Baking Soda: Chemical Formula - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the science behind baking soda and how this common household substance works!
What is Baking Soda?

Baking soda, also known as sodium bicarbonate, is a white crystalline powder that appears naturally in mineral deposits. It's a chemical compound that has been used for centuries in baking, cleaning, and even medicine.
You might have baking soda in your kitchen right now! It's commonly used in baking because it helps baked goods like cakes, cookies, and breads rise and become fluffy. But baking soda has many other interesting uses too, which we'll explore later.
Science Fact!
Baking soda has been used since ancient times. The ancient Egyptians used a form of sodium bicarbonate as a cleaning agent and in their mummification processes.
Chemical Formula and Name
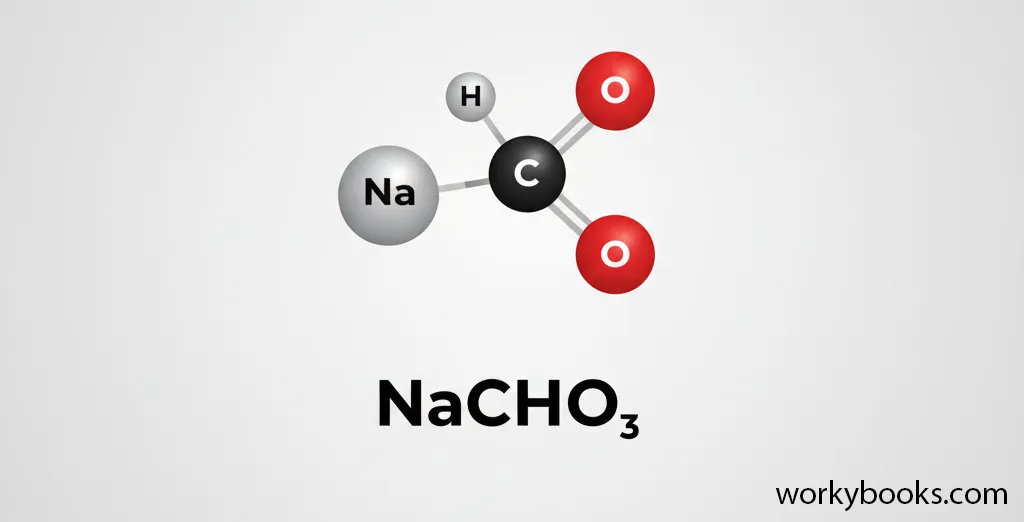
Baking soda has a specific chemical formula that tells us exactly what atoms it contains. The chemical formula for baking soda is NaHCO3.
Let's break down what this formula means:
Sodium
One atom of sodium
Hydrogen
One atom of hydrogen
Carbon
One atom of carbon
Oxygen
Three atoms of oxygen
The scientific name for baking soda is sodium bicarbonate. Sometimes it's also called bicarbonate of soda. All these names refer to the same compound with the formula NaHCO3.
Properties of Baking Soda
Baking soda has several interesting properties that make it useful for many different applications:
Physical Properties
Baking soda is a white, crystalline powder. It dissolves in water and has a slightly salty, alkaline taste.
Solubility
Baking soda dissolves in water, but its solubility decreases as the water temperature increases.
Thermal Decomposition
When heated above 50°C (122°F), baking soda gradually decomposes to sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide.
pH Level
Baking soda is a base with a pH of about 8.3, which means it's slightly alkaline. This is why it can neutralize acids.
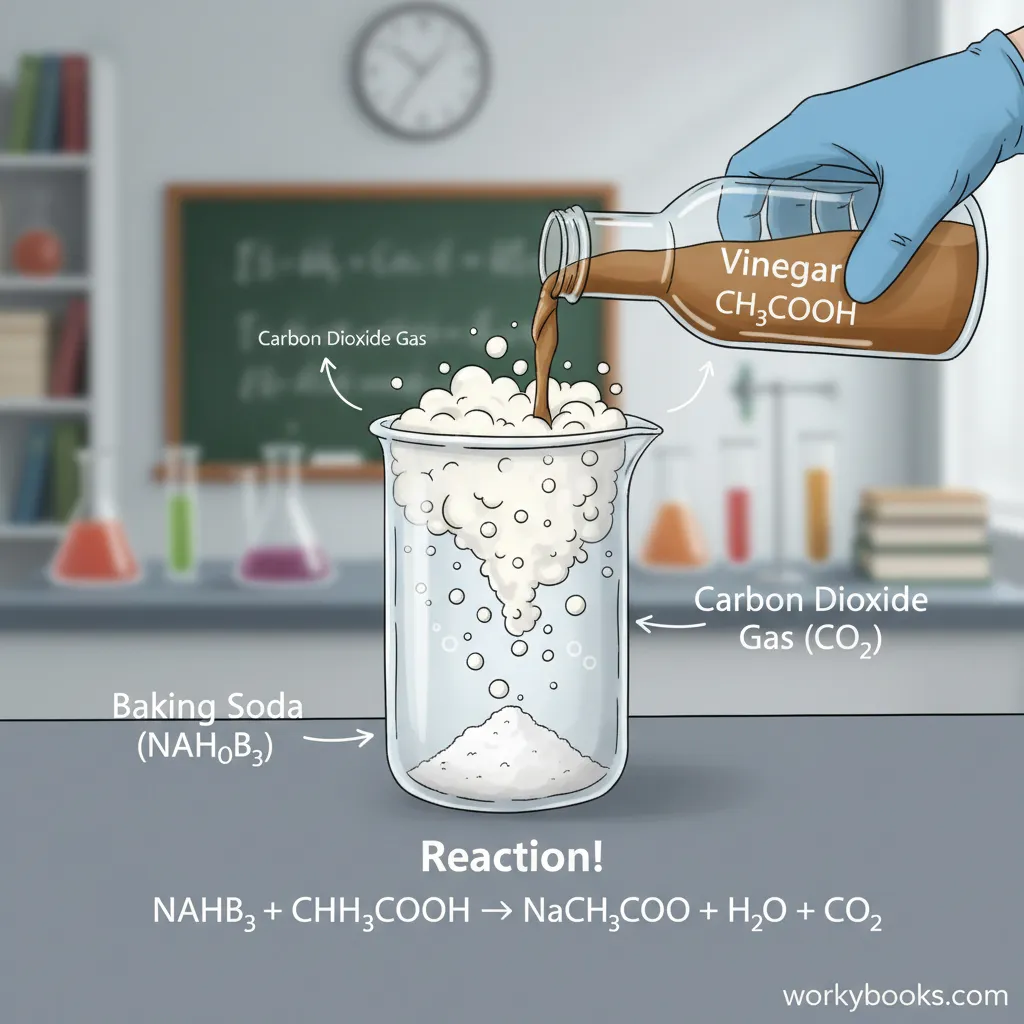
One of the most important chemical properties of baking soda is that it reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide gas. This is why it's used in baking - the gas bubbles make dough rise! The reaction looks like this:
Chemical Reaction
NaHCO3 + H+ → Na+ + H2O + CO2
This means: Sodium bicarbonate + Acid → Sodium salt + Water + Carbon dioxide gas
Uses of Baking Soda
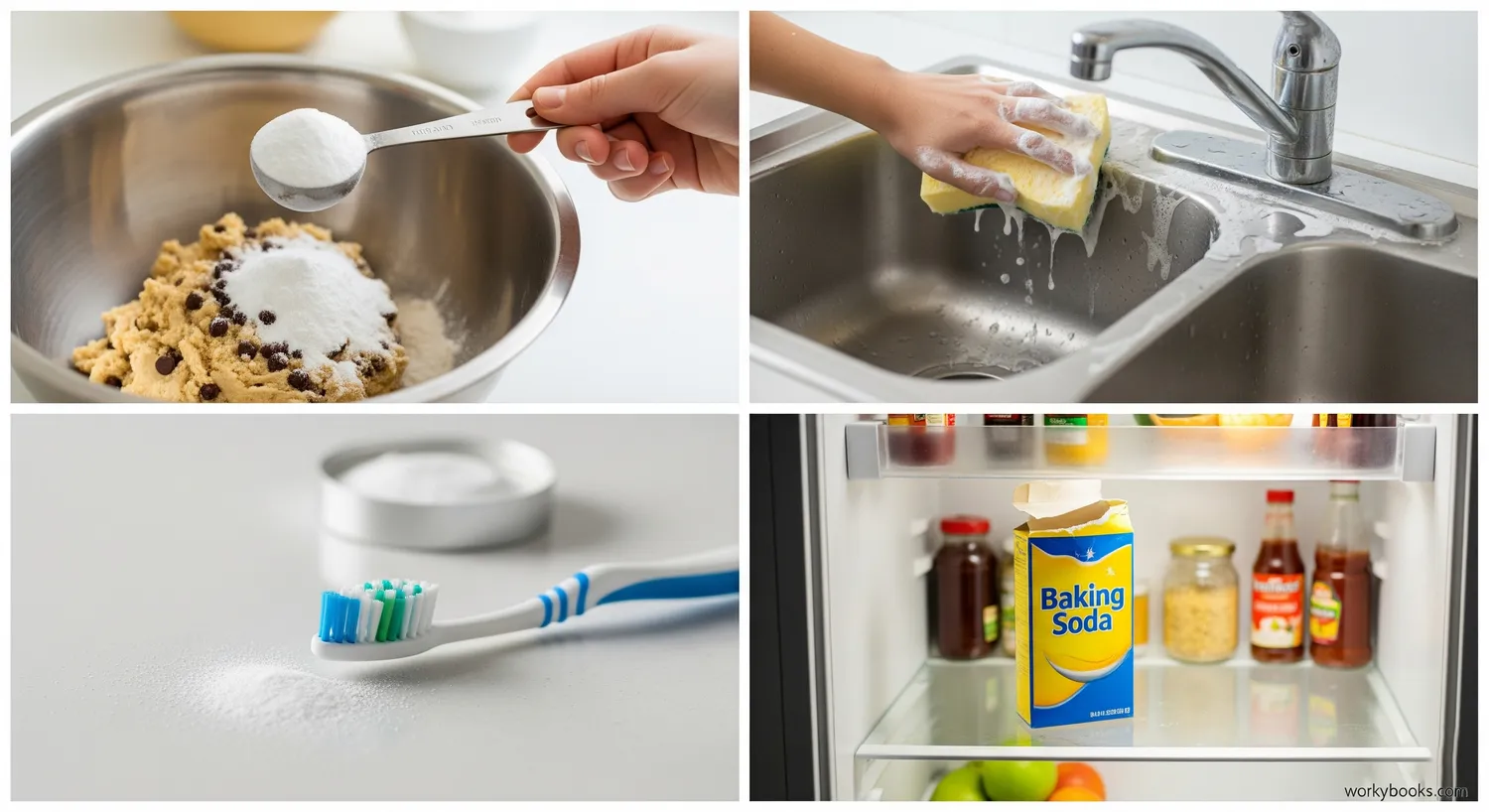

Baking soda is incredibly versatile! Here are some of its most common uses:
Baking
As a leavening agent in baked goods like cakes, cookies, and breads. It helps them rise by producing carbon dioxide gas when mixed with acidic ingredients.
Cleaning
As a mild abrasive cleaner for surfaces like sinks, countertops, and cookware. It's also great for removing odors from refrigerators and other spaces.
Personal Care
In toothpaste as a mild abrasive that helps remove plaque, and in some deodorants to neutralize odor-causing acids.
Fire Extinguisher
In some dry chemical fire extinguishers, particularly for grease and electrical fires, because it can smother flames and release CO2.
Medicine
As an antacid to relieve heartburn and acid indigestion by neutralizing stomach acid.
These are just some of the many uses of baking soda. Its versatility comes from its chemical properties - especially its ability to react with acids and its mild abrasive quality.
Chemistry Quiz
Test your understanding of baking soda with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about baking soda:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about baking soda!
Ancient Origins
While baking soda as we know it was first manufactured in the 1840s, natural deposits of sodium bicarbonate have been used since ancient times. The ancient Egyptians used natron, a natural deposit that contains sodium bicarbonate, in their mummification process.
How It's Made
Most baking soda today is produced through the Solvay process, which involves reacting sodium chloride (salt), ammonia, and carbon dioxide in water. This process was developed in the 1860s by Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay and made baking soda much more affordable and widely available.
Classic Science Experiment
The baking soda and vinegar volcano is one of the most popular science experiments for students. It demonstrates an acid-base reaction that produces carbon dioxide gas, creating the "eruption" effect. This simple experiment has introduced countless children to chemical reactions!
Many Uses
Baking soda is one of the most versatile substances known. It has over 100 documented uses, ranging from cooking and cleaning to personal care and even as a medicine. This versatility comes from its chemical properties as a mild base and its physical properties as a gentle abrasive.





