Boreal Forest - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the world's largest land biome and its importance to our planet
What is the Boreal Forest?

The boreal forest, also known as the taiga biome, is a vast expanse of coniferous forests that circles the Earth just below the Arctic Circle. It's the world's largest land biome, covering about 17% of Earth's land surface!
These forests are found across northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. In North America, the boreal forest stretches across Alaska, Canada, and parts of the northern United States. The name "boreal" comes from Boreas, the Greek god of the north wind.
Quick Fact!
The boreal forest stores nearly twice as much carbon as tropical forests, making it incredibly important for our planet's climate!
Boreal Forest Ecosystem
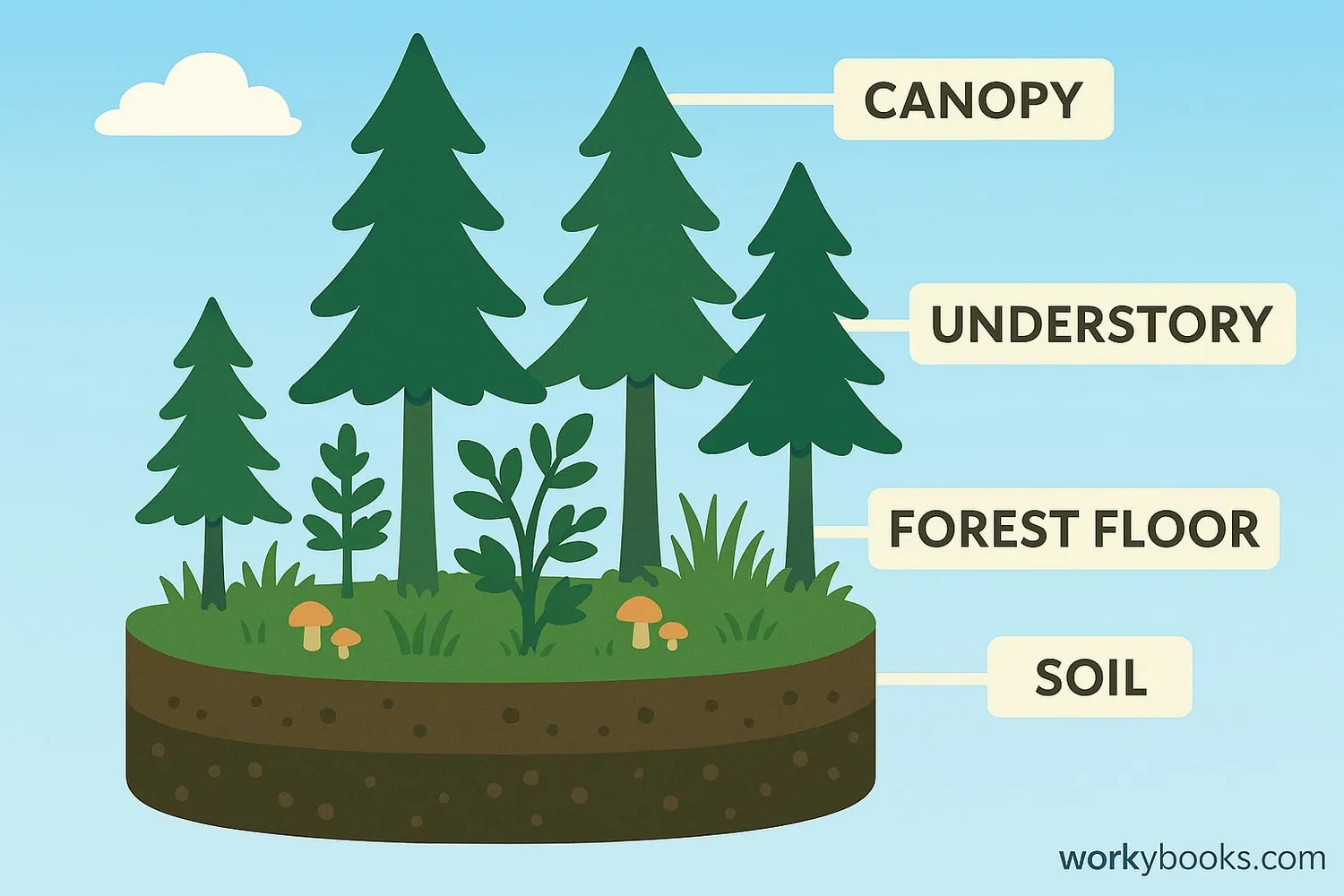
The boreal forest ecosystem has unique characteristics that allow it to thrive in cold northern climates:
Climate
Long, cold winters (down to -65°F) and short, mild summers
Soil
Thin, acidic soil with permafrost in many areas
Water
Numerous lakes, rivers, and wetlands throughout
Seasons
Distinct seasonal changes with snow cover 6-8 months
Fire Ecology
Natural forest fires renew the ecosystem periodically
The boreal forest ecosystem is specially adapted to survive extreme conditions. The cold temperatures slow decomposition, creating thick layers of moss and peat. This unique environment supports a diverse community of plants and animals that have developed special adaptations for survival.
Boreal Forest Plants

Boreal forests are dominated by conifer trees that have adapted to survive the harsh climate. Their special features include:
Conifer Trees
Spruce, pine, fir, and larch trees with needle-like leaves
Needle Adaptations
Waxy coating prevents water loss in winter
Conical Shape
Sloping branches shed heavy snow easily
Other common boreal plants include:
• Deciduous trees: Birch, aspen, and willow
• Shrubs: Blueberry, cranberry, and Labrador tea
• Ground cover: Mosses, lichens, and ferns
• Wildflowers: Fireweed and twinflower during short summers
These plants form distinct layers in the forest, creating diverse habitats for animals.
Boreal Forest Animals
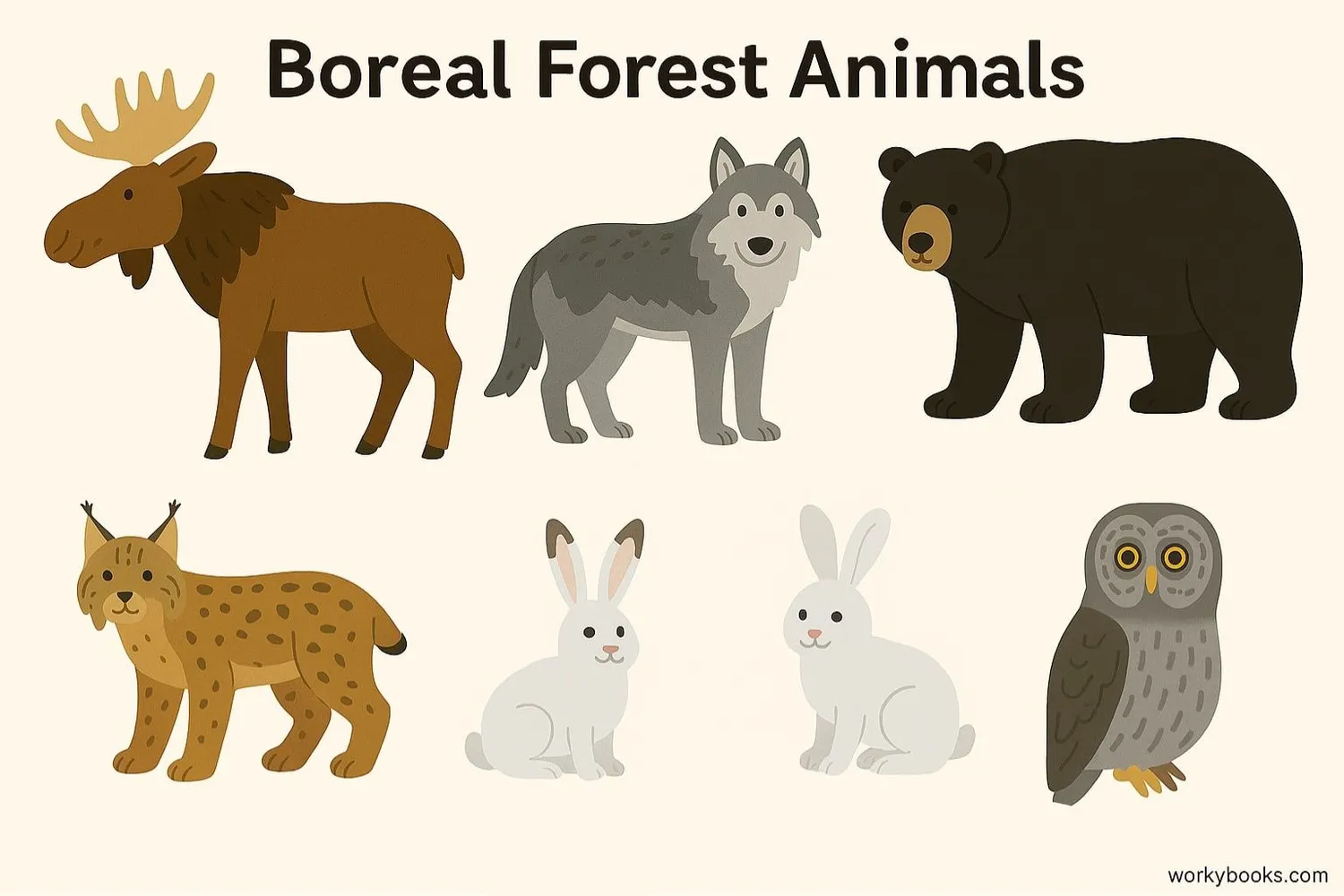

The boreal forest supports a rich diversity of wildlife that has adapted to survive the extreme seasons. Animals have developed special strategies like hibernation, migration, and camouflage.
Large Mammals
Moose, black bears, wolves, lynx, and caribou
Birds
Over 300 bird species including owls, woodpeckers, and migratory songbirds
Aquatic Life
Fish like northern pike, lake trout, and whitefish in countless lakes
Many boreal forest animals have special adaptations:
• Snowshoe hares change color from brown to white in winter
• Lynx have large paws that act as snowshoes
• Birds migrate south during the harsh winter months
• Bears hibernate through the coldest period
• Insects like mosquitoes thrive during the short summer
Why Boreal Forests Are Important
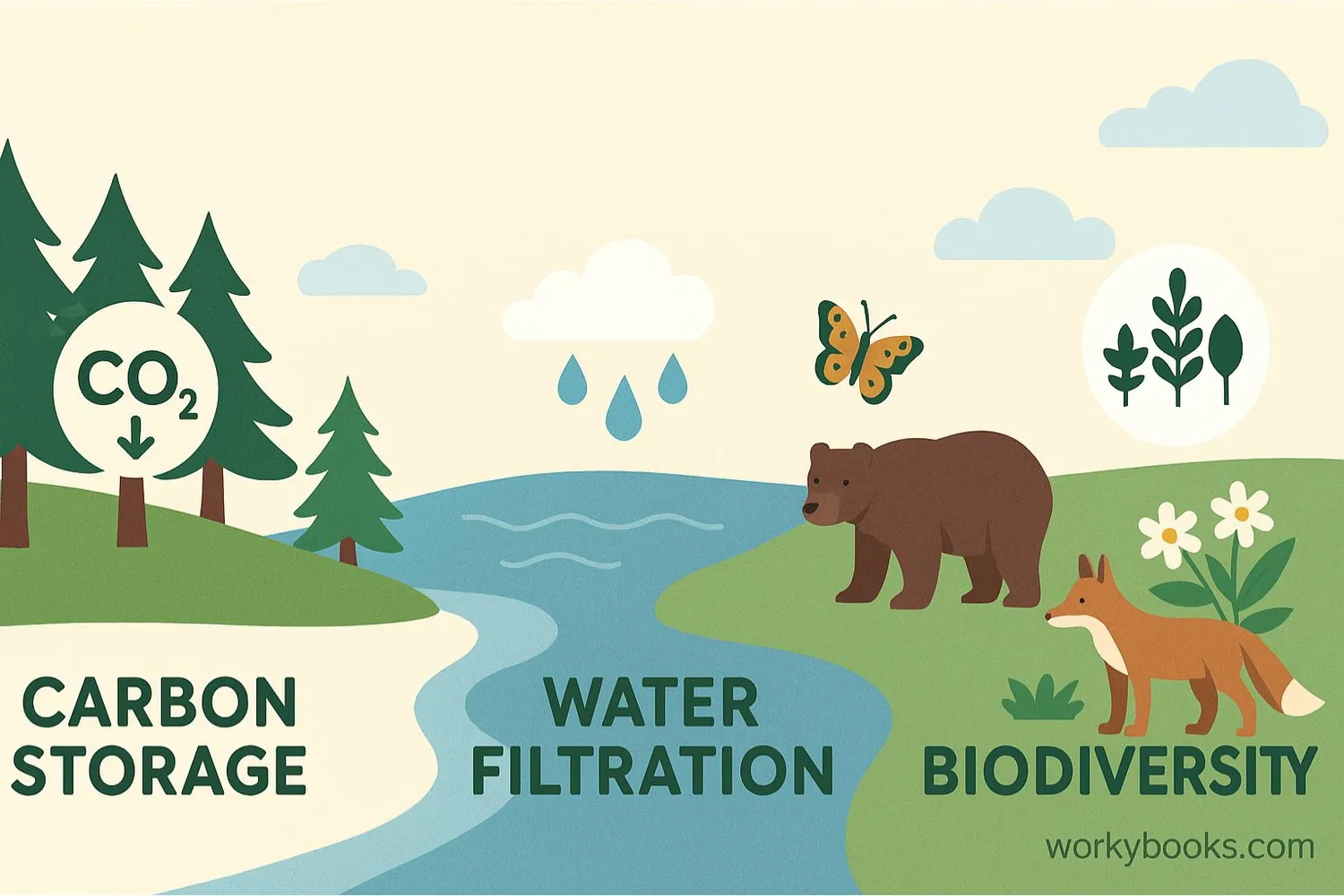
Boreal forests play crucial roles that benefit the entire planet:
Climate Regulation
Store massive amounts of carbon, helping combat climate change
Water Cycle
Filter and regulate freshwater for millions of people
Biodiversity
Support thousands of plant and animal species
Additional important roles include:
• Home to Indigenous communities with rich cultural traditions
• Source of timber and other forest products
• Natural barrier against permafrost thaw
• Recreation and tourism opportunities
• Scientific research on climate and ecosystems
Protecting boreal forests is essential for maintaining global ecological balance.
Boreal Forest Quiz
Test your boreal forest knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about boreal forests:
Fun Boreal Forest Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about boreal forests!
Massive Scale
The boreal forest is the world's largest land-based biome, covering approximately 11% of Earth's land surface - that's about 17 million square kilometers!
Carbon Superhero
Boreal forests store more carbon than any other terrestrial ecosystem - about 703 gigatons! That's nearly twice as much as tropical forests per hectare.
Freshwater Source
The boreal forest holds about one-third of Earth's surface freshwater in its countless lakes, rivers, and wetlands. It's often called "North America's water tower."
Bird Nursery
Nearly half of North America's bird species depend on boreal forests for breeding. Up to 3 billion birds migrate from the boreal forest each fall!




