Cell Theory - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the fundamental principles that explain all living things
What is Cell Theory?
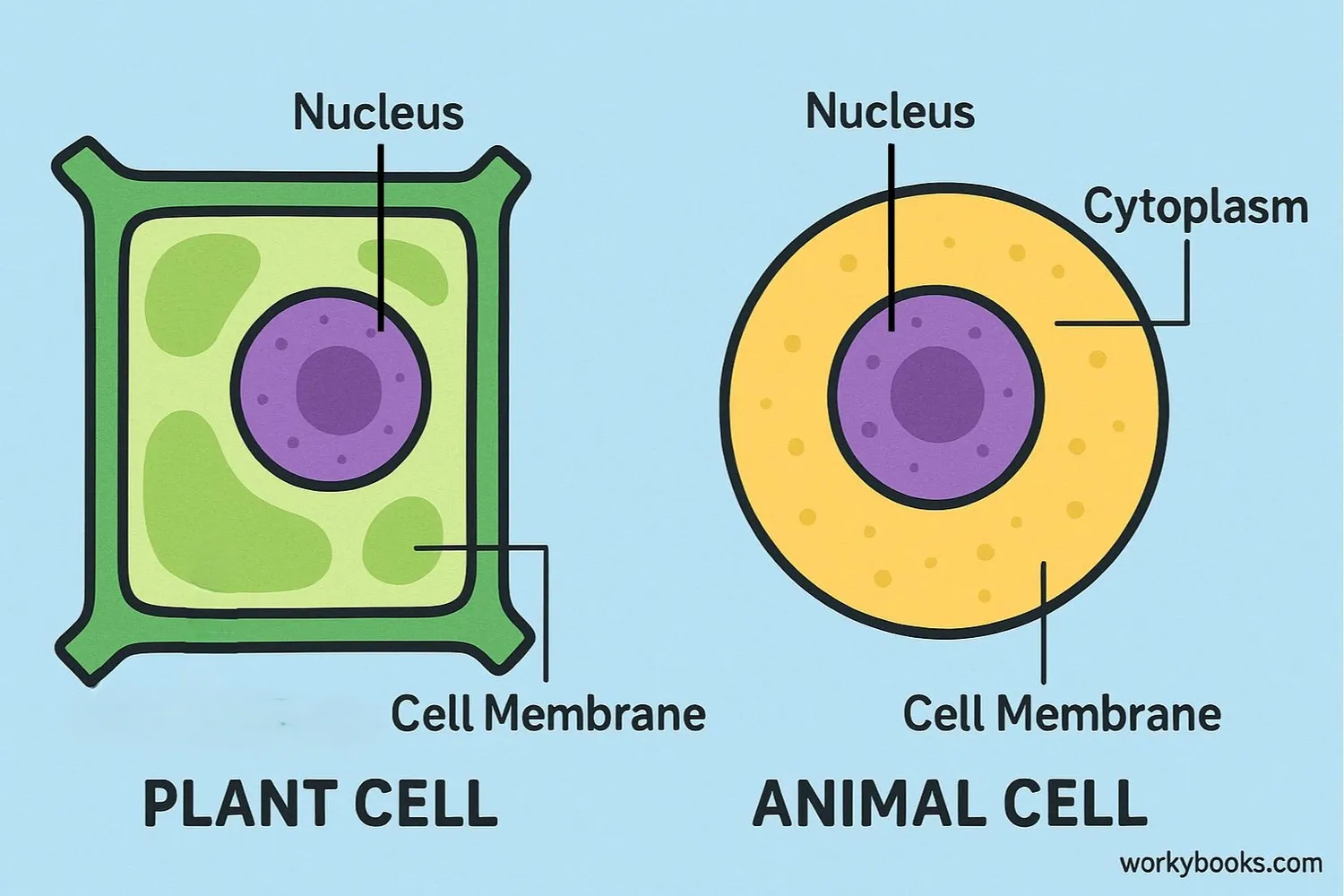
Cell theory is one of the most important ideas in biology! It explains that:
1. All living things are made of cells - From tiny bacteria to giant whales, every living thing is composed of cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function - Cells are like the building blocks of life.
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells - New cells are created when existing cells divide.
Think of cells as the "atoms" of living things - they're the smallest units that have all the characteristics of life. Cells can take in nutrients, grow, respond to their environment, and reproduce.
Science Fact!
The human body has about 37 trillion cells! That's 37,000,000,000,000 cells working together to keep you alive.
History of Cell Theory

The discovery of cells and development of cell theory took many years and the work of several scientists:
Robert Hooke
Looked at cork through a microscope and saw tiny compartments he called "cells" because they reminded him of monks' rooms in a monastery.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
First to observe living cells! He saw tiny "animalcules" (bacteria) in pond water using his improved microscope.
Matthias Schleiden
Studied plants and concluded that all plants are made of cells.
Theodor Schwann
Studied animals and concluded that all animals are made of cells.
Rudolf Virchow
Proposed that all cells come from pre-existing cells, completing the three main principles of cell theory.
Microscope Fact!
Early microscopes could only magnify objects about 30 times. Today's electron microscopes can magnify up to 10 million times!
Main Tenets of Cell Theory
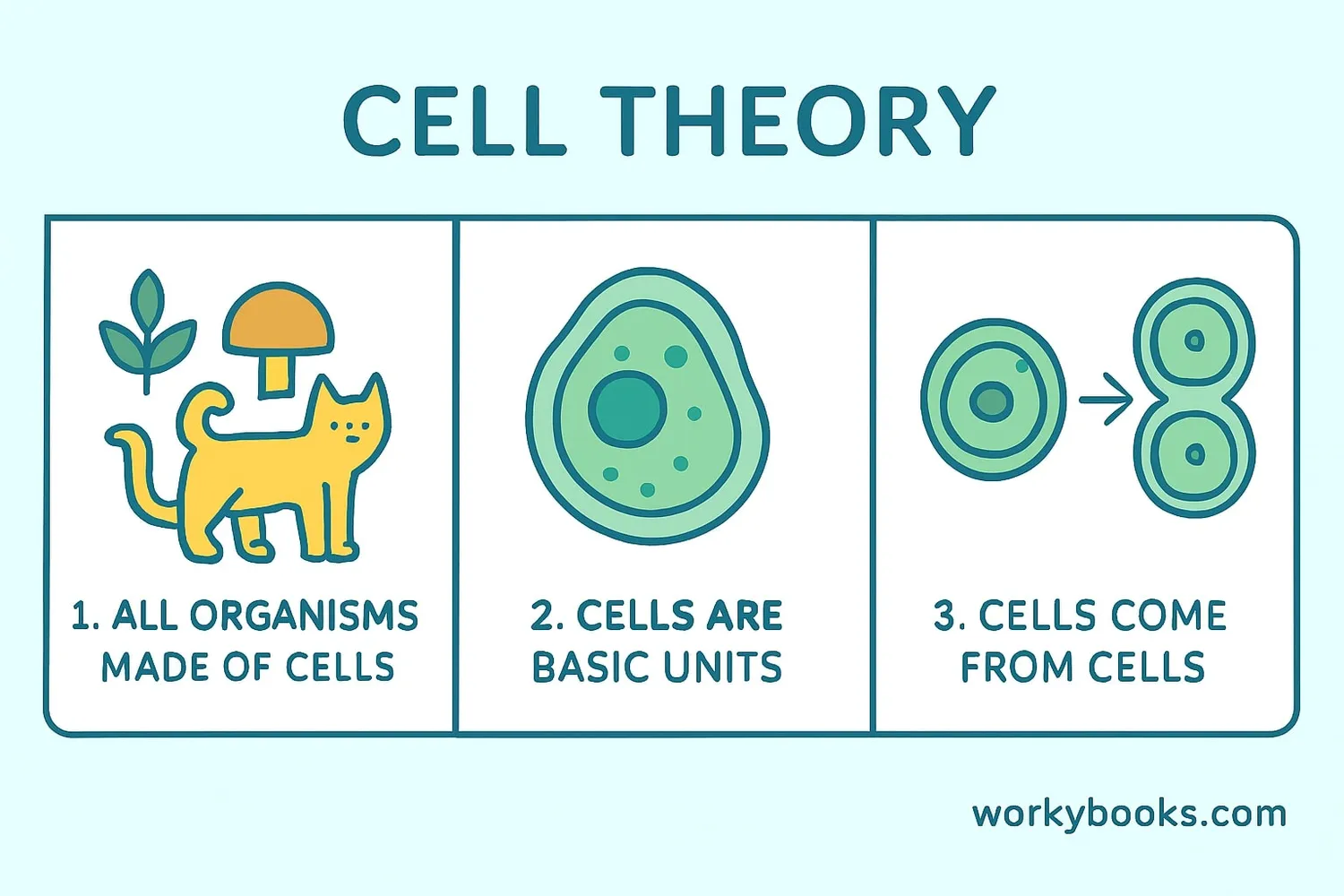
The classic cell theory has three fundamental principles:
All Living Things
Every organism, from the smallest bacteria to the largest tree or animal, is composed of one or more cells.
Basic Units
Cells are the basic building blocks of structure and organization in all living things.
Cell Division
New cells are formed only from pre-existing cells through cell division.
These principles help scientists understand how living things are organized and how they grow. When you scrape your knee, new cells form to heal the wound. When you grow taller, your cells are dividing and multiplying. All of this happens because of the principles of cell theory!
Modern Cell Theory
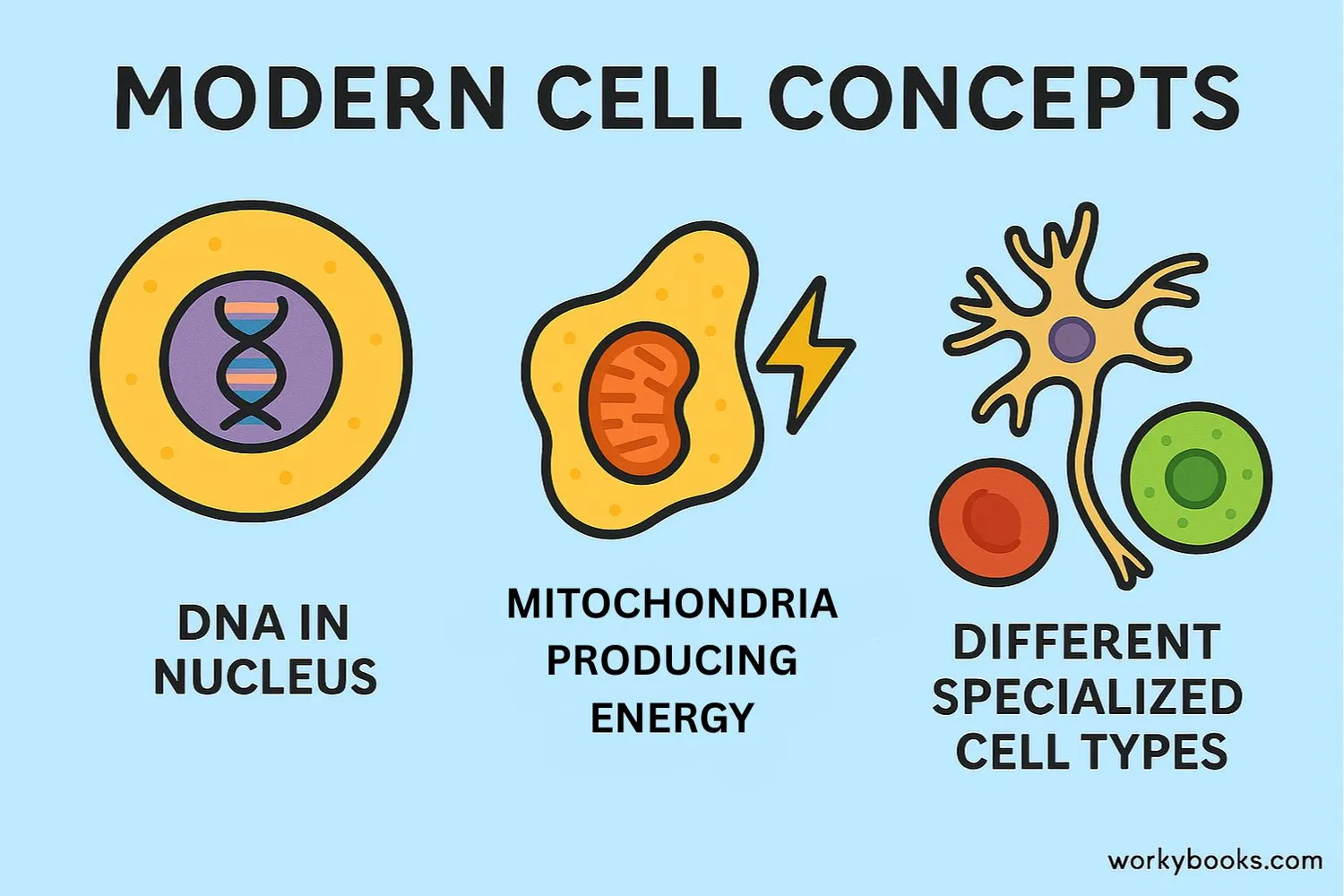
Since the original cell theory was developed, scientists have added new ideas based on discoveries:
Genetic Material
Cells contain DNA which is passed from cell to cell during division
Energy Flow
Energy flow (metabolism) occurs within cells
Similar Chemistry
All cells have similar chemical composition
Disease Understanding
Disease results from problems at the cellular level
These modern additions help us understand how cells work together in complex organisms. For example, in humans, we have over 200 different types of cells - nerve cells, blood cells, muscle cells - each with specialized functions but all following the same basic principles.
Key Contributors to Cell Theory
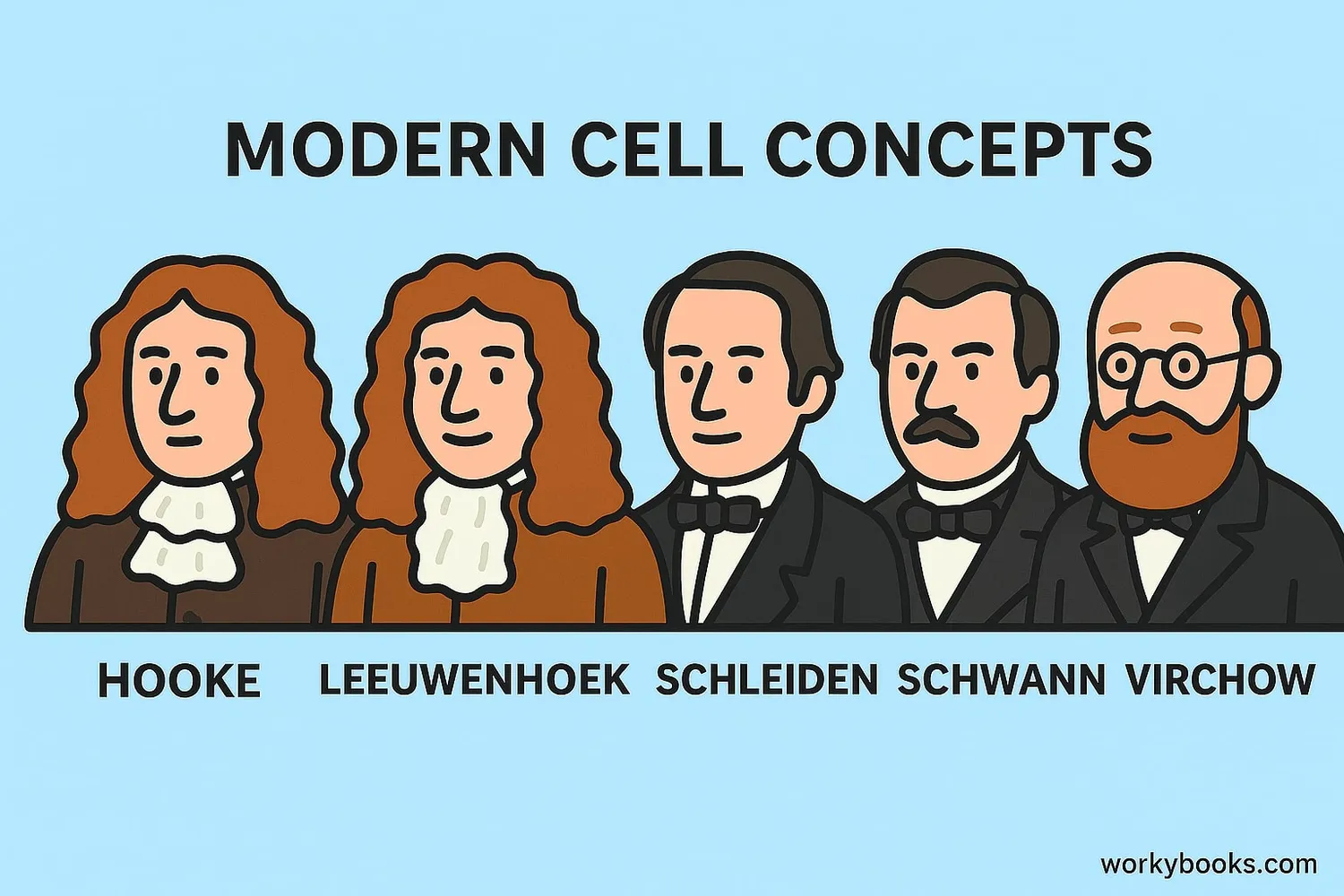
Several important scientists contributed to our understanding of cells:
Robert Hooke
First to use the term "cell" (1665)
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
First to observe living cells (1674)
Matthias Schleiden
Concluded all plants are made of cells (1838)
Theodor Schwann
Concluded all animals are made of cells (1839)
Rudolf Virchow
Proposed cells come from pre-existing cells (1855)
These scientists built on each other's work over nearly 200 years to develop the complete cell theory we know today. Without their careful observations and experiments, we wouldn't understand how living things are organized at the cellular level!
Cell Theory Quiz
Test your cell theory knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about cell theory:
Fun Cell Theory Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about cells and cell theory!
Size Matters
About 10,000 human cells could fit on the head of a pin! The average human cell is 10-30 micrometers wide.
Brain Power
Your brain has about 86 billion neurons (nerve cells). If you counted one every second, it would take you over 2,700 years to count them all!
Bacterial Majority
There are more bacterial cells in your body than human cells! Scientists estimate you have about 39 trillion bacterial cells.
Cellular Lifespan
Different cells have different lifespans. White blood cells live about 13 days, while cells in your brain can live your entire lifetime!





