Omnivores - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover animals that enjoy both plants and animals in their diet!
What is an Omnivore?

An omnivore is an animal that eats both plants and animals. The word "omnivore" comes from Latin words meaning "all-eater" - "omni" meaning all, and "vore" meaning eater.
Unlike herbivores (plant-eaters) or carnivores (meat-eaters), omnivores have a flexible diet that allows them to eat many different types of food. This flexibility helps omnivores survive in many different environments because they can eat whatever food is available.
Did You Know?
Humans are omnivores too! Our teeth and digestive systems are designed to process both plant and animal foods.
Key Characteristics of Omnivores
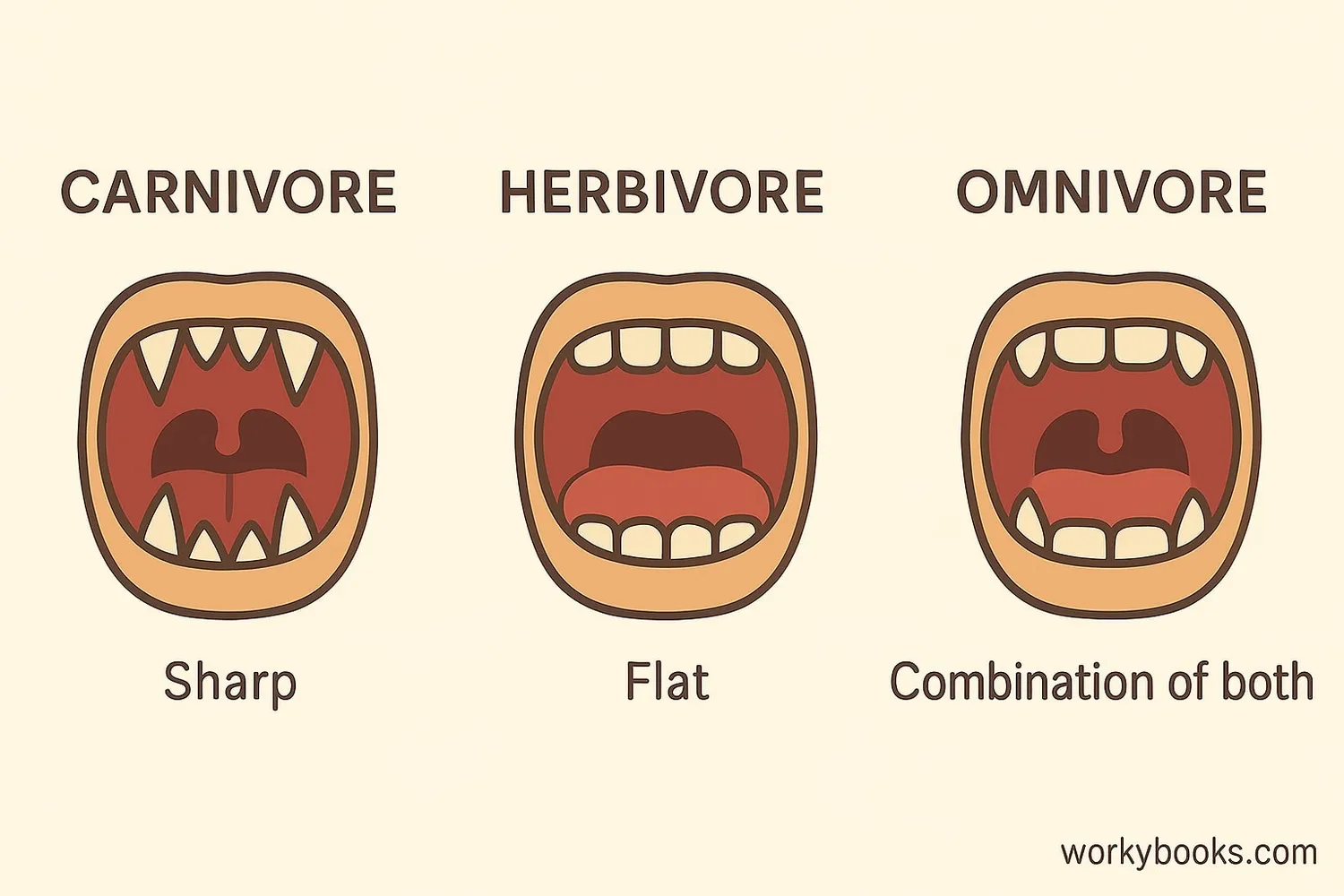
Omnivores have special adaptations that allow them to eat both plants and animals:
Versatile Teeth
Combination of sharp teeth for meat and flat teeth for grinding plants
Digestive System
Can digest both plant and animal matter efficiently
Opportunistic Feeders
Eat whatever food is available in their environment
Adaptable Behavior
Can hunt, forage, or scavenge depending on food sources
These adaptations make omnivores very successful in many environments. They can change their diet with the seasons - eating fruits and berries when they're available, and insects or small animals at other times.
Examples of Omnivores
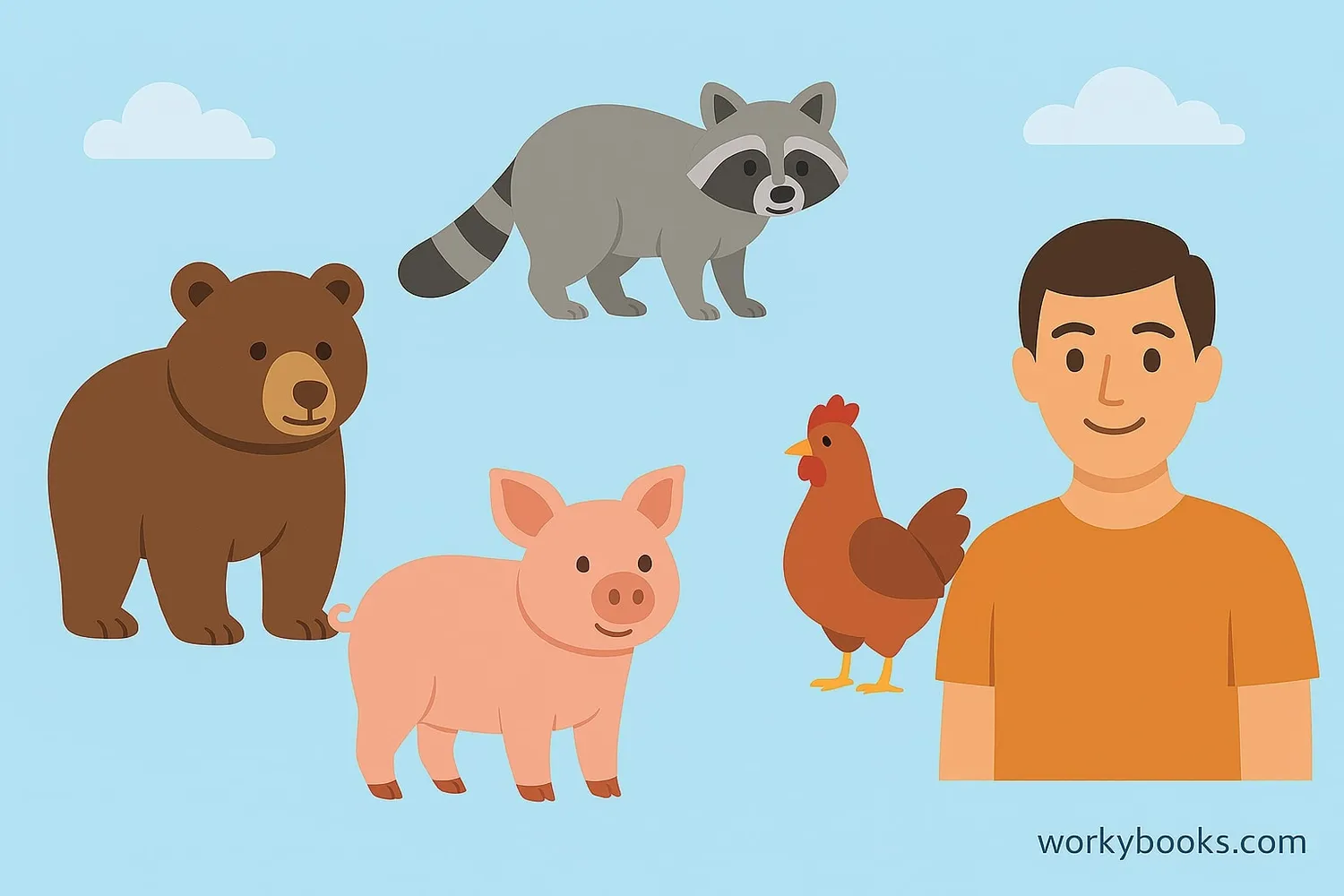

Omnivores come in all sizes and live in many different habitats. Here are some common examples:
Bears
Eat berries, fish, insects, and small mammals
Raccoons
Eat fruits, nuts, insects, eggs, and small animals
Pigs
Eat roots, fruits, small animals, and insects
Chickens
Eat seeds, insects, worms, and small reptiles
Turtles
Many species eat both plants and small aquatic animals
Humans
Our diverse diet includes both plant and animal foods
Surprising Omnivores
Some animals you might think are carnivores are actually omnivores! For example, many dog species eat berries and other plant materials along with meat.
Role of Omnivores in Nature
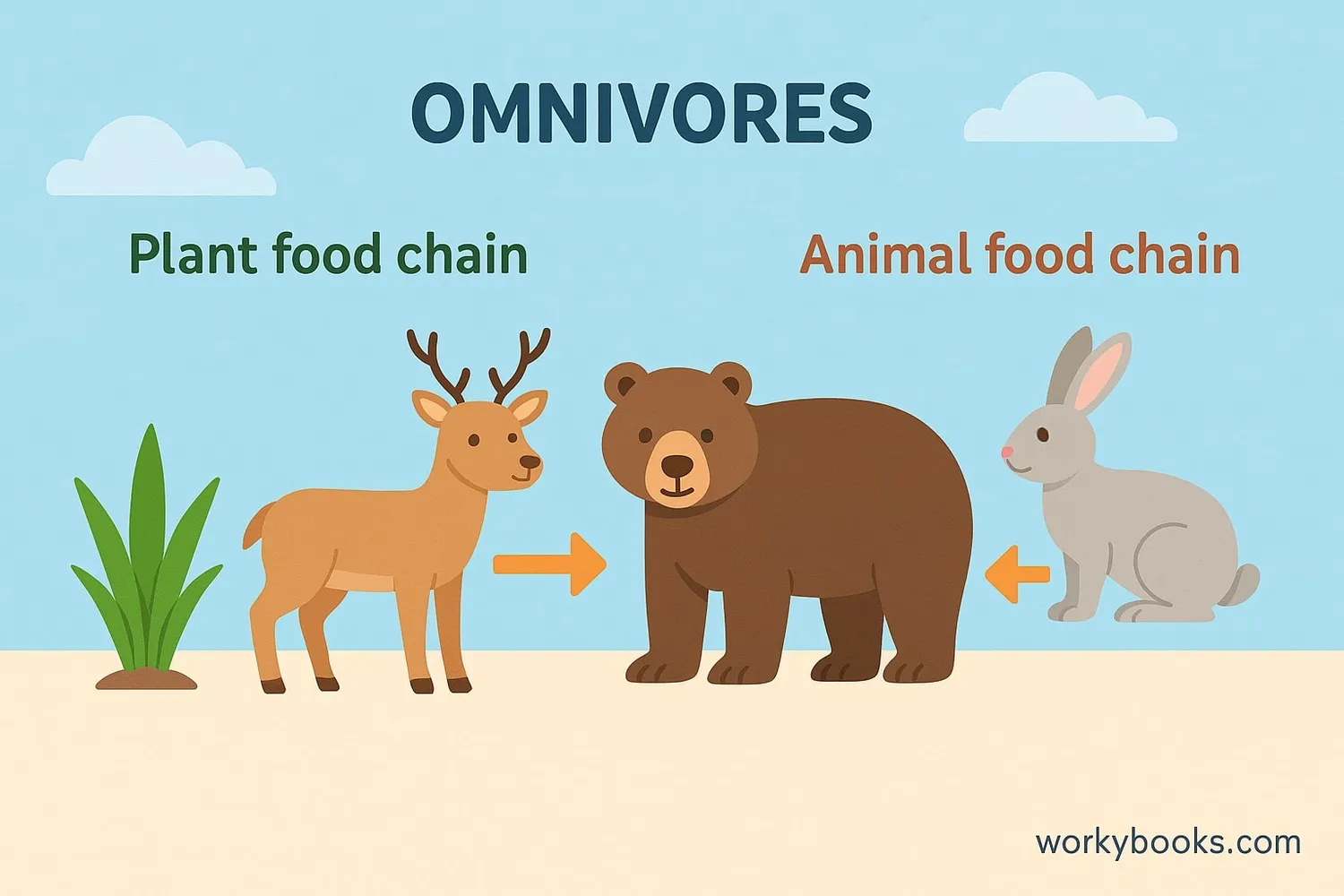
Omnivores play several important roles in ecosystems:
Seed Dispersal
They spread seeds through their droppings after eating fruits
Population Control
Help control populations of both plants and small animals
Food Web Connections
Connect plant-based and animal-based food chains
Because they eat both plants and animals, omnivores can adapt to changes in their environment. If one food source becomes scarce, they can switch to another. This makes them resilient to environmental changes.
Omnivores also help cycle nutrients through ecosystems. When they eat both plants and animals, they move nutrients between different parts of the food web.
Omnivore Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about omnivores with this quiz! Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about omnivores:
Omnivore Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about omnivores:
Evolutionary Advantage
Omnivores often survive better than specialized eaters when environments change. Their flexible diet helped them survive ice ages and other major climate shifts.
Human Omnivores
Humans are among the most adaptable omnivores. Our ancestors' ability to eat diverse foods contributed to the development of larger brains and global migration.
Insect Omnivores
Many insects are omnivores! Ants eat both plant materials and other insects. Some species even "farm" fungi or tend to aphids for their honeydew.
Bear Diets
Bears' diets change dramatically with seasons. Grizzly bears might eat up to 90% plant material in summer, but focus on fish and meat before hibernation.





