The Doppler Effect - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how moving objects change sound and light waves!
What is the Doppler Effect?

The Doppler Effect is a change in the frequency of sound or light waves that occurs when the source of the waves is moving relative to an observer. It was discovered by Austrian physicist Christian Doppler in 1842.
You've probably heard the Doppler Effect without knowing what it was called. When an ambulance passes by with its siren on, the pitch of the siren seems to change - higher as it approaches you and lower as it moves away. That change in sound is the Doppler Effect in action!
Definition: The Doppler Effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source.
Did You Know?
The Doppler Effect works with all types of waves, including sound, light, and even water waves!
How the Doppler Effect Works
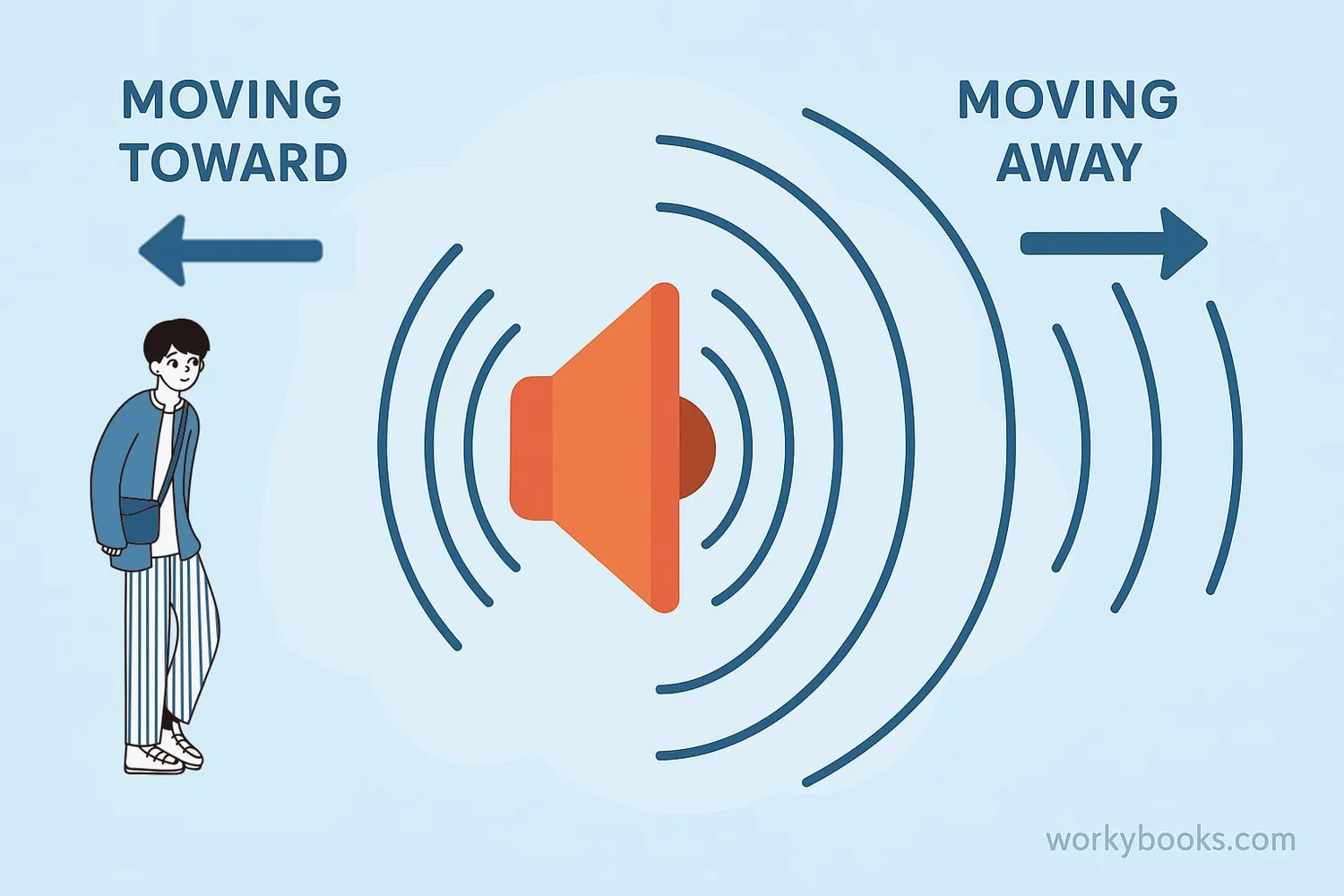
The Doppler Effect happens because waves get compressed when the source is moving toward you and stretched when it's moving away. Let's break this down:
Source Approaching
When a sound source moves toward you, the sound waves get compressed, increasing the frequency (higher pitch)
Source Moving Away
When the source moves away, the sound waves stretch out, decreasing the frequency (lower pitch)
Observer Moving
The effect also happens if the observer is moving instead of the source
The formula for the Doppler Effect in sound is:
f' = f × (v ± v₀) / (v ∓ vₛ)
Where:
• f' = observed frequency
• f = actual frequency
• v = speed of sound
• v₀ = speed of observer
• vₛ = speed of source
Wave Fact!
The Doppler Effect is more noticeable with fast-moving objects than slow ones. That's why you hear it clearly with emergency vehicles but not with slowly passing cars.
Doppler Effect in Sound and Light
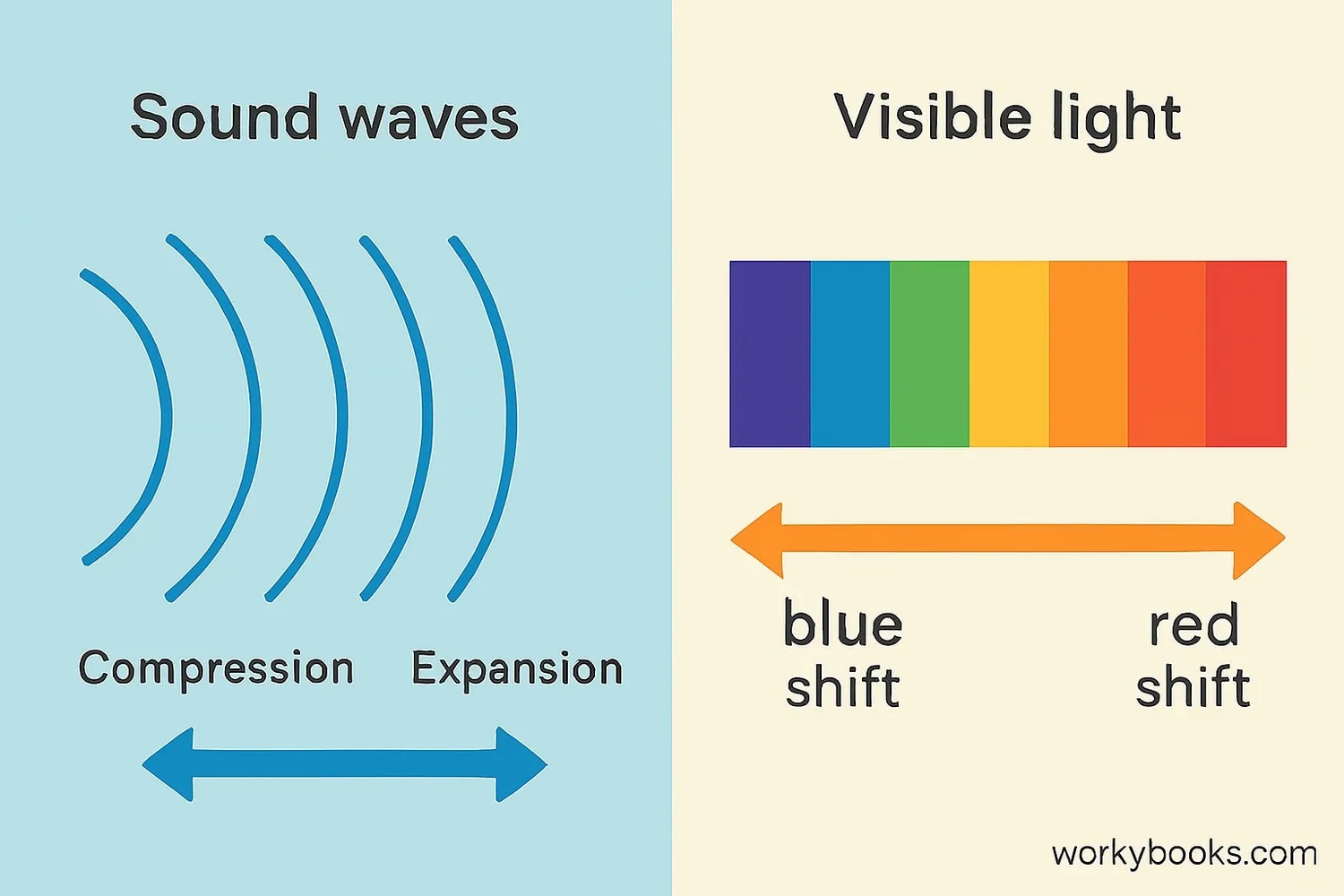
While we most often notice the Doppler Effect with sound, it also affects light waves. The difference is in how we perceive the changes:
Sound Waves
• Approaching source: Higher pitch (frequency increases)
• Receding source: Lower pitch (frequency decreases)
Light Waves
• Approaching source: Blue shift (shorter wavelength)
• Receding source: Red shift (longer wavelength)
Red Shift and Blue Shift:
When astronomers look at light from distant stars and galaxies, they often see a red shift. This tells us those objects are moving away from us. Blue shift is less common but tells us an object is moving toward us.
Example: The famous Doppler radar used in weather forecasting uses the same principle. It sends out radio waves and measures how their frequency changes when they bounce back from rain or snow. This helps determine how fast precipitation is moving and in what direction.
Real-World Applications
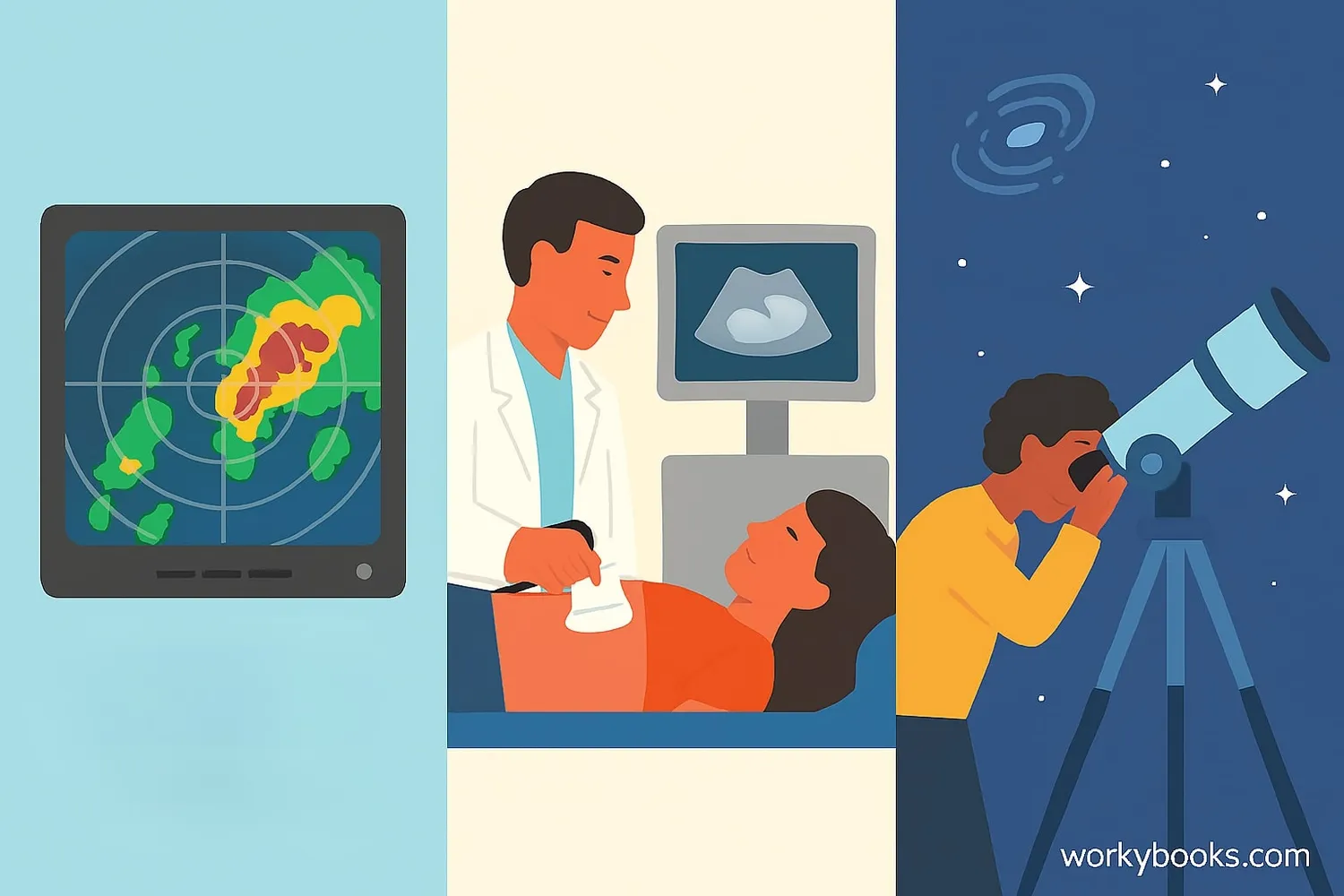
The Doppler Effect isn't just a scientific curiosity - it has many practical applications in our daily lives:
Weather Radar
Measures speed and direction of precipitation to predict storms
Medical Ultrasound
Measures blood flow speed in arteries and veins
Police Radar
Detects vehicle speed using radio waves
Astronomy
Measures how fast stars and galaxies are moving
Interesting Fact: The Doppler Effect helped astronomers discover that our universe is expanding! By measuring the red shift of light from distant galaxies, Edwin Hubble determined that galaxies are moving away from us, and the farther away they are, the faster they're moving.
Doppler Effect Quiz
Test your understanding of the Doppler Effect with these questions. Choose the best answer for each.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Doppler Effect:
Amazing Doppler Effect Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about the Doppler Effect:
Cosmic Speedometer
Astronomers use the Doppler Effect to measure how fast galaxies are moving. The most distant galaxies are moving away from us at over 90% of the speed of light!
Life-Saving Technology
Doppler ultrasound can detect blood flow as slow as 1 cm per second. This helps doctors find blocked arteries before they cause serious problems.
Bat Navigation
Bats use a natural form of Doppler radar! They adjust for the Doppler shift in their echolocation calls to accurately detect how fast insects are flying.
Beyond Sound and Light
The Doppler Effect works with any type of wave - even ocean waves! If you move through water, the wave frequency changes relative to your motion.





