Gregor Mendel - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how a monk's pea plant experiments revealed the secrets of inheritance
Who Was Gregor Mendel?

Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and scientist who lived from 1822 to 1884. He is called the father of genetics because his experiments with pea plants revealed how traits are passed from parents to offspring.
Mendel worked in a monastery but had a deep interest in science. He spent years carefully breeding pea plants and recording his results. His work wasn't fully appreciated during his lifetime, but today we recognize his discoveries as the foundation of modern genetics.
Science Fact!
Mendel studied over 28,000 pea plants during his experiments, carefully tracking seven different traits!
Mendel's Pea Plant Experiments
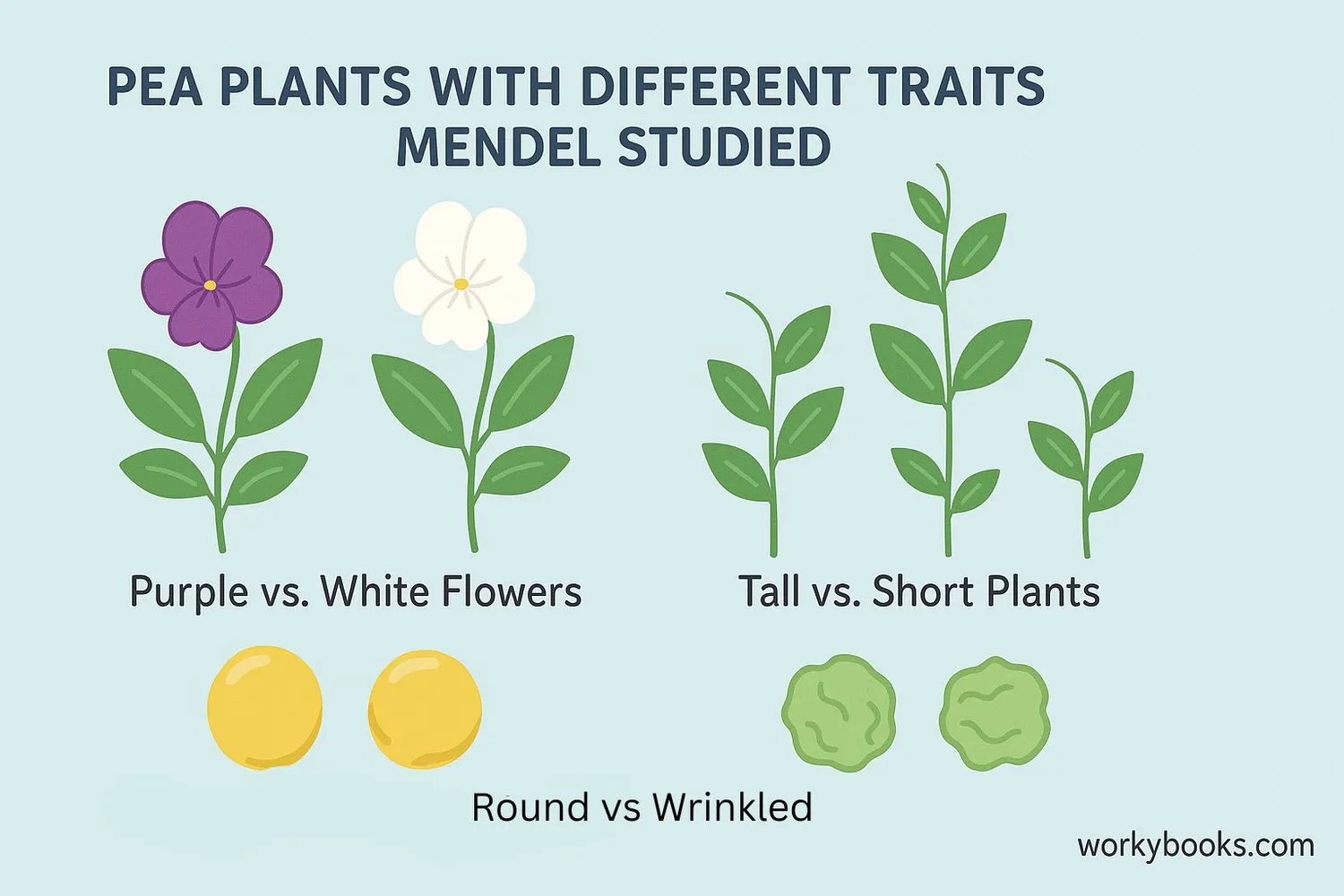
Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments because they:
Clear Traits
Had easily distinguishable characteristics like flower color and seed shape
Fast Growth
Grew quickly, allowing many generations to be studied
Self-Pollinate
Could control which plants bred with which
Mendel cross-pollinated plants with different traits (like purple vs white flowers) and carefully counted the results in each generation. He discovered mathematical patterns in how traits appeared and disappeared.
Scientific Method
Mendel was one of the first scientists to use mathematics to explain biological patterns, making his work very advanced for its time.
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
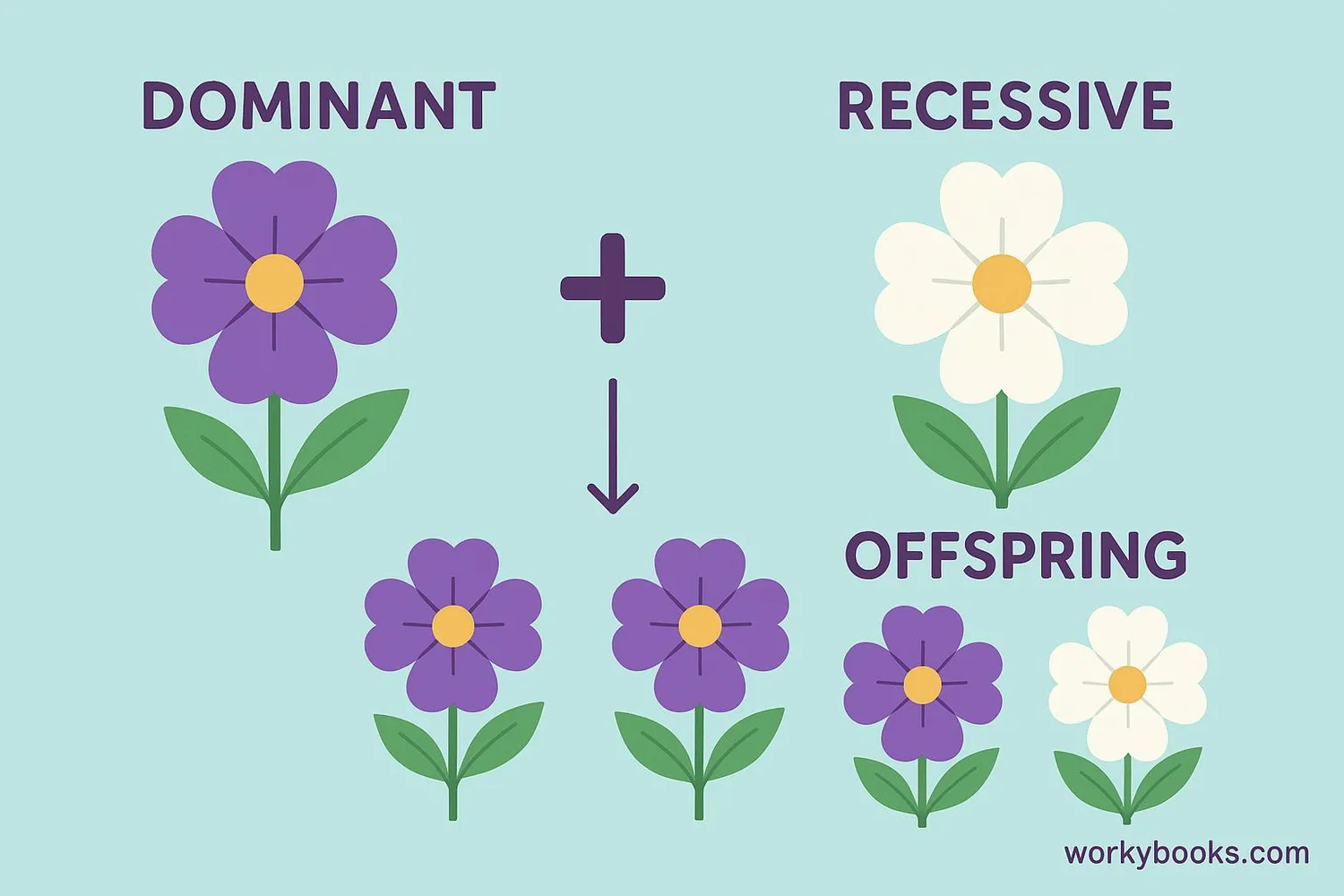
From his experiments, Mendel developed three important laws of inheritance:
Law of Dominance
Some traits (dominant) mask others (recessive) when both are present
Law of Segregation
Each parent passes only one copy of each trait to offspring
Law of Independent Assortment
Different traits are inherited independently of each other
These laws explain why you might have your mother's eye color but your father's hair texture. Each trait is inherited separately, and dominant traits will show up even if only one parent passes them on.
Genetics Quiz
Test your knowledge about Gregor Mendel and genetics with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Gregor Mendel and his work:
Science Facts About Genetics
Discover some amazing facts about genetics and inheritance:
Hidden Traits
You can carry recessive traits (like blue eyes) without showing them! These traits can appear in your children if both parents pass on the recessive version.
Scientific Method
Mendel was one of the first scientists to use statistics in biology. His mathematical approach was very advanced for the 1860s!
Pea Plant Choice
Pea plants were perfect for Mendel's experiments because they have both male and female parts and can self-pollinate, allowing for controlled breeding.
Lost and Found
Mendel's original paper was cited only about 3 times in 35 years after publication. It was "rediscovered" by three scientists simultaneously in 1900.





