Catalysts - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how catalysts speed up chemical reactions without being used up!
What is a Catalyst?
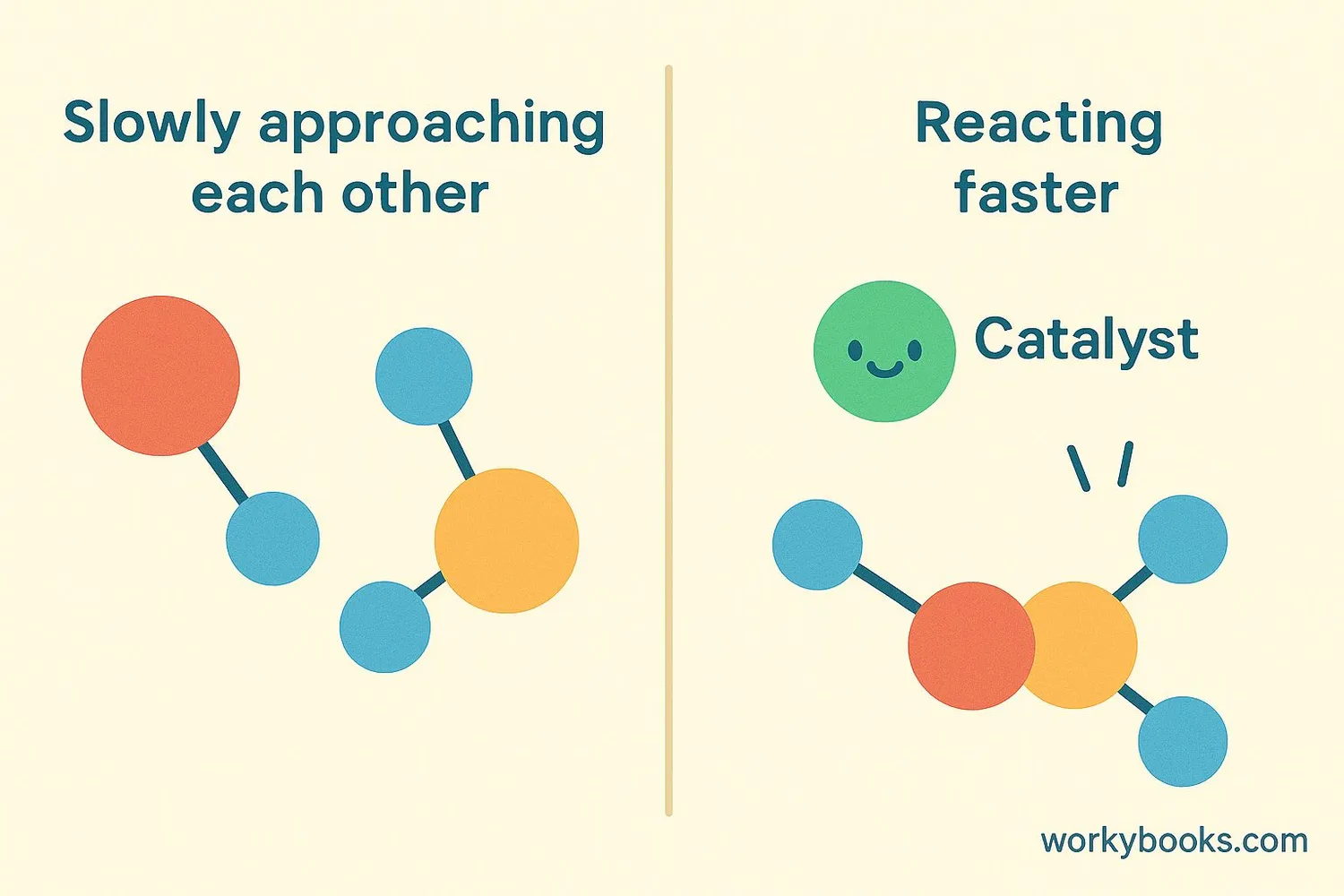
A catalyst is a special substance that helps chemical reactions happen faster without being used up in the reaction! It's like a coach who helps players perform better without playing the game themselves.
Catalysts are amazing because they:
• Speed up chemical reactions
• Aren't changed by the reaction
• Aren't used up in the reaction
• Help make reactions more efficient
Think of a catalyst as a helpful friend who brings two shy people together to talk. Once they're talking, the friend can walk away and help others!
Science Fact!
Catalysts can speed up reactions by over a million times without changing themselves!
How Catalysts Work
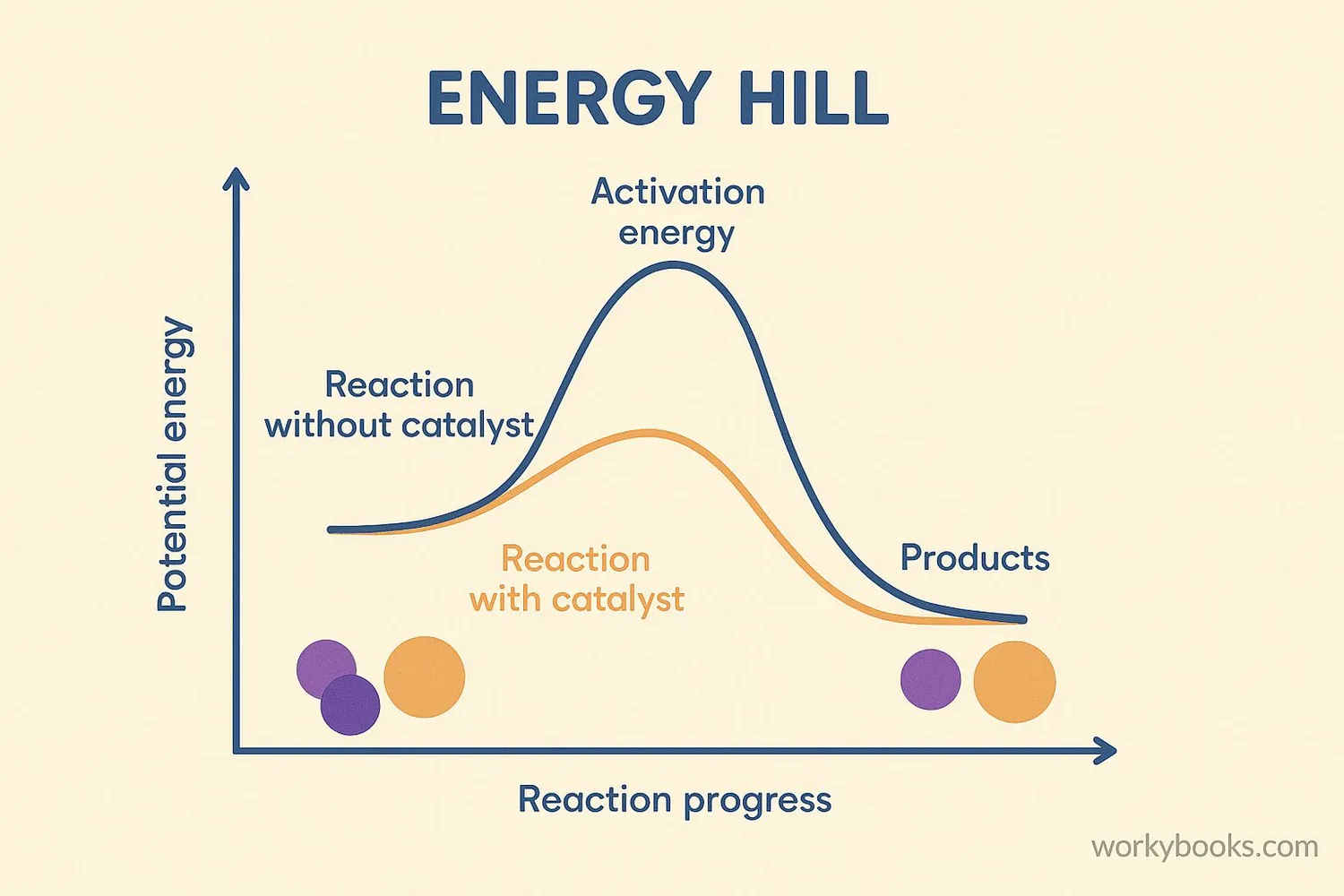
Catalysts work by providing an easier path for chemical reactions. They lower the activation energy needed for reactions to start. Activation energy is like the push you need to start rolling a ball down a hill.
Here's how catalysts help reactions happen:
Bring Together
Catalyst helps reactant molecules meet
Lower Barrier
Reduces energy needed for reaction
Form Product
Helps form the reaction products
Release
Catalyst is released unchanged
Imagine trying to climb over a tall fence to get to your friend's house. A catalyst is like giving you a ladder to climb over more easily. You still get to the same place, but with less effort!
Energy Saver!
Catalysts help industries save huge amounts of energy by making reactions happen faster at lower temperatures.
Types of Catalysts
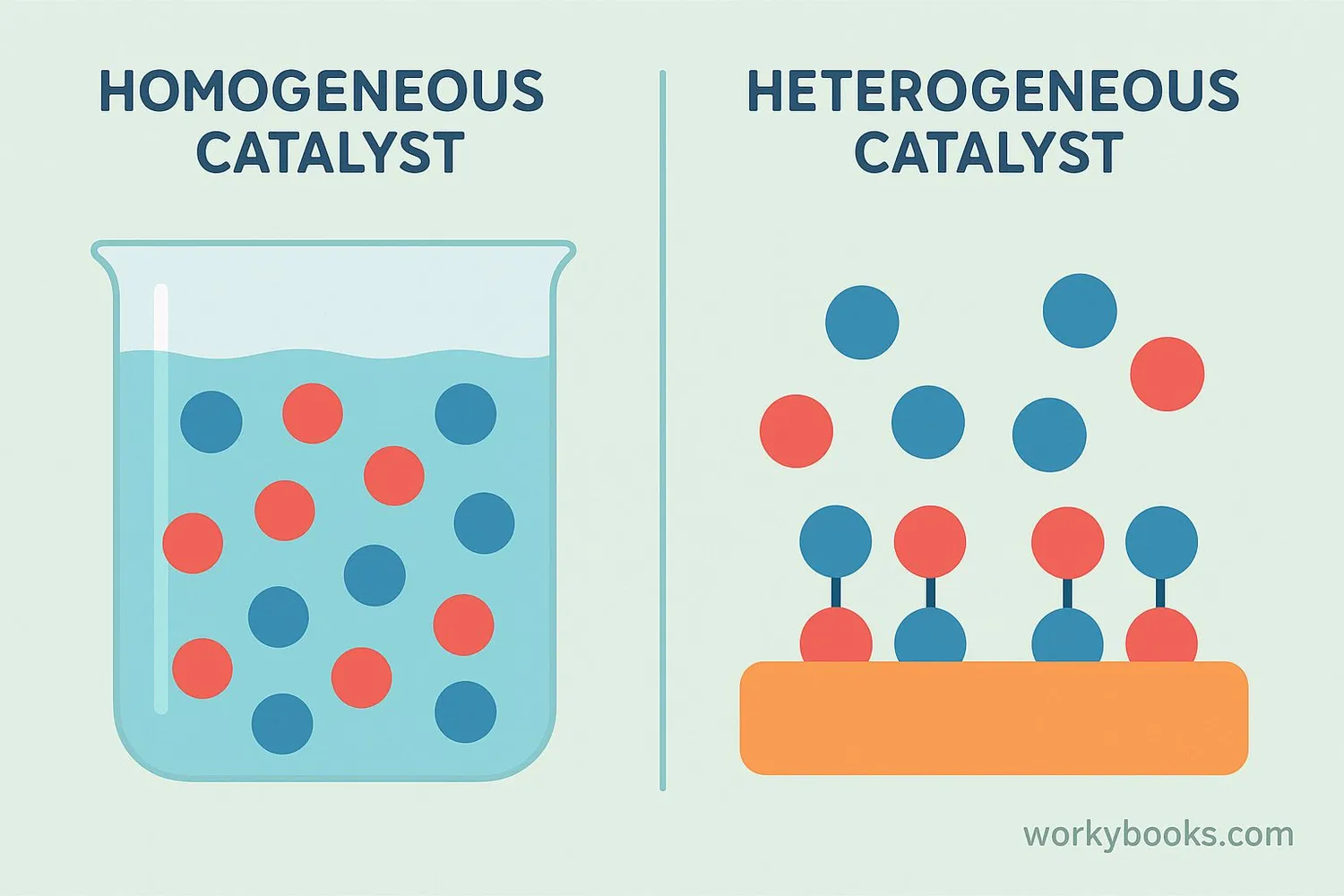
There are two main types of catalysts:
Homogeneous Catalysts
Same phase as reactants (e.g., liquid catalyst in liquid reaction)
Example: Enzymes in your body fluids
Heterogeneous Catalysts
Different phase from reactants (e.g., solid catalyst in gas reaction)
Example: Catalytic converters in cars
Homogeneous catalysts mix completely with the reactants like sugar dissolves in water. Heterogeneous catalysts work at the surface, like a dance floor where molecules meet to react.
Enzyme Catalysts
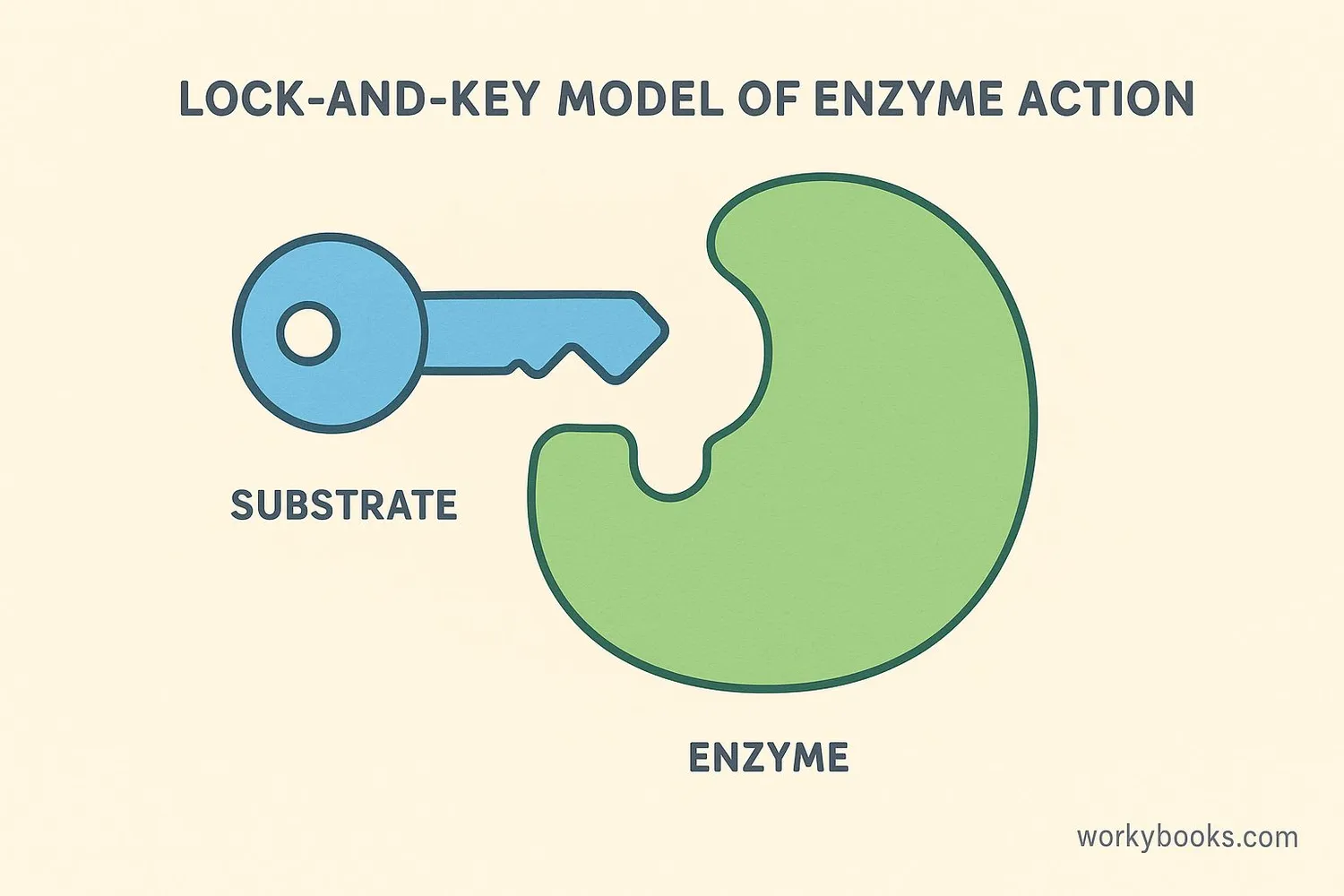
Enzymes are special biological catalysts made of protein that speed up reactions in living things. Almost every chemical reaction in your body uses an enzyme!
Key facts about enzymes:
• They're highly specific - each enzyme works on one type of reaction
• They work best at certain temperatures and pH levels
• They're reusable and not changed by reactions
• They help with digestion, energy production, and more!
Digestion
Enzymes in saliva break down food
Energy
Enzymes help convert food to energy
DNA
Enzymes help copy DNA during cell division
Body Fact!
Your body contains over 75,000 different enzymes working constantly to keep you alive and healthy!
Catalyst Quiz
Test your catalyst knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about catalysts:
Fun Catalyst Trivia
Discover amazing facts about catalysts!
Cleaner Air
Catalytic converters in cars use platinum and palladium to convert harmful gases into safer ones. Since 1975, they've reduced pollution from cars by over 90%!
Food Catalysts
The enzyme in pineapple (bromelain) breaks down proteins. That's why pineapple juice makes meat tender! But it also means adding fresh pineapple to gelatin prevents it from setting.
Nobel Catalysis
The Haber process, which uses iron catalysts to make ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, feeds nearly half the world's population through fertilizer production. Its inventor won a Nobel Prize in 1918!
Super Speed
The fastest known enzyme is carbonic anhydrase, found in red blood cells. It can process 1 million molecules per second! This helps your blood carry carbon dioxide to your lungs.





