Platypus - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover one of nature's most unusual mammals that lays eggs!
What is a Platypus?

The platypus is one of the most unusual animals on Earth! It's a semi-aquatic mammal that lays eggs instead of giving birth to live babies. Found only in Australia, this unique creature combines features from different animals:
Duck-like Bill
A soft, flexible bill perfect for finding food underwater
Webbed Feet
Excellent for swimming with webbed front feet
Beaver Tail
A flat, paddle-shaped tail that helps with swimming
Scientists were so surprised when they first saw a platypus that they thought it was a fake animal made from different animal parts! But this amazing creature is very real and belongs to a special group of mammals called monotremes - mammals that lay eggs.
Science Fact!
Platypuses are one of only five living species of monotremes - the others are four species of echidna!
Physical Features
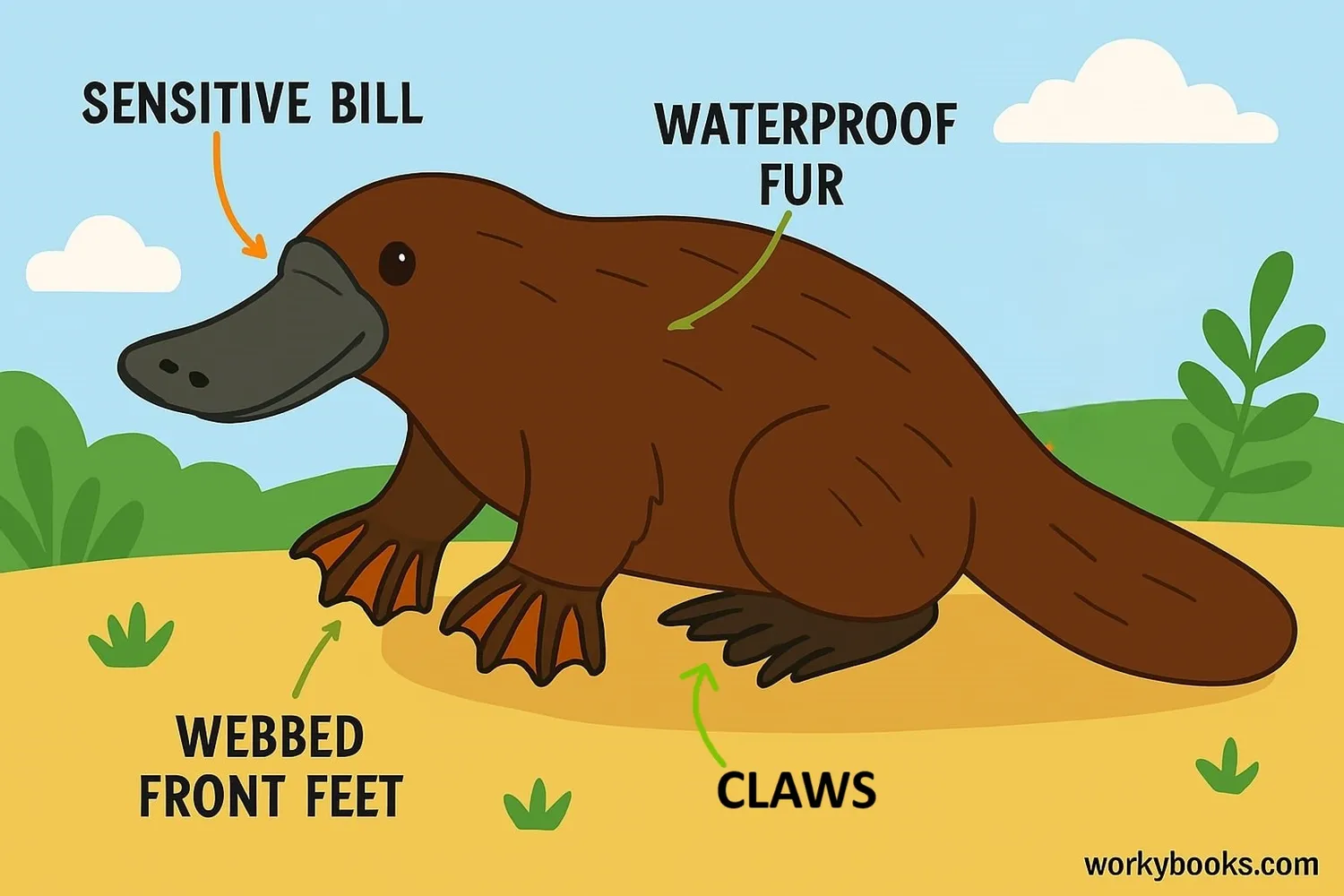
Platypuses have a combination of features that make them perfectly adapted to their watery environment:
Size & Weight
Adults are 15-24 inches long and weigh 1.5-5.5 pounds
Waterproof Fur
Dense, waterproof fur keeps them warm and dry
Webbed Feet
Front feet are webbed for swimming, back feet for digging
Special Bill
Rubbery bill with electroreceptors to detect prey
Venomous Spur
Males have a venomous spur on their hind legs
The platypus bill might look like a duck's, but it's actually very different! It's soft and flexible, covered in sensitive skin that can detect the tiny electrical signals made by moving prey. This special ability is called electroreception.
Habitat & Diet
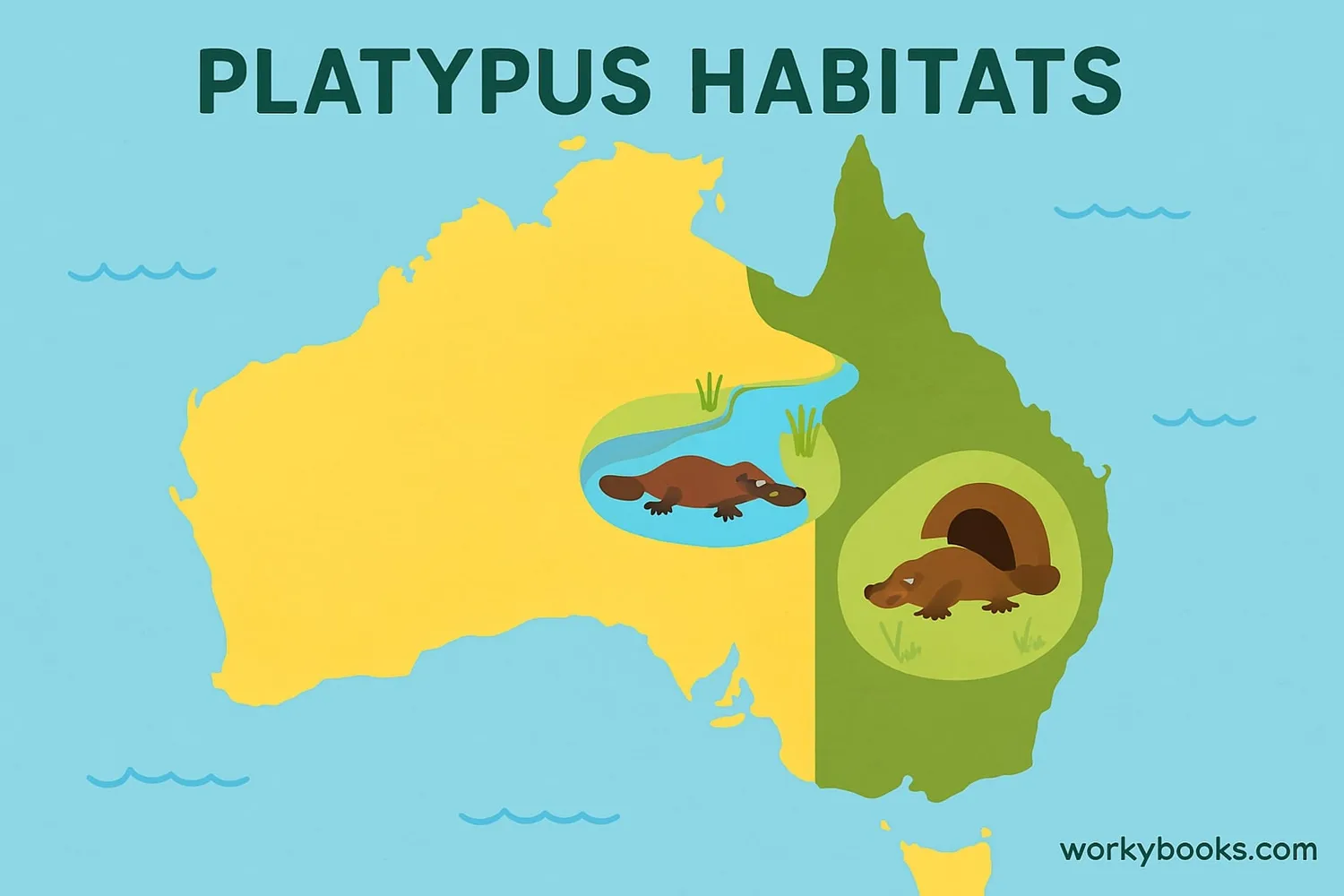
Platypuses live in freshwater environments in eastern Australia, including Tasmania. They prefer:
River Homes
Clear rivers and streams with earth banks for burrows
Food Sources
Aquatic insects, larvae, worms, and shrimp
Swimming Skills
Excellent swimmers that hunt underwater
Platypuses are most active at dawn and dusk, hunting for food underwater. They close their eyes, ears, and nose when diving, relying completely on their sensitive bill to find food. A platypus might eat up to 20% of its body weight each day!
Feeding Fact!
Platypuses store food in special cheek pouches while hunting, then come to the surface to eat it!
Babies & Reproduction
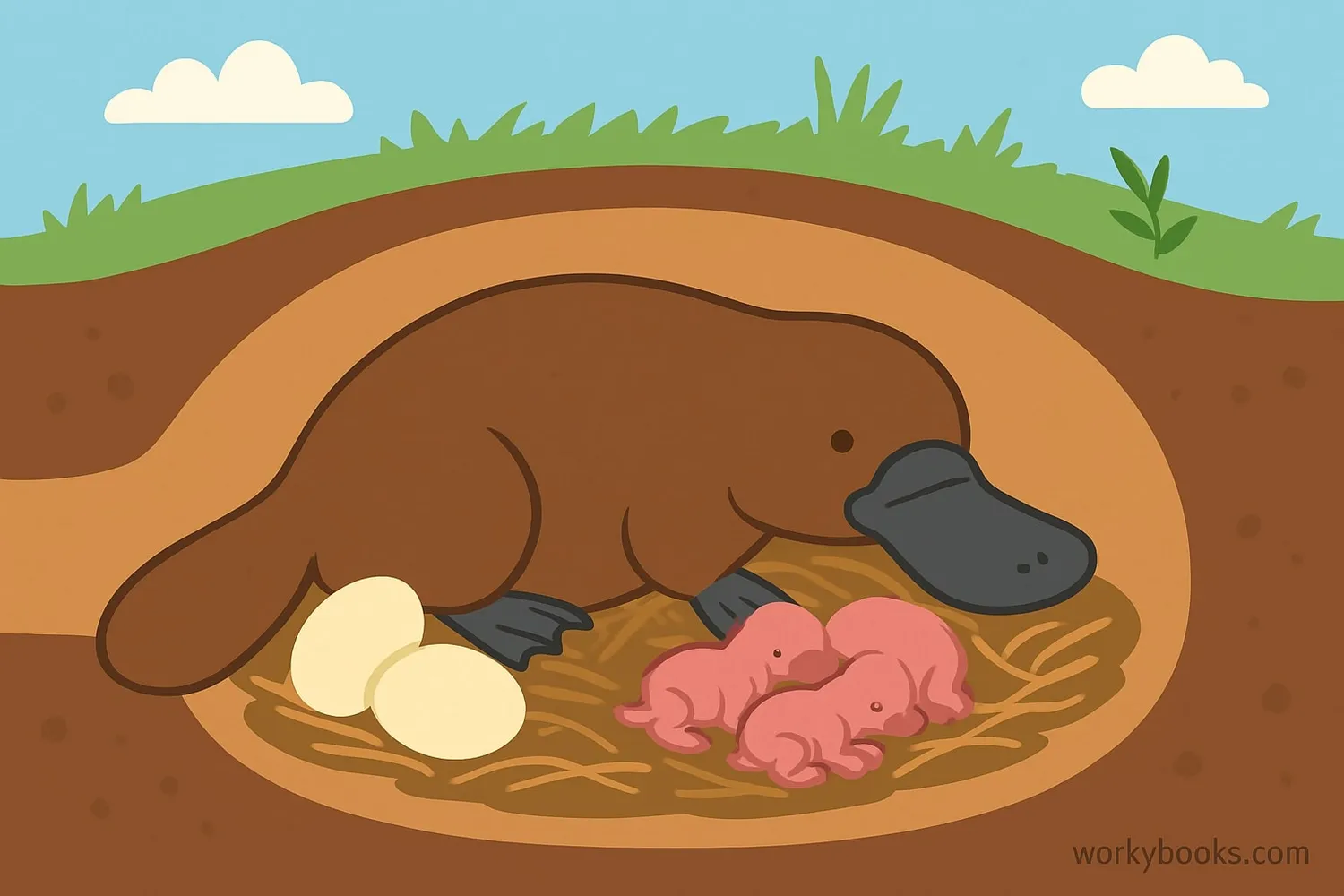

Platypus reproduction is truly unique among mammals:
Egg Laying
Females lay 1-3 leathery eggs in a nesting burrow
Incubation
Mother curls around eggs for about 10 days
Baby Puggles
Babies hatch blind and hairless, called "puggles"
Milk Feeding
Mother feeds milk through patches on her belly
Growing Up
Puggles stay in the burrow for 3-4 months
Platypus mothers don't have nipples like other mammals. Instead, milk oozes from special patches on their belly, and the babies lick it up. After about four months, the young platypuses leave the burrow to begin life on their own.
Special Abilities

Platypuses have some amazing abilities that make them truly unique:
Electroreception
Detects electrical signals from prey in murky water
Venomous Spur
Males have a spur that delivers painful venom
Swimming Skills
Uses webbed feet and tail to swim efficiently
The platypus bill contains around 40,000 electroreceptors that help it find food even with its eyes closed! Meanwhile, the venom in males isn't usually deadly to humans, but it causes severe pain that can last for weeks. Scientists think males use this venom mainly during mating season competitions.
Platypus Quiz
Test your platypus knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about platypuses:
Platypus Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about platypuses!
Swimming Champions
Platypuses can stay underwater for up to 10 minutes! They close their eyes, ears, and nostrils when diving, relying completely on their electroreception to find food.
Scientific Surprise
When the first platypus specimen arrived in England in 1799, scientists thought it was a hoax! They tried to remove the "sewn-on" bill, believing it was fake.
Low Body Temperature
Platypuses have the lowest body temperature of any mammal at about 90°F (32°C), compared to 98.6°F (37°C) for humans. This helps them conserve energy.
Unique Brain Structure
Platypuses have a unique brain structure that processes electroreception separately from touch sensations, giving them a sort of "sixth sense" for hunting underwater.




