Sonar - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how sound waves help us explore underwater worlds!
What is Sonar?
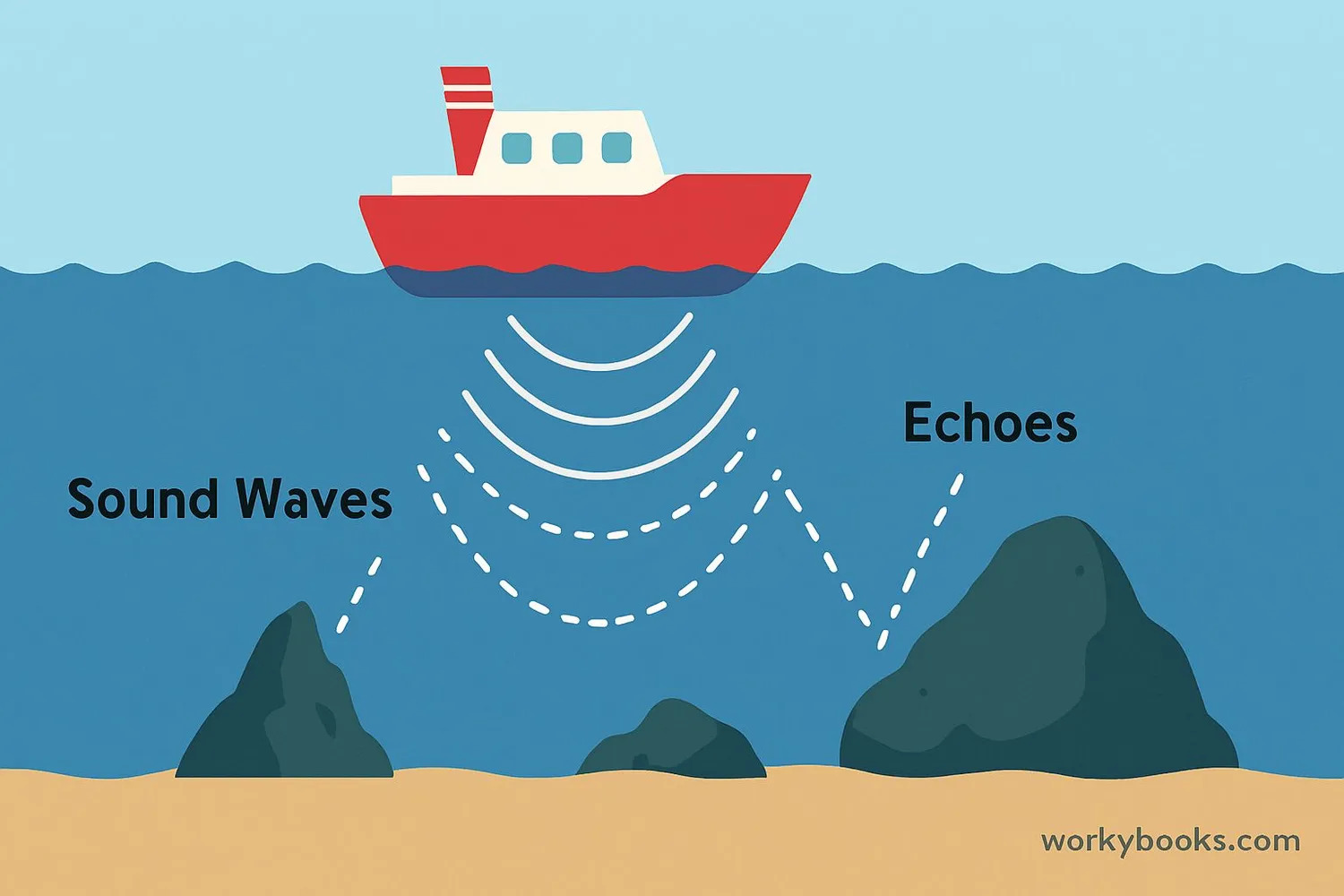
Sonar (which stands for SOund NAvigation and Ranging) is a technology that uses sound waves to detect objects underwater and measure distances. It works like echolocation that dolphins and bats use!
Think of sonar as having underwater "eyes" made of sound. Since light doesn't travel well through water, but sound does, sonar helps us "see" what's beneath the surface. Ships use sonar to map the ocean floor, locate underwater objects, and navigate safely.
Sound Fact!
Sound travels about 4.3 times faster in water than in air! This makes it perfect for underwater detection.
How Sonar Works
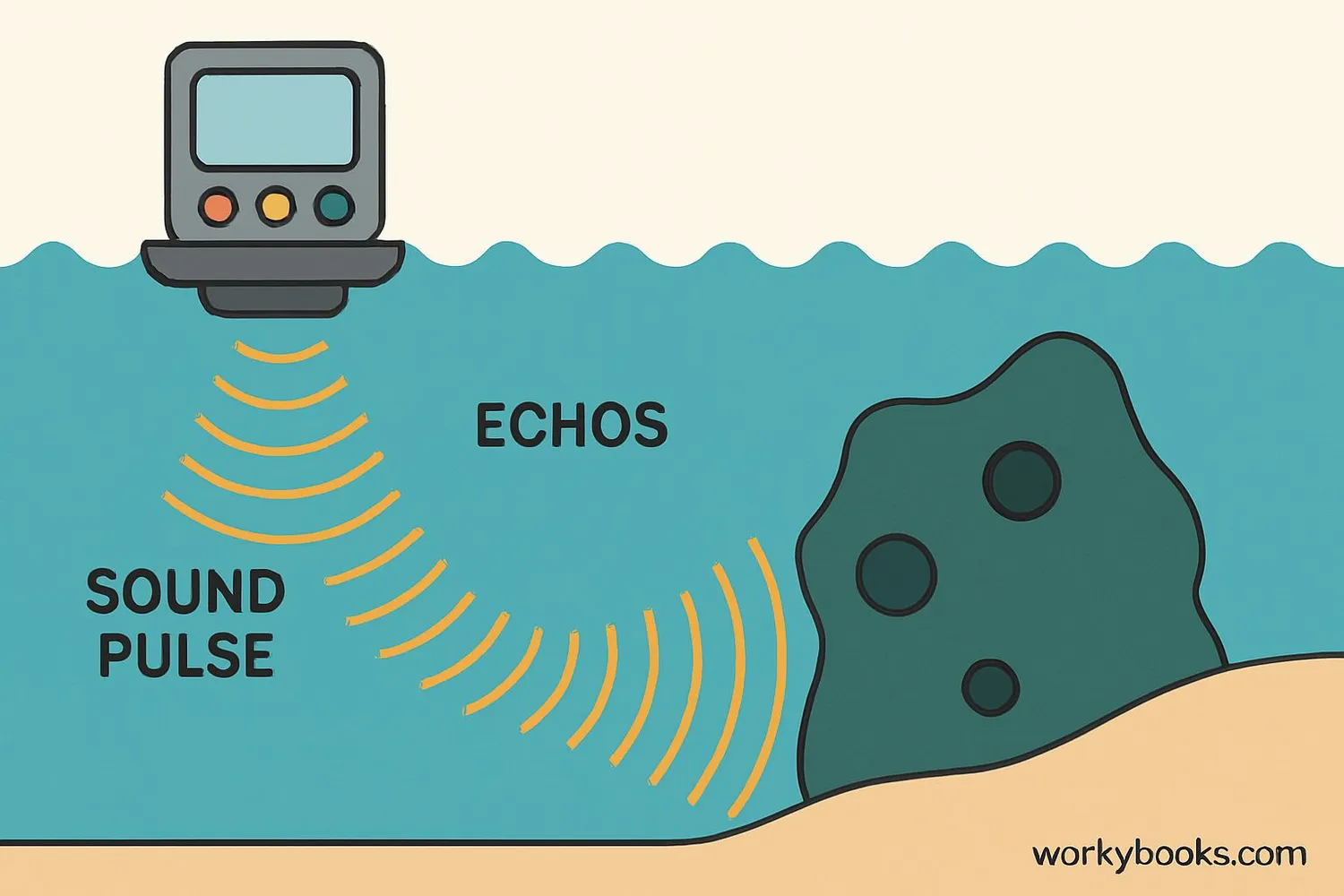
Sonar works by sending out sound waves and listening for their echoes. Here's how this amazing detection process works:
Sound Transmission
A transmitter sends out sound pulses into the water
Wave Travel
Sound waves travel through water until they hit an object
Echo Creation
Sound waves bounce off objects and create echoes
Echo Reception
A receiver detects the returning echoes
Distance Calculation
The system calculates distance based on echo return time
The time it takes for the echo to return tells us how far away the object is. Since we know how fast sound travels in water (about 1,500 meters per second), we can calculate distance using this formula:
Distance = (Speed of Sound × Time) ÷ 2
We divide by 2 because the sound travels to the object and back.
Two Types of Sonar!
Active sonar sends out sound pulses and listens for echoes. Passive sonar only listens for sounds made by other objects.
Why Sonar is Important
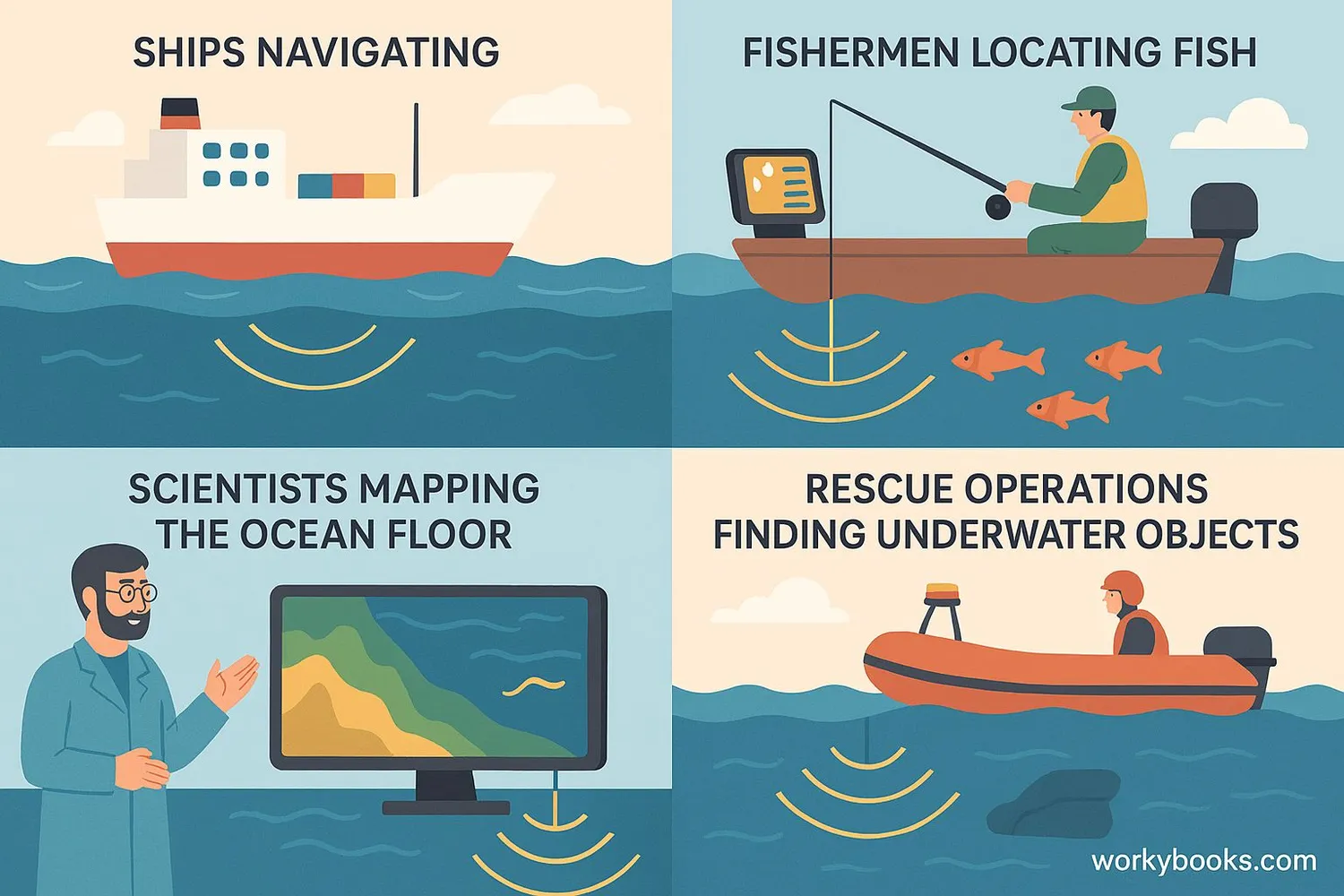
Sonar technology is essential for many underwater activities! Here's why it's so important:
Safe Navigation
Helps ships avoid underwater obstacles like rocks, reefs, and icebergs
Fishing Industry
Helps fishermen locate schools of fish and map fishing grounds
Search and Rescue
Used to find underwater wreckage, missing objects, or rescue operations
Sonar also helps with:
• Scientific research and ocean exploration
• Mapping the ocean floor and underwater terrain
• Military applications for submarine detection
• Offshore construction and pipeline inspection
• Studying marine life and their behaviors
Without sonar, we would know much less about the underwater world that covers more than 70% of our planet!
Sonar Technology Quiz
Test your sonar knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about sonar:
Fun Sonar Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about sonar technology!
Nature's Sonar
Dolphins have natural sonar that is even more precise than human-made technology! They can determine the size, shape, and texture of objects using echolocation.
Deep Discoveries
Sonar helped discover the deepest part of the ocean—the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench—which is nearly 11,000 meters (36,000 feet) deep!
Titanic Discovery
Sonar technology helped locate the wreck of the RMS Titanic in 1985, 73 years after it sank. The wreck was found at a depth of about 3,800 meters (12,500 feet).
Space Sonar
Scientists are developing sonar-like technology for space exploration! It could help future missions navigate through Saturn's moon Titan's methane lakes.





