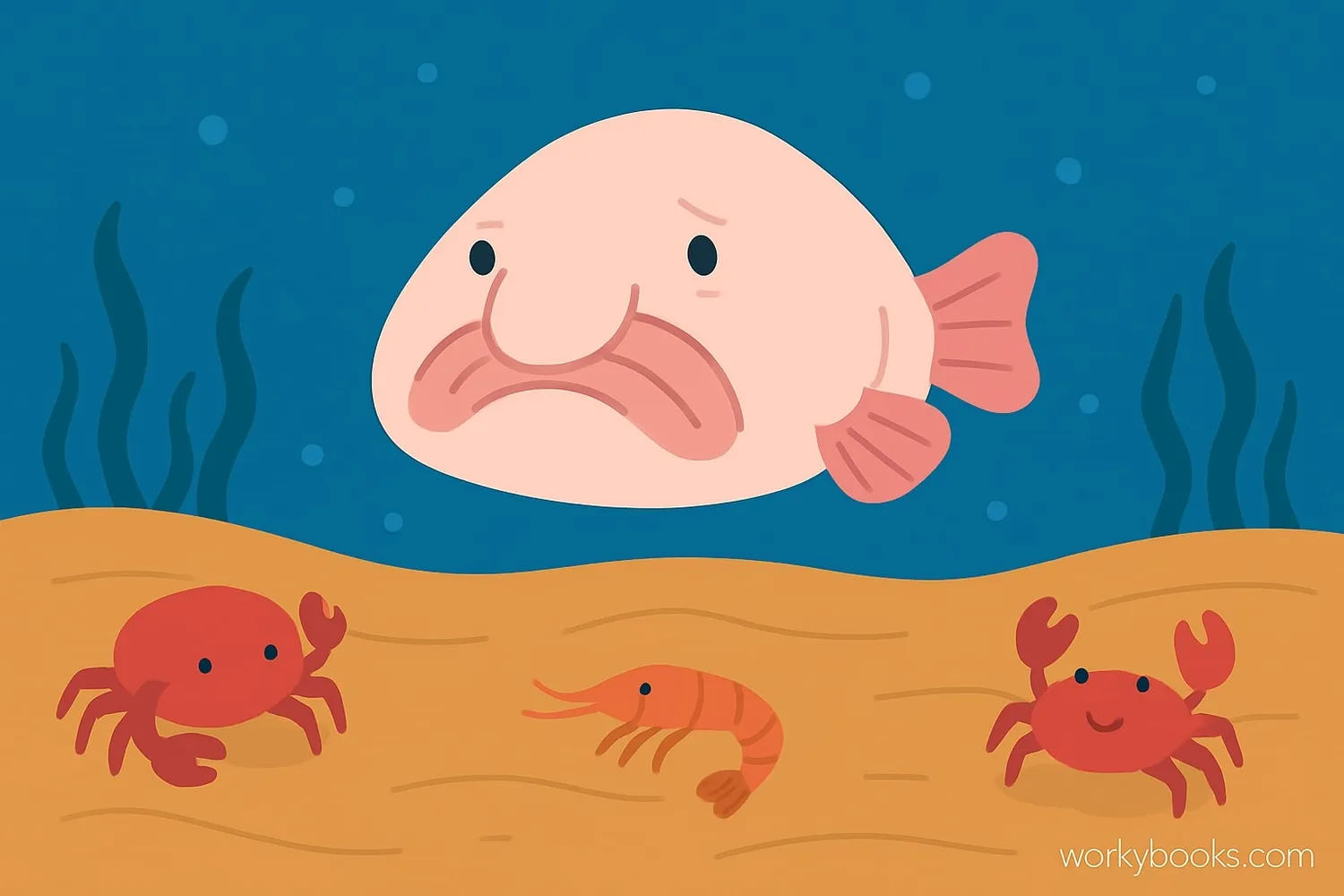
Diet: Blobfish are carnivores that eat:
• Sea urchins
• Crabs and other crustaceans
• Mollusks
• Anything else edible that floats by
They don't chase their food. Instead, they float passively and open their large mouths when prey comes near. Their gelatinous bodies require less energy than bony fish, so they don't need to eat as often.
Reproduction: Female blobfish lay thousands of pink eggs on the seafloor. Both parents guard the eggs until they hatch. The gelatinous body of the blobfish actually helps protect the eggs by covering them like a blanket!
Conservation Status
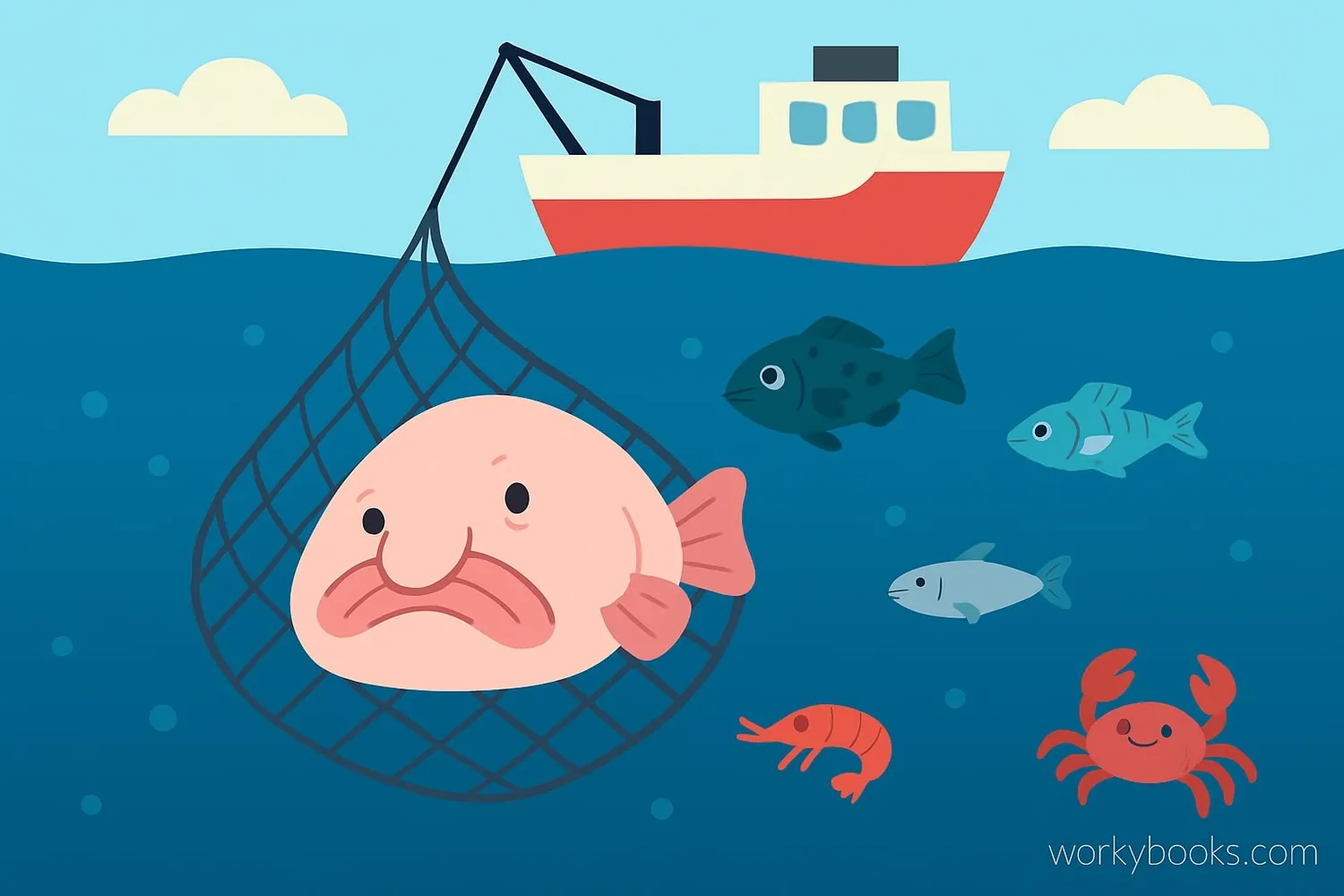

The blobfish faces several threats to its survival:
Deep-sea Trawling
Main threat as they get caught in nets
Climate Change
Ocean warming affects deep-sea ecosystems
Ocean Pollution
Plastics and chemicals reach deep waters
Endangered Status: The blobfish is classified as endangered by several conservation organizations. Their population has declined significantly due to deep-sea trawling where they are caught accidentally as bycatch.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting blobfish requires:
• Restrictions on deep-sea trawling
• Marine protected areas
• Research to understand their population
• Public education about deep-sea ecosystems
Since blobfish live in such deep water, they are difficult to study, which makes conservation challenging. Scientists estimate that their numbers have declined by more than 80% in recent decades.
Blobfish Quiz
Test your knowledge about blobfish with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about blobfish:
Amazing Blobfish Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about blobfish:
Pressure Champions
Blobfish live under pressure 120 times greater than at sea level. That's like having 10 cars stacked on every square inch of your body!
Recent Discovery
Blobfish were only discovered by scientists in 1983! The deep ocean is less explored than the surface of Mars, with new species discovered regularly.
Ugly Mascot
In 2013, the blobfish was voted the "World's Ugliest Animal" and became the official mascot of the Ugly Animal Preservation Society.
Minimal Movement
Blobfish are among the least active fish. They move less than 1% of the time, mostly just opening their mouths to eat passing food.




