Terrestrial - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the amazing world of land-based habitats, animals, and plants!
What is Terrestrial?

Terrestrial means "relating to the Earth or land." When we talk about terrestrial environments, we're describing land-based habitats where plants and animals live. This includes forests, grasslands, deserts, mountains, and even your backyard!
Terrestrial habitats are different from aquatic (water-based) habitats. While aquatic animals live in water, terrestrial animals live on land. But remember - some animals like frogs can live in both environments!
The word "terrestrial" comes from the Latin word "terra," which means Earth. So when you hear scientists talk about terrestrial planets, they mean rocky planets like Earth, Mars, Venus, and Mercury that have solid surfaces.
Science Fact!
About 29% of Earth's surface is terrestrial land, while the remaining 71% is covered by water!
Terrestrial Habitats and Ecosystems
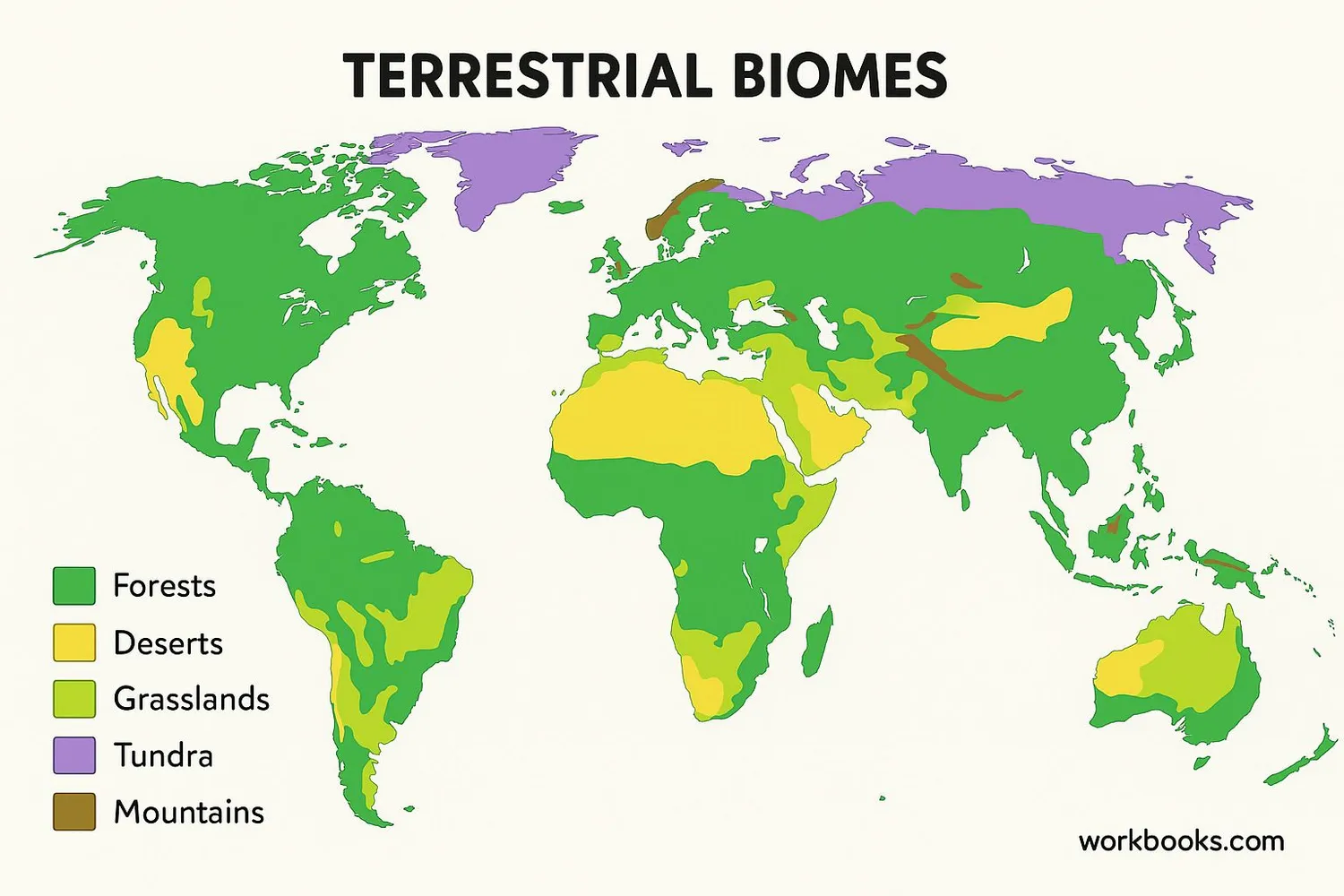
Terrestrial ecosystems are communities of living things interacting with each other and their physical environment on land. Scientists divide these into several major types called biomes:
Forests
Dense tree-covered areas with high rainfall
Grasslands
Open areas dominated by grasses and few trees
Deserts
Dry areas with very little rainfall
Tundra
Cold, treeless regions with frozen soil
Mountains
High elevation areas with changing climates
Terrestrial vs. Aquatic Environments
| Feature | Terrestrial Environments | Aquatic Environments |
|---|---|---|
| Location | On land | In water |
| Oxygen Source | From the air | Dissolved in water |
| Support | Solid ground | Buoyancy of water |
| Temperature Changes | Wide daily and seasonal variations | More stable temperatures |
| Example Animals | Lions, deer, eagles | Fish, whales, corals |
Ecosystem Fact!
The Amazon Rainforest is the largest terrestrial ecosystem on Earth, covering about 5.5 million square kilometers!
Terrestrial Life

Terrestrial life includes all the plants and animals that live primarily on land. These organisms have special adaptations that help them survive in their environments:
Animal Adaptations
Legs for walking, lungs for breathing air, fur/feathers for temperature control
Plant Adaptations
Roots to absorb water, stems to stand upright, waxy leaves to prevent drying
Climate Adaptations
Hibernation, migration, shedding leaves, water storage
Examples of Terrestrial Life
Terrestrial animals:
• Mammals: Lions, deer, bears, elephants
• Birds: Eagles, sparrows, ostriches
• Reptiles: Snakes, lizards, tortoises
• Insects: Ants, butterflies, beetles
Terrestrial plants:
• Trees: Oaks, pines, maples
• Flowers: Roses, daisies, tulips
• Grasses: Wheat, corn, bamboo
• Desert plants: Cacti, succulents
Each species has unique adaptations that help it survive in its specific terrestrial habitat. For example, cacti store water in their stems, while camels store water in their bodies to survive in deserts!
Terrestrial Knowledge Check
Test your knowledge about terrestrial environments with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about terrestrial environments:
Amazing Terrestrial Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about terrestrial life:
Tiny Giants
Ants are the most numerous terrestrial animals. Scientists estimate there are about 10 quadrillion ants living on Earth right now! That's more than 1 million ants for every human.
Ancient Forests
The oldest known terrestrial organism is Pando, a quaking aspen colony in Utah that's over 80,000 years old! This massive grove of trees shares a single root system.
Desert Survivors
The Sahara Desert ant can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F)! They make the most of their brief foraging windows by running at speeds equivalent to 400 miles per hour in human terms.
High Altitude Life
Yaks are adapted to live at altitudes up to 6,000 meters (20,000 feet) in the Himalayas. They have larger lungs and hearts than cattle at lower elevations to survive the thin air.





