Photon - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the amazing world of light particles and how they help scientists explore our universe!
What is a Photon?
A photon is the smallest possible piece of light! It's like a tiny packet of energy that travels at the speed of light. Photons are the building blocks of all light, whether it's from the sun, a light bulb, or your phone screen.
Think of photons as the messengers of light. They carry energy and information across space. Even though they're incredibly small, photons are powerful enough to help scientists see inside objects and even inside our bodies!
Photon Fact!
Photons have no mass, which is why they can travel at the fastest speed possible - the speed of light (299,792,458 meters per second)!
How Photons are Created
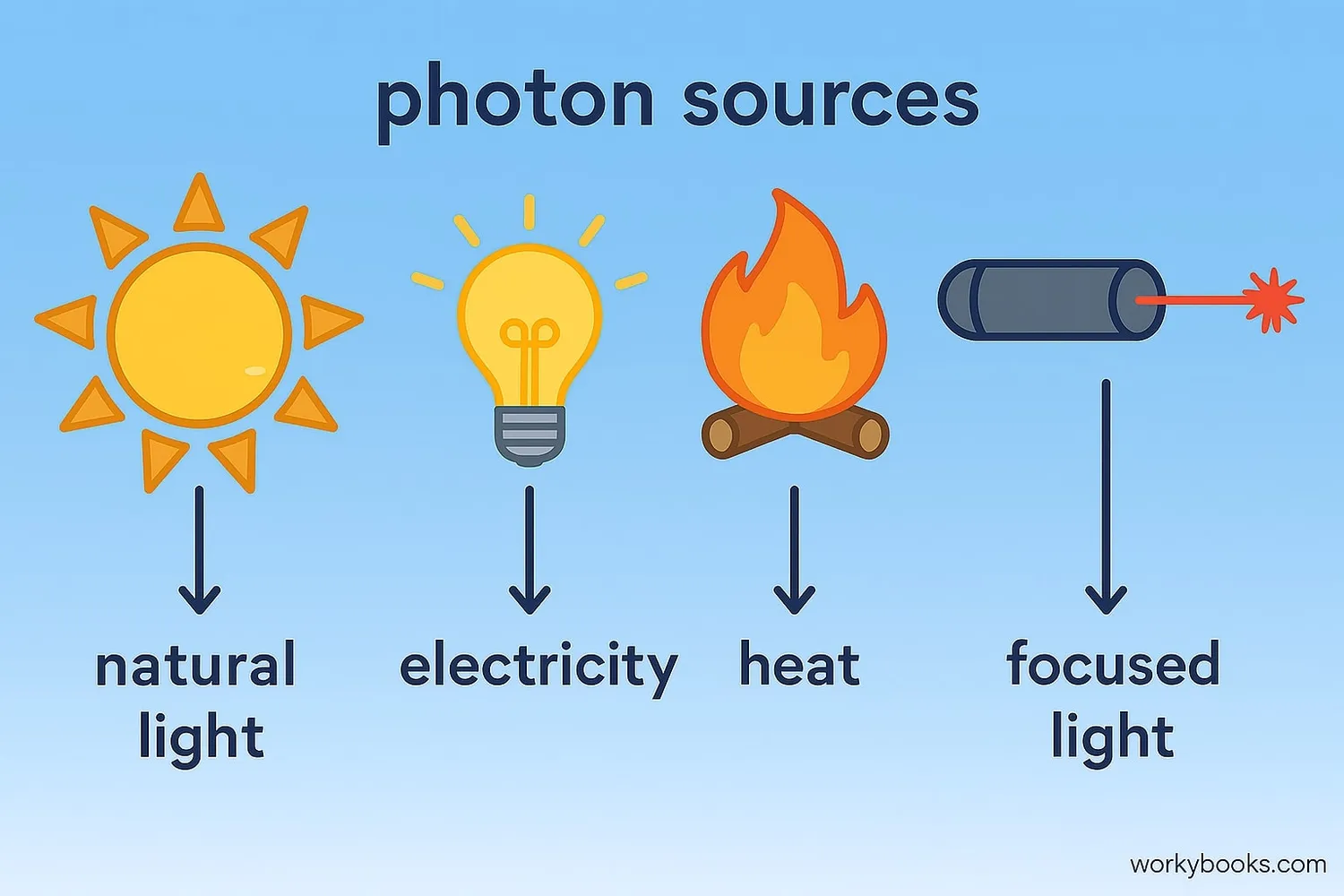
Photons can be created in many different ways! Scientists have developed special machines to create powerful photon beams for research:
Natural Sources
The sun, stars, fire, and even living things like fireflies produce photons
Electric Sources
Light bulbs create photons when electricity passes through a filament
Synchrotrons
Particle accelerators that create bright X-ray light by accelerating electrons
Free Electron Lasers
Powerful machines that create extremely bright, laser-like X-ray pulses
Scientists use synchrotrons and free electron lasers (FELs) to create special X-ray photons that can help them see things at the atomic level! These machines are like super-powered microscopes that use photons instead of lenses.
Amazing Fact!
The brightest artificial light sources on Earth are free electron lasers, which can be a billion times brighter than the sun!
Photon Science in Action

Photon science helps us understand our world in amazing ways! Scientists use special photon sources to:
Medical Research
Studying viruses and developing new medicines using X-ray crystallography
Materials Science
Creating stronger materials and better electronics by seeing atomic structures
Environmental Studies
Understanding pollution and developing clean energy solutions
Photon science is especially important for:
• X-ray diffraction: Seeing how atoms are arranged in crystals
• Spectroscopy: Studying how materials absorb and emit light
• Imaging: Creating detailed pictures of tiny structures
• Quantum physics: Understanding the fundamental nature of light and matter
Without photons, we couldn't see the world at its most basic level!
Photon Science Quiz
Test your photon knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about photons and light:
Amazing Light Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about photons and light:
Speed of Light
Photons travel at 299,792,458 meters per second! At this speed, light could circle the Earth 7.5 times in just one second.
Ancient Sunlight
The sunlight reaching Earth today began its journey about 8 minutes ago. But the photons in the center of the sun take thousands of years to reach the surface!
Human Photon Fact
Your body emits photons too! All warm objects, including humans, emit infrared photons that we feel as heat.
Quantum Mystery
Photons behave as both particles and waves! This "wave-particle duality" is one of the most fascinating mysteries in quantum physics.





