Respiration - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how cells convert nutrients into energy through respiration
What is Respiration?
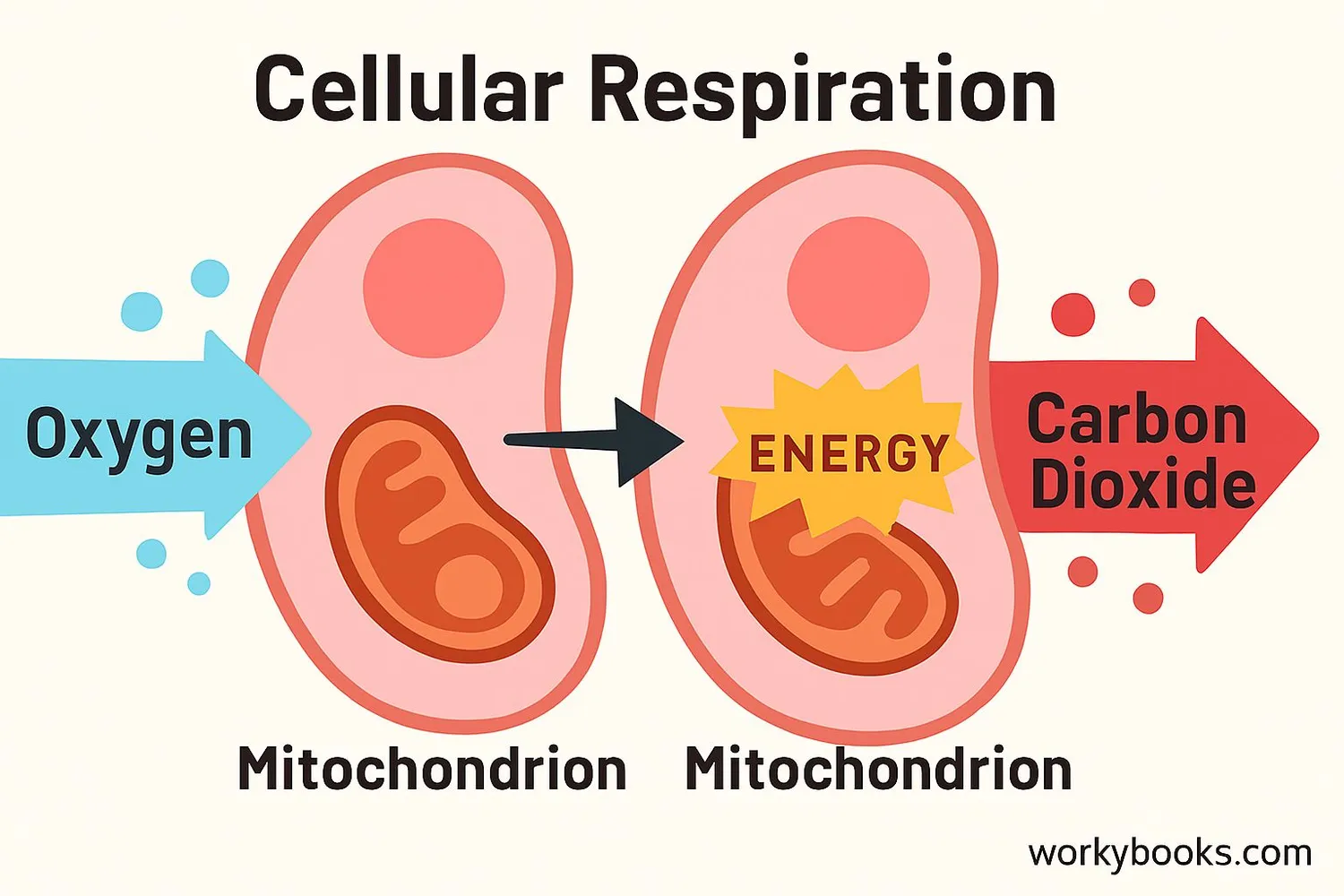
Respiration is the process by which living organisms convert nutrients into usable energy. At the cellular level, this process involves breaking down glucose (sugar) in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells.
Think of respiration as your body's energy factory. Just like a factory needs raw materials to produce goods, your cells need oxygen and nutrients to produce energy. This energy powers everything from muscle movement to brain function.
Did You Know?
Even plants perform respiration! During the day, they make food through photosynthesis, and both day and night, they perform respiration to get energy from that food.
Types of Respiration
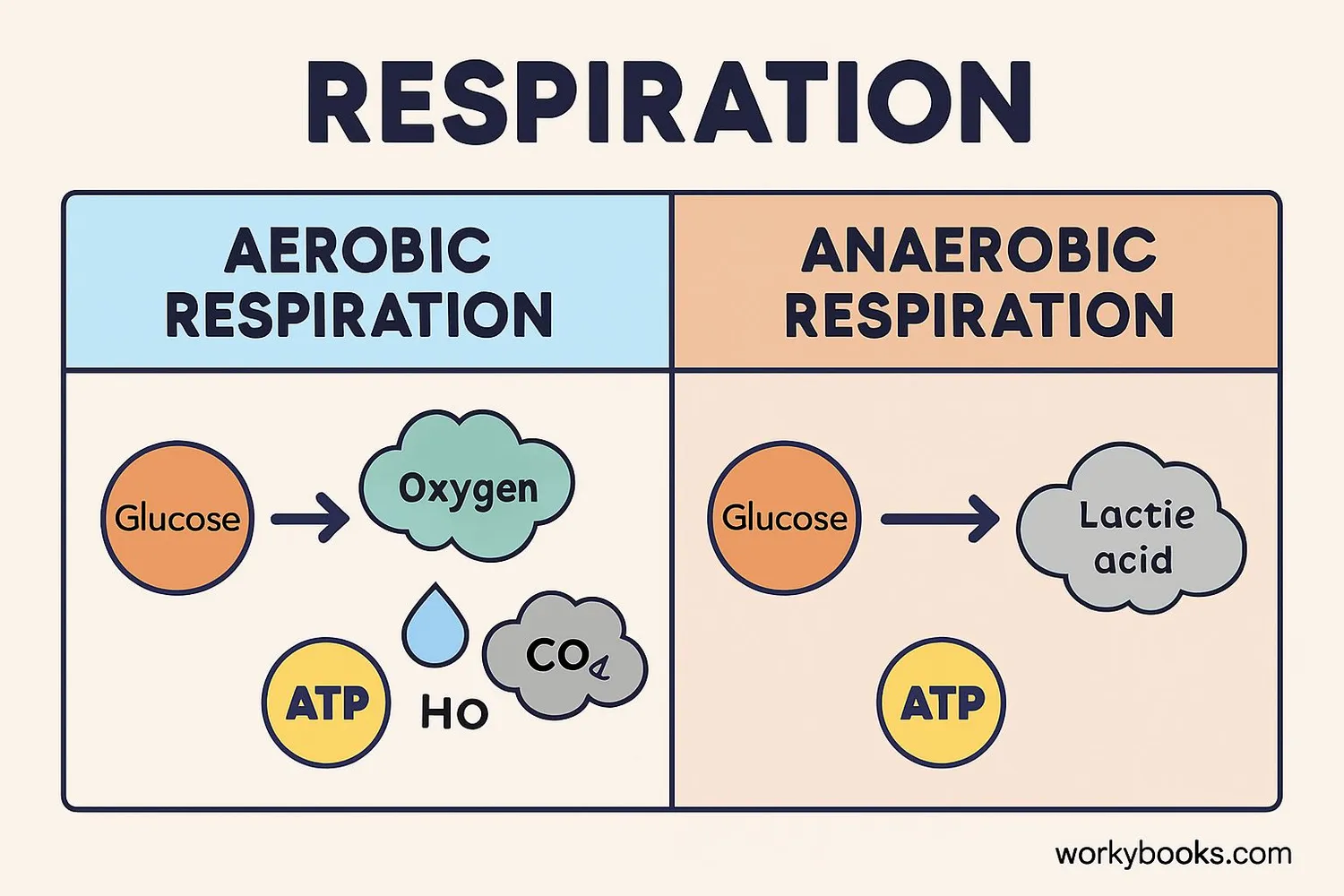
There are two main types of respiration in living organisms:
Aerobic Respiration
Requires oxygen to break down glucose completely
Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs without oxygen, producing less energy
Aerobic respiration is the most efficient way for cells to produce energy. It occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. This process happens in the mitochondria and produces 36 ATP molecules per glucose molecule.
Anaerobic respiration occurs when oxygen is scarce. In humans, this produces lactic acid and only 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. Yeast and some bacteria perform alcoholic fermentation, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide.
How Respiration Works
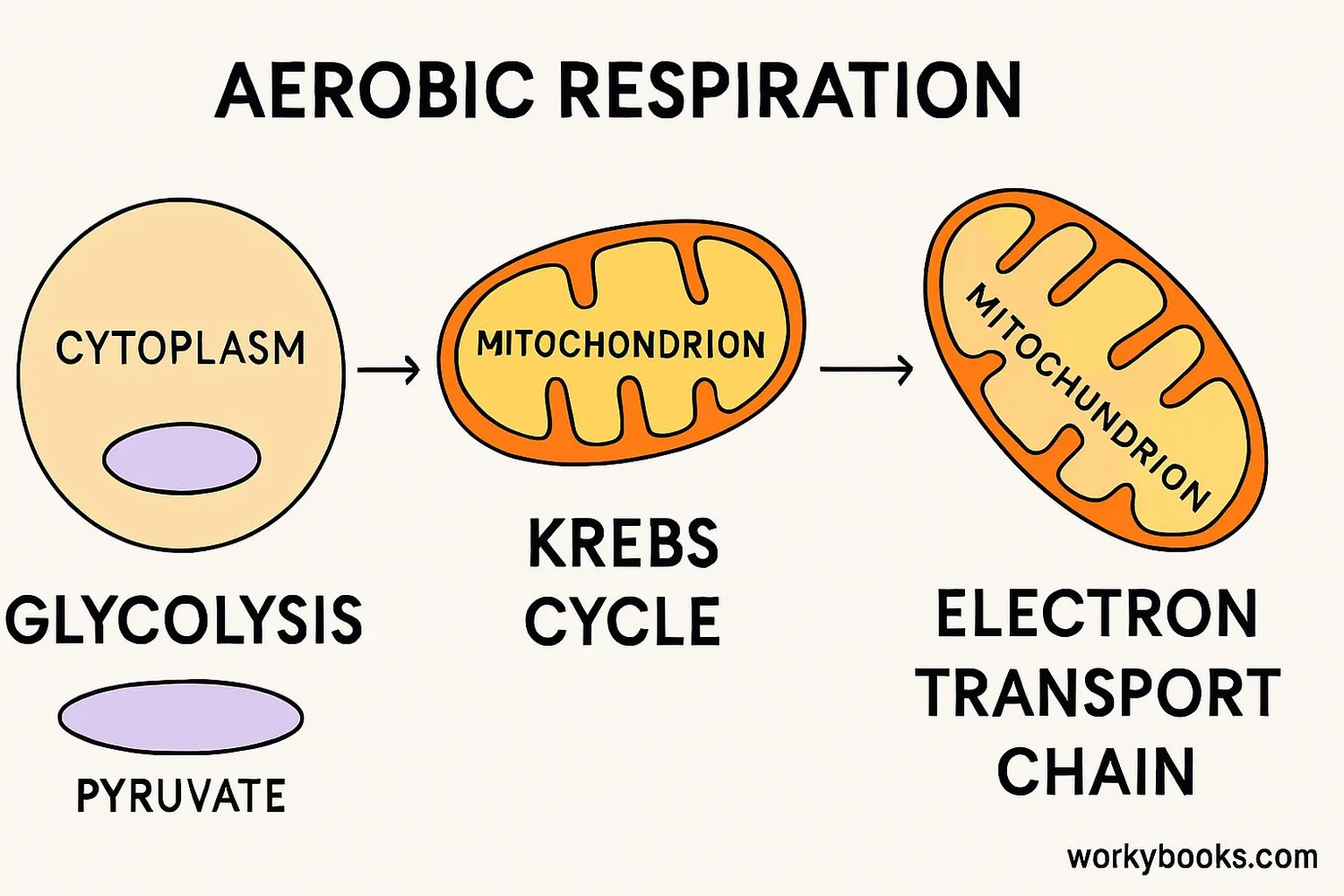
The complete process of aerobic respiration involves three interconnected stages:
Glycolysis
Glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm
Krebs Cycle
Pyruvate is further broken down in mitochondria
Electron Transport
Produces most ATP using oxygen as final electron acceptor
The chemical equation for aerobic respiration is:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP)
Which means: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
This process happens continuously in your cells to provide the energy needed for all life processes.
Importance of Respiration
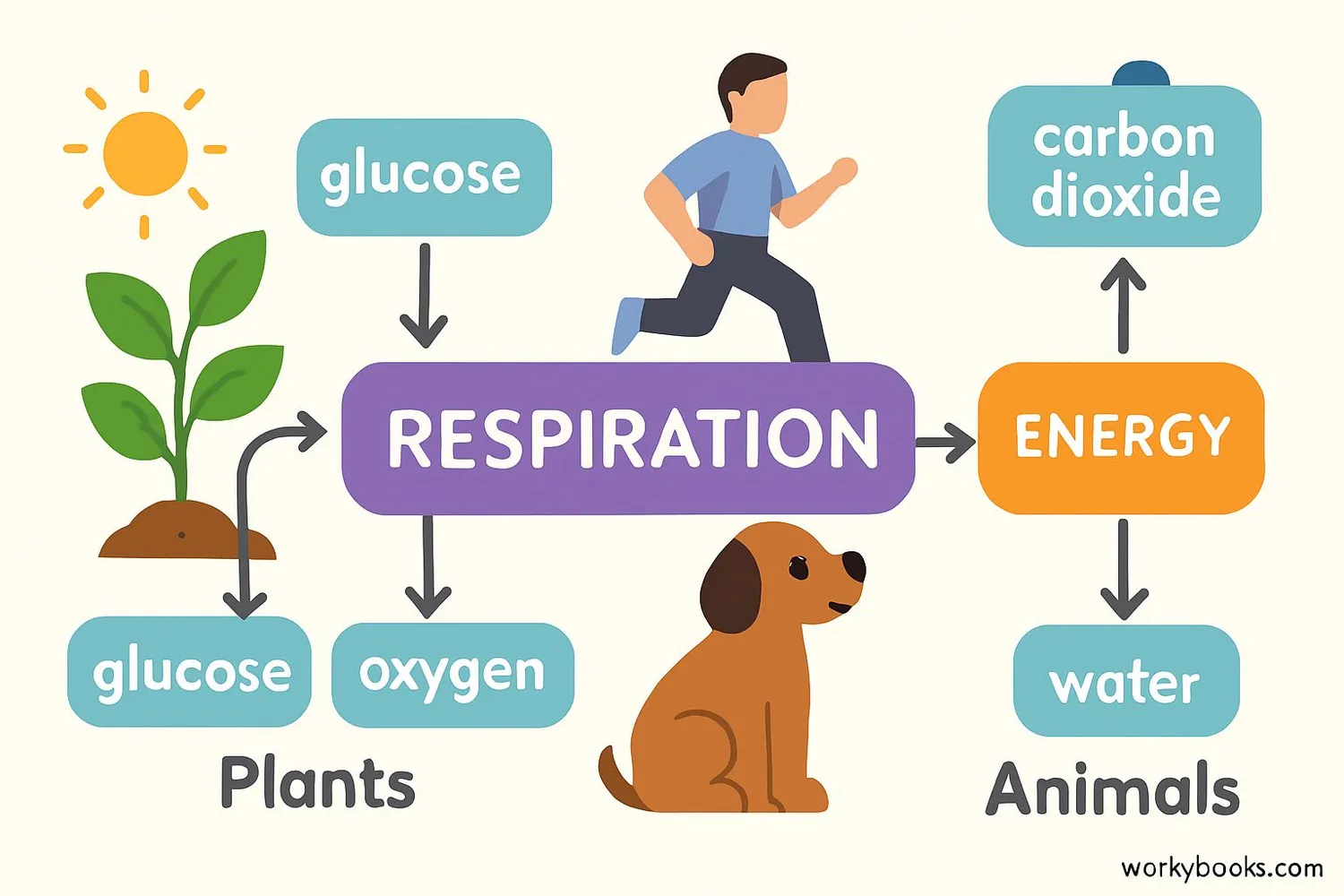
Respiration is essential for all living organisms because:
Energy Production
Creates ATP for cellular activities and functions
Metabolism
Breaks down nutrients to release stored energy
Ecosystem Balance
Completes the carbon cycle with photosynthesis
Without respiration, living things would have no way to access the energy stored in food. This energy powers:
• Muscle contractions for movement
• Nerve impulses for thinking and sensing
• Protein synthesis for growth and repair
• Active transport across cell membranes
• Maintaining body temperature
Respiration Quiz
Test your knowledge about respiration with these questions:
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about respiration:
Respiration Trivia
Interesting facts about respiration:
Energy Production
Your body produces about 150 pounds of ATP every day! But since ATP gets recycled so quickly, you only have about 1 ounce in your body at any moment.
Aquatic Respiration
Some aquatic animals like fish perform respiration using gills that extract oxygen from water. Their gills have a large surface area to maximize oxygen absorption.
Space Breathing
Astronauts' respiration patterns change in microgravity. Without gravity, carbon dioxide doesn't rise away from their faces, requiring special ventilation systems.
Ancient Origins
The first forms of respiration were anaerobic, evolving before oxygen was abundant in Earth's atmosphere. Aerobic respiration developed later as oxygen levels increased.





